(Press-News.org) Cellular agriculture – the production of meat from cells grown in bioreactors rather than harvested from farm animals – is taking leaps in technology that are making it a more viable option for the food industry. One such leap has now been made at the Tufts University Center for Cellular Agriculture (TUCCA), led by David Kaplan, Stern Family Professor of Engineering, in which researchers have created bovine (beef) muscle cells that produce their own growth factors, a step that can significantly cut costs of production.
Growth factors, whether used in laboratory experiments or for cultivated meat, bind to receptors on the cell surface and provide a signal for cells to grow and differentiate into mature cells of different types. In this study published in the journal Cell Reports Sustainability, researchers modified stem cells to produce their own fibroblast growth factor (FGF) which triggers growth of skeletal muscle cells – the kind one finds in a steak or hamburger.
“FGF is not exactly a nutrient,” said Andrew Stout, then lead researcher on the project and now Director of Science at Tufts Cellular Agriculture Commercialization Lab. “It’s more like an instruction for the cells to behave in a certain way. What we did was engineer bovine muscle stem cells to produce these growth factors and turn on the signaling pathways themselves.”
Until now, growth factors had to be added to the surrounding liquid, or media. Made from recombinant protein and sold by industrial suppliers, growth factors contribute to a majority of the cost of production for cultivated meat (up to or above 90%). Since the growth factors don’t last long in the cell culture media, they also have to be replenished every few days. This limits the ability to provide an affordable product to consumers. Taking that ingredient out of the growth media leads to an enormous cost savings.
Stout is leading several research projects at Tufts University Cellular Agriculture Commercialization Lab —a technology incubator space which is set up to take innovations at the university and develop them to the point at which they can be applied at an industrial scale in a commercial setting.
“While we significantly cut the cost of media, there is still some optimization that needs to be done to make it industry-ready,” said Stout. “We did see slower growth with the engineered cells, but I think we can overcome that.” Strategies may include changing the level and timing of expression of FGF in the cell or altering other cell growth pathways. “In this strategy, we’re not adding foreign genes to the cell, just editing and expressing genes that are already there” to see if they can improve growth of the muscle cells for meat production. That approach could also lead to simpler regulatory approval of the ultimate food product, since regulation is more stringent for addition of foreign genes vs editing of native genes.
Will the strategy work for other types of meat, like chicken, pork, or fish? Stout thinks so. “All muscle cells and many other cell types typically rely on FGF to grow,” said Stout. He envisions the approach will be applied to other meats, although there may be variability for the best growth factors to express in different species.
“Work is continuing at TUCCA and elsewhere to improve cultivated meat technology,” said Kaplan, “including exploring ways to reduce the cost of nutrients in the growth media, and improving the texture, taste, and nutritional content of the meat. Products have already been awarded regulatory approval for consumption in the U.S. and globally, although costs and availability remain limiting. I think advances like this will bring us much closer to seeing affordable cultivated meat in our local supermarkets within the next few years.”
END
Cultivated meat production costs could fall significantly with new cells created at Tufts University
Bovine muscle cells were made to produce their own growth signals, removing the costly ingredients from the production process
2024-01-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers discover why one type of chemotherapy works best in bladder cancer
2024-01-26
Tisch Cancer Institute researchers discovered that a certain type of chemotherapy improves the immune system’s ability to fight off bladder cancer, particularly when combined with immunotherapy, according to a study published in Cell Reports Medicine in January.
These findings may explain why the approach, cisplatin chemotherapy, can lead to cure in a small subset of patients with metastatic, or advanced, bladder cancer. Researchers also believe that their findings could explain why clinical trials combining another type of chemotherapy, carboplatin-based chemo, with immunotherapy have not been ...
Emergency contraception related ER visits dropped significantly over 14 year period
2024-01-26
Following federal approval for over the counter emergency contraception in 2006, emergency departments across the U.S. saw dramatic decreases in related visits and medical charges, a new study suggests.
Emergency room visits related to emergency contraception fell by 96 %, from 17,019 to 659, while total related hospital expenses decreased by $7.2 million – from $7.6 million to $385,946 – between 2006 and 2020. The most notable decrease was between 2006-2007 for people primarily seen for emergency contraception.
The Michigan Medicine led findings appear in JAMA Network ...
Job flows into and out of health care before and after the pandemic
2024-01-26
About The Study: The results of this study of approximately 18 million health care industry employees suggest a substantial and persistent increase in health care workforce turnover after the pandemic, which may have long-lasting implications for workers’ willingness to remain in health care jobs. Policymakers and health care organizations may need to act to prevent further losses of experienced staff.
Authors: Karen Shen, Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, is the corresponding ...
Incidence of fit test failure during N95 respirator reuse and extended use
2024-01-26
About The Study: In this study of 824 N95s used by 412 emergency department health care workers practicing N95 reuse, fit failure occurred in 38.7% of masks after one shift. Trifold N95s had higher incidence of fit failure compared with dome N95s. These results may inform pandemic preparedness, specifically policies related to N95 selection and reuse practices.
Authors: Ralph C. Wang, M.D., M.A.S., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.53631)
Editor’s ...
Clinical risk and outpatient therapy utilization for COVID-19 in the Medicare population
2024-01-26
About The Study: In this study of patients enrolled in Medicare in 2022, those at the highest risk for severe COVID-19 infection received COVID-19 therapy less often than those with the least risk. Disparities in therapy access were found by patient age, race and ethnicity, Medicaid eligibility, and nursing home residence.
Authors: Michael L. Barnett, M.D., of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.5044)
Editor’s ...
Brain drain - nasopharyngeal lymphatics found to be crucial for cerebrospinal fluid outflow
2024-01-26
In a groundbreaking study published in Nature, South Korean researchers led by Director KOH Gou Young of the Center for Vascular Research within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) have uncovered a distinctive network of lymphatic vessels at the back of the nose that plays a critical role in draining cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the brain. The study, sheds light on a previously unknown route for CSF outflow, potentially unlocking new avenues for understanding and treating neurodegenerative conditions.
In our brains, ...
CityU neuroscientists uncover the therapeutic potential of low-dose ionizing radiation for traumatic brain injury and ischemic stroke
2024-01-26
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) and ischemic stroke are major public health concerns and leading causes of death and disability worldwide. A research team led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) neuroscientists recently discovered that low-dose ionizing radiation (LDIR), such as X-ray irradiation, can reduce lesion size and reverse motor deficits in TBI and ischemic stroke mice, demonstrating that LDIR may be a promising therapeutic strategy for TBI and stroke patients.
Nearly half of TBI and stroke survivors experience lifelong motor impairment and disability. “Usually, secondary brain damage worsens over time after primary ...
Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology study shows positive results for patients with muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma
2024-01-26
Patients with muscle-invasive urothelial cancer and a high risk of recurrence after surgery may have a new treatment option. The Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology today announced positive results from the phase III AMBASSADOR (A031501) trial for the adjuvant treatment of patients with localized muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma (MIUC) and locally advanced urothelial carcinoma. Late-breaking data from the trial are being presented during an oral abstract session at the 2024 American Society of Clinical ...
Neural network enables objective assessment of breast symmetry
2024-01-26
Waltham — January 25, 2024 — A newly developed neural network is highly accurate in identifying key landmarks important in breast surgery – opening the potential for objective assessment of breast symmetry, suggests a study in the February issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Neural networks and machine learning have the potential to improve evaluation of breast symmetry in reconstructive ...
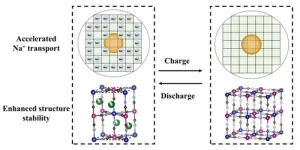
Boosting the sodium storage performance of Prussian blue analogues via effective etching
2024-01-26
This study is led by Prof. Yuliang Cao and Prof. Yongjin Fang (College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University). The experiments were performed by using ammonia etching on highly crystalline Na2NiFe(CN)6 (denoted as NaNiHCF) to activate the sodium storage sites and accelerate the Na+ transport.
Fe(CN)6 vacancies and the water molecules in the lattice, which are concomitant during the synthesis, however, lead to poor electrochemical performance. Hence, optimizing the crystal structures of PBAs to boost their electrochemical performance is currently a hot spot in the research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Cultivated meat production costs could fall significantly with new cells created at Tufts UniversityBovine muscle cells were made to produce their own growth signals, removing the costly ingredients from the production process