(Press-News.org) A valuable molecule sourced from the soapbark tree and used as a key ingredient in vaccines, has been replicated in an alternative plant host for the first time, opening unprecedented opportunities for the vaccine industry.
A research collaboration led by the John Innes Centre used the recently published genome sequence of the Chilean soapbark tree (Quillaja saponaria) to track down and map the elusive genes and enzymes in the complicated sequence of steps needed to produce the molecule QS-21.
Using transient expression techniques developed at the John Innes Centre, the team reconstituted the chemical pathway in a tobacco plant, demonstrating for the first time ‘free-from 'tree’ production of this highly valued compound.
Professor Anne Osbourn FRS, group leader at the John Innes Centre said: “Our study opens unprecedented opportunities for bioengineering vaccine adjuvants. We can now investigate and improve these compounds to promote the human immune response to vaccines and produce QS-21 in a way which does not depend on extraction from the soapbark tree.”
Vaccine adjuvants are immunostimulants which prime the body’s response to the vaccine – and are a key ingredient of human vaccines for shingles, malaria, and others under development.
QS-21, a potent adjuvant, is sourced directly from the bark of the soapbark tree, raising concerns about the environmental sustainability of its supply.
For many years researchers and industrial partners have been looking for ways to produce the molecule in an alternative expression system such as yeast or tobacco plants. But the complex structure of the molecule and lack of knowledge about its biochemical pathway in the tree have so far prevented this.
Previously researchers in the group of Professor Osbourn had assembled the early part of the pathway which makes up the scaffold structure for QS-21. However, the search for the longer full pathway, the acyl chain which forms one crucial part of the molecule that stimulates immune cells, remained unfinished.
In a new study which appears in Nature Chemical Biology, researchers at the John Innes Centre used a range of gene discovery approaches to identify around 70 candidate genes and transferred them to tobacco plants.
By analyzing gene expression patterns and products, supported by the Metabolomic and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) platforms at the John Innes Centre, they were able to narrow the search down to the final 20 genes and enzymes which make up the QS-21 pathway.
First author Dr Laetitia Martin said: “This is the first time QS-21 has been produced in a heterologous expression system. This means we can better understand how this molecule works and how we might address issues of scale and toxicity.
“What is so rewarding is that this molecule is used in vaccines and by being able to make it more sustainably my project has an impact on people’s lives. It's amazing to think that something so scientifically rewarding can bring such good to society.”
“On a personal level this research was scientifically extremely rewarding. I am not a chemist so I could not have done this without the support of the John Innes Centre metabolomics platform and chemistry platform.”
The team have partnered with Plant Bioscience Limited PBL (Plant Bioscience Limited) Norwich Limited who are leading commercialization of this project.
Complete Biosynthesis of the potent vaccine adjuvant QS-21 appears in Nature Chemical Biology
END
Soap bark discovery offers a sustainability booster for the global vaccine market
Study opens unprecedented opportunities for bioengineering vaccine adjuvants
2024-01-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Writing by hand may increase brain connectivity more than typing on a keyboard
2024-01-26
As digital devices progressively replace pen and paper, taking notes by hand is becoming increasingly uncommon in schools and universities. Using a keyboard is recommended because it’s often faster than writing by hand. However, the latter has been found to improve spelling accuracy and memory recall.
To find out if the process of forming letters by hand resulted in greater brain connectivity, researchers in Norway now investigated the underlying neural networks involved in both modes of writing.
“We ...
Computers are quick and reliable in counting seals
2024-01-26
Computers can count seals from aerial photographs with lightning speed and reliability. Based on their spatial patterns, the tiny dots on the aerial images can even be assigned to one of the two major species of seals in the Wadden Sea. That is shown in the thesis that marine biologist Jeroen Hoekendijk will defend on January 26 in Wageningen. "To better understand if and how marine mammals like seals are affected by climate change and the disappearance of sea ice, this help from artificial intelligence (AI) in observations is crucial," Hoekendijk said. Hoekendijk carried out his research at the Royal Netherlands Institute ...
Estuarine Management and Technologies: A brand new journal streamlines innovation in the conservation of estuarine ecosystems
2024-01-26
Where freshwater rivers meet seas and oceans lies a scientifically intriguing and ecologically important type of ecosystem. As estuarine ecosystems provide various and diverse services to humanity and the planet at large, including food security and natural buffers and filters in the events of storms and water pollution, there has been an increasing need to facilitate and support the exchange of research findings and ideas related to their conservation and sustainable management by means of new-age technology and novel approaches.
This is how a team of renowned and passionate ...
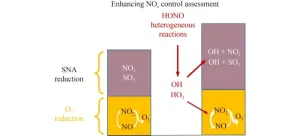
The missing link: Recent study explores the connection between NOx control and SNA, O3 reduction
2024-01-26
Sulfate-nitrate-ammonium (SNA) and other atmospheric aerosols play a significant role in influencing both atmospheric and environmental conditions. These aerosols impact climate directly through scattering and absorbing solar radiation, thus influencing the Earth's radiative balance. The presence of high concentrations of aerosols can lead to the formation of haze and reduce air quality, affecting human health and transportation. Furthermore, the fine particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) within aerosols poses health risks ...
Cultural encounters of landscape architects Xiaoxiang Sun and Lawrence Halprin
2024-01-26
“From nature to nature” is the major goal of landscape design. The former is the idea of nature, i.e., landscape architects regard nature as the archetype of design; the latter is the experience of nature, i.e., landscape architects hope people can perceive the natural atmosphere through designed landscape. In this sense, the transformation from idea to experience of nature refers to the process of landscape design, which materializes landscape. According to this, this article focuses on the following topics: 1) what role does nature play as the origin of the landscape design theory; 2) how does nature as an idea promote ...
First demonstration of predictive control of fusion plasma by digital twin
2024-01-26
Fusion energy is being developed as a solution to global energy problems. In particular, the magnetic confinement method, in which ultra-high temperature plasma is confined by a magnetic field, is the most advanced and is considered to be the most promising method for fusion reactors. By this method, the plasma is confined in the reactor in a high-temperature, high-density state by a magnetic field, and the energy released by the fusion reaction in the plasma is converted into electricity. To realize this power generation method, it is essential to predict and control the complex behavior of fusion plasma. One possible control method is digital twin control, in which the fusion plasma ...
Single dose typhoid conjugate vaccine (TCV) provides lasting efficacy in children
2024-01-26
A single dose of the typhoid conjugate vaccine, Typbar TCV®, provides lasting efficacy in preventing typhoid fever in children ages 9 months to 12 years old, according to a new study conducted by researchers at University of Maryland School of Medicine’s (UMSOM) Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health (CVD) and led by in-country partners at the Malawi-Liverpool Wellcome Trust (MLW) Clinical Research Programme.
Results from the phase 3 clinical study were published today in The Lancet.
The ...
'Old smokers' and 'squalling newborns' among hidden stars spotted for first time
2024-01-26
'Hidden' stars including a new type of elderly giant nicknamed an 'old smoker' have been spotted for the first time by astronomers.
The mystery objects exist at the heart of our Milky Way galaxy and can sit quietly for decades – fading almost to invisibility – before suddenly puffing out clouds of smoke, according to a new study published today in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
An international team of scientists led by Professor Philip Lucas, of the University of Hertfordshire, made their ground-breaking discovery after monitoring almost a billion stars in infrared light during a 10-year survey ...
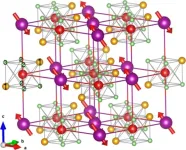
In search of muons: Why they switch sites in antiferromagnetic oxides
2024-01-26
Muon spectroscopy is an important experimental technique that scientists use to study the magnetic properties of materials. It is based on “implanting” a spin-polarized muon in the crystal and measuring how its behavior is affected by the surroundings. The technique relies on the idea that the muon will occupy a well-identified site that is mainly determined by electrostatic forces, and that can be found by calculating the material’s electronic structure.
But a new study led by scientists in Italy, Switzerland, UK and Germany has found that, at least for some materials, that is not the end of the story: the muon site ...
Locked-in syndrome is predominant outcome when children survive drowning, larger study confirms
2024-01-26
SAN ANTONIO, Jan. 25, 2024 — It is a far cry from the traditionally thought-of “vegetative state” in which the mind is absent while the body lives on. Indeed, it is the opposite. Children with “locked-in syndrome,” unable to move or speak, are awake and fully aware of their surroundings.
Researchers from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) were the first to report in peer-reviewed medical literature that, after non-fatal drownings, children would be locked in. The team, directed by Peter T. Fox, MD, professor of radiology and neurology and director of UT ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
[Press-News.org] Soap bark discovery offers a sustainability booster for the global vaccine marketStudy opens unprecedented opportunities for bioengineering vaccine adjuvants