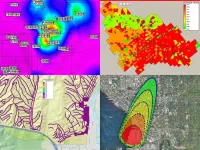
(Press-News.org) RICHLAND, Wash.—Visual Sample Plan (VSP), a free software tool developed at the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) that boosts statistics-based planning, has been recognized with a 2024 Federal Laboratory Consortium (FLC) Award.
The FLC represents over 300 federal laboratories, agencies, and research centers. The annual FLC awards program recognizes agencies for their contributions to technology transfer, which turns innovative research into impactful products and services.
Judges bestowed PNNL’s VSP with the FLC Impact Award, which honors FLC member laboratories whose technology transfer efforts have made a tangible and lasting impact on the populace or marketplace ranging across local and global scales. As of 2023, VSP has more than 5,000 active users from multiple U.S. federal, state and local agencies and in over 70 countries around the world, and has tracked over 8,000 downloads since 2018.
All-in-one software solution
“Over my time working on VSP, I have seen how impactful it is for our users to have a simple all-in-one solution for developing statistical sampling plans,” said Lisa Newburn, a computer scientist and team lead in Software Engineering Architectures who oversees the VSP program along with Debbie Fagan and Jen Willis. “It’s hugely gratifying to have that impact recognized by the FLC award.”
VSP provides a unique capability for developing site maps and statistical sampling designs. From its easily accessible website to robust training resources, VSP shows users that PNNL is open for partnership and building a user community that continually expands VSP applicability to new areas of impact.
The software program’s most meaningful impact is its use for national and global security, helping U.S. agencies such as the National Nuclear Security Administration and the Department of Defense and British government agencies such as the UK Atomic Weapons Establishment and the UK Government Decontamination Service. Additionally, VSP has helped a wide range of U.S. agencies: The Offices of Environmental Management, Health, Safety, and Security, and Legacy Management; the Environmental Protection Agency; the Centers for Disease Control; the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health; the Nuclear Regulatory Commission; and many others.
It’s free, for the greater good
“Making technologies available for use by industry, academia and government agencies is an integral part of the Laboratory’s mission,” said Kannan Krishnaswami, a PNNL commercialization manager. “This is a great example of how we use different technology transfer models to achieve maximum impact for and on behalf of our federal sponsors.”
Newburn said the VSP team is continuing to develop and improve the software program.
“Recent releases include major improvements to building modeling and visualization, including added support for uneven ceilings and improved handling of furniture sampling,” she said. “Major new additions are planned to address the challenges and needs of subsurface sampling and analysis and expanding VSP’s spatial analysis capabilities from 2D to 3D.”
Under development and improvement for decades
Newburn credited VSP pioneers at PNNL for providing the base of work that resulted in the FLC award. Development of the software program began in 1997.
“Brent Pulsipher, who retired from PNNL in 2015, pioneered VSP and its distribution strategy,” she said. “Jim Davidson and John Wilson co-created the initial statistical spatial sampling code that formed VSP’s foundation.”
Wilson, a PNNL computer scientist, has continued to lead development of VSP since its inception, and created the overall VSP platform that accommodates new operating systems and computing updates.
“When VSP entered the world, billions of dollars had been spent by the federal government on sample design and collection, often without understanding the sampling goals or decisions to be made,” Wilson said. “Today, VSP’s standardized approach to sampling and decision-making has changed the state of sampling for agencies throughout the United States and abroad.”
FLC award recipients will be honored at the 2024 FLC Awards Ceremony and Banquet, held during the FLC National Meeting, April 9–11 at the Sheraton Dallas Hotel in Dallas. This year marks the fiftieth anniversary of the FLC.
###
About PNNL
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory draws on its distinguishing strengths in chemistry, Earth sciences, biology and data science to advance scientific knowledge and address challenges in sustainable energy and national security. Founded in 1965, PNNL is operated by Battelle for the Department of Energy’s Office of Science, which is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States. DOE’s Office of Science is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit https://energy.gov/science. For more information on PNNL, visit PNNL's News Center. Follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
PNNL Software Technology wins FLC Award
Impact Award goes to Visual Sample Plan for its global use
2024-01-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
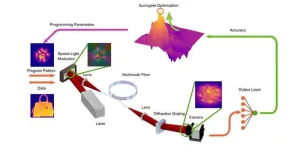
Programming light propagation creates highly efficient neural networks
2024-01-25
Current artificial intelligence models utilize billions of trainable parameters to achieve challenging tasks. However, this large number of parameters comes with a hefty cost. Training and deploying these huge models require immense memory space and computing capability that can only be provided by hangar-sized data centers in processes that consume energy equivalent to the electricity needs of midsized cities. The research community is presently making efforts to rethink both the related computing hardware and the machine learning algorithms to sustainably keep the development of artificial intelligence at its current pace.
Optical implementation ...
Advincula earns prestigious NAI fellow honor
2024-01-25
Rigoberto “Gobet” Advincula has been awarded one of the highest honors of his profession.
Advincula, the University of Tennessee-Oak Ridge National Laboratory Governor’s Chair of Advanced and Nanostructured Materials, has been elected National Academy of Inventors (NAI) Fellow.
Advincula is a leader in the polymer field with inventions and many publications in polymer nanocomposites, graphene nanomaterials, polymer layered films, and coatings. He has been granted 14 US patents and has 21 published filings related to graphene nanomaterials, solid-state device fabrication, smart coatings and films, ...
Sweat-analyzing temporary tattoo research funded in NSF grant to UMass Amherst researcher
2024-01-25
AMHERST – University of Massachusetts Amherst researchers have received an award to develop a new type of sweat monitor that can be applied to the skin just like a temporary tattoo and assess the molecules present, such as cortisol. The tattoos will ultimately give individuals better insight into their health and serve as a tool for researchers to discover new early indications of diseases.
“There are a lot of vital biomolecules that are present in sweat that we need to measure to really understand overall human performance and correlation to different ...
Simulations show how HIV sneaks into the nucleus of the cell
2024-01-25
Because viruses have to hijack someone else’s cell to replicate, they’ve gotten very good at it—inventing all sorts of tricks.
A new study from two University of Chicago scientists has revealed how HIV squirms its way into the nucleus as it invades a cell.
According to their models, the HIV capsid, which is cone-shaped, points its smaller end into the pores of the nucleus and then ratchets itself in. Once the pore is open enough, the capsid is elastic enough to squeeze through. Importantly, the scientists ...
White House rule dramatically deregulated wetlands, streams and drinking water
2024-01-25
The 1972 Clean Water Act protects the "waters of the United States" but does not precisely define which streams and wetlands this phrase covers, leaving it to presidential administrations, regulators, and courts to decide. As a result, the exact coverage of Clean Water Act rules is difficult to estimate.
New research led by a team at the University of California, Berkeley, used machine learning to more accurately predict which waterways are protected by the Act. The analysis found that a 2020 Trump administration rule removed Clean Water Act ...
How an ant invasion led to lions eating fewer zebra in a Kenyan ecosystem
2024-01-25
The invasion of non-native species can sometimes lead to large and unexpected ecosystem shifts, as Douglas Kamaru and colleagues demonstrate in a unique, careful study that traces the links between big-headed ants, acacia trees, elephants, lions, zebras, and buffalo at a Kenyan conservancy. The invasive big-headed ant species disrupted a mutualism between native ants and the region’s thorny acacia trees, in which the native ants protected the trees from grazers in exchange for a place to live. Through a combination of observations, experimental plots, and animal tracking at Ol Pejeta Conservancy, Kamaru et al. followed the ecosystem chain reaction prompted by this disruption. ...
Total organic carbon concentrations measured over Canadian oil sands reveal huge underestimate of emissions
2024-01-25
New measurements of total gaseous organic carbon concentrations in the air over the Athabasca oil sands in Canada suggest that traditional methods of estimating this pollution can severely underestimate emissions, according to an analysis by Megan He and colleagues. Using aircraft-based measurements, He et al. conclude that the total gaseous organic carbon emissions from oil sands operations exceed industry-reported values by 1900% to over 6300% across the studied facilities. “Measured facility-wide emissions represented approximately 1% of extracted petroleum, resulting in total organic ...
Machine learning model identifies waters protected under different interpretations of the U.S. Clean Water Act
2024-01-25
The U.S. Clean Water Act is a critically important part of federal water quality regulation, but the act does not define the exact waters that fall under its jurisdiction. Now, Simon Greenhill and colleagues have developed a machine learning model that helps to clarify which waters are protected from pollution under the United States’ Clean Water Act, and how recent rule changes affect protection. The model demonstrates that the waters protected under the act differ substantially depending on whether the act’s regulations follow a 2006 U.S. Supreme Court ruling or a 2020 White House rule. Under the 2006 Rapanos Supreme Court ruling, the model suggests that the Clean ...
Gamma ray observations of a microquasar demonstrate electron shock acceleration
2024-01-25
Observations of gamma rays, emitted by relativistic jets in a microquasar system, demonstrate the acceleration of electrons by a shock front, reports a new study. The microquasar SS 433 is a binary system made up of a compact object, probably a black hole, and a supergiant star. The black hole pulls material off the star and ejects plasma jets, which move at close to the speed of light. The High Energy Stereoscopic System (H.E.S.S.) is an array of five telescopes in Namibia that observe gamma rays. The H.E.S.S. ...
Astrophysical jet caught in a “speed trap”
2024-01-25
The science fiction author Arthur C. Clarke selected his own seven wonders of the world in a BBC television series in 1997. The only astronomical object he included was SS 433. It had attracted attention already in the late 1970s due to its X-ray emission and was later discovered to be at the center of a gas nebula that is dubbed the manatee nebula due to its unique shape resembling these aquatic mammals.
SS 433 is a binary star system in which a black hole, with a mass approximately ten times that of the Sun, and a star, with a similar mass but occupying a much larger volume, orbit each other with ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
[Press-News.org] PNNL Software Technology wins FLC AwardImpact Award goes to Visual Sample Plan for its global use