(Press-News.org) CAMBRIDGE, MA – An intricate, honeycomb-like structure of struts and beams could withstand a supersonic impact better than a solid slab of the same material. What’s more, the specific structure matters, with some being more resilient to impacts than others.
That’s what MIT engineers are finding in experiments with microscopic metamaterials — materials that are intentionally printed, assembled, or otherwise engineered with microscopic architectures that give the overall material exceptional properties.
In a study appearing today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the engineers report on a new way to quickly test an array of metamaterial architectures and their resilience to supersonic impacts.
In their experiments, the team suspends tiny printed metamaterial lattices between microscopic support structures, then fires even tinier particles at the materials, at supersonic speeds. With high-speed cameras, the team then captures images of each impact and its aftermath, with nanosecond precision.
Their work has identified a few metamaterial architectures that are more resilient to supersonic impacts compared to their entirely solid, nonarchitected counterparts. The researchers say the results they observed at the microscopic level can be extended to comparable macroscale impacts, to predict how new material structures across length scales will withstand impacts in the real world.
“What we’re learning is, the microstructure of your material matters, even with high-rate deformation,” says study author Carlos Portela, the Brit and Alex d'Arbeloff Career Development Professor in Mechanical Engineering at MIT. “We want to identify impact-resistant structures that can be made into coatings or panels for spacecraft, vehicles, helmets, and anything that needs to be lightweight and protected.”
Other authors on the study include first author and MIT graduate student Thomas Butruille, and Joshua Crone of DEVCOM Army Research Laboratory.
Pure impact
The team’s new high-velocity experiments build off their previous work, in which the engineers tested the resilience of an ultralight, carbon-based material. That material, which was thinner than the width of a human hair, was made from tiny struts and beams of carbon, which the team printed and placed on a glass slide. They then fired microparticles toward the material, at velocities exceeding the speed of sound.
Those supersonic experiments revealed that the microstructured material withstood the high-velocity impacts, sometimes deflecting the microparticles and other times capturing them.
“But there were many questions we couldn’t answer because we were testing the materials on a substrate, which may have affected their behavior,” Portela says.
In their new study, the researchers developed a way to test freestanding metamaterials, to observe how the materials withstand impacts purely on their own, without a backing or supporting substrate.
In their current setup, the researchers suspend a metamaterial of interest between two microscopic pillars made from the same base material. Depending on the dimensions of the metamaterial being tested, the researchers calculate how far apart the pillars must be in order to support the material at either end while allowing the material to respond to any impacts, without any influence from the pillars themselves.
“This way, we ensure that we’re measuring the material property and not the structural property,” Portela says.
Once the team settled on the pillar support design, they moved on to test a variety of metamaterial architectures. For each architecture, the researchers first printed the supporting pillars on a small silicon chip, then continued printing the metamaterial as a suspended layer between the pillars.
“We can print and test hundreds of these structures on a single chip,” Portela says.
Punctures and cracks
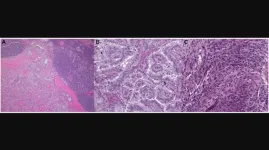
The team printed suspended metamaterials that resembled intricate honeycomb-like cross-sections. Each material was printed with a specific three-dimensional microscopic architecture, such as a precise scaffold of repeating octets, or more faceted polygons. Each repeated unit measured as small as a red blood cell. The resulting metamaterials were thinner than the width of a human hair.
The researchers then tested each metamaterial’s impact resilience by firing glass microparticles toward the structures, at speeds of up to 900 meters per second (more than 2,000 miles per hour) — well within the supersonic range. They caught each impact on camera and studied the resulting images, frame by frame, to see how the projectiles penetrated each material. Next, they examined the materials under a microscope and compared each impact’s physical aftermath.
“In the architected materials, we saw this morphology of small cylindrical craters after impact,” Portela says. “But in solid materials, we saw a lot of radial cracks and bigger chunks of material that were gouged out.”
Overall, the team observed that the fired particles created small punctures in the latticed metamaterials, and the materials nevertheless stayed intact. In contrast, when the same particles were fired at the same speeds into solid, nonlatticed materials of equal mass, they created large cracks that quickly spread, causing the material to crumble. The microstructured materials, therefore, were more efficient in resisting supersonic impacts as well as protecting against multiple impact events. And in particular, materials that were printed with the repeating octets appeared to be the most hardy.
“At the same velocity, we see the octet architecture is harder to fracture, meaning that the metamaterial, per unit mass, can withstand impacts up to twice as much as the bulk material,” Portela says. “This tells us that there are some architectures that can make a material tougher which can offer better impact protection.”
Going forward, the team plans to use the new rapid testing and analysis method to identify new metamaterial designs, in hopes of tagging architectures that can be scaled up to stronger and lighter protective gear, garments, coatings, and paneling.
“What I’m most excited about is showing we can do a lot of these extreme experiments on a benchtop,” Portela says. “This will significantly accelerate the rate at which we can validate new, high-performing, resilient materials.”
###
This work was funded in part by DEVCOM ARL Army Research Office through the MIT Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies (ISN).
END
Benchtop test quickly identifies extremely impact-resistant materials
High-speed experiments will help identify lightweight, protective “metamaterials” for spacecraft, vehicles, helmets, or other objects.
2024-01-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Do tree-planting campaigns follow best practices for successful forest restoration?
2024-01-29
Global tree-planting campaigns have reached fad-like proportions over the past decade, and it’s easy to understand their appeal. Healthy forests help in the fight against climate change by absorbing some of our excess carbon dioxide emissions, and they can provide wildlife habitat and quality-of-life benefits for local human communities too. So why not plant more trees? It seems like an easy win.
But the problem is, there’s a huge difference between simply planting a tree and making sure that trees survive and grow over the long-term. And without the necessary ecological understanding or long-term planning and ...
Nearly two-thirds of low-risk pulmonary embolism patients are hospitalized after ED visit
2024-01-29
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 29 January 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
Prenatal air pollution exposure linked to severe newborn respiratory distress
2024-01-29
HERSHEY, Pa. — Prenatal exposure to air pollution increases the risk of severe respiratory distress in newborn babies, according to new research conducted at the Penn State College of Medicine in collaboration with the Maternal-Infant Research on Environmental Chemicals (MIREC) Study led by Health Canada. The risk increases with exposure specifically to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), which occur in wildfire and cigarette smoke and vehicle emissions, among other sources.
The findings, which published on Jan. 25 in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, reveal a better understanding of ...
How a walk in nature restores attention
2024-01-29
New research from University of Utah psychology researchers is helping prove what American authors John Muir and Henry David Thoreau tried to teach more than 150 years ago: Time spent in nature is good for the heart and soul.
Amy McDonnell and David Strayer are showing it is good for your brain, too. Their latest research, conducted at the university’s Red Butte Garden, uses electroencephalography (EEG), which records electrical activity in the brain with small discs attached to the scalp, to measure participants’ attentional capacity.
“A walk in nature enhances certain executive control processes in the brain above and beyond the benefits associated with exercise,” ...
What is medical extended reality? New AMXRA guideline
2024-01-29
A new guideline to help define the emerging field of Medical Extended Reality. Which seeks to standardize terminology, categorize existing work, and provide a structured framework for future research development in MXR.
END ...
Emergency cardiovascular care impact goal outlines 3 target needs
2024-01-29
Statement Highlights:
Despite significant advances in research, education, clinical practice and community-based programs, survival from cardiac arrest remains low.
Significant disparities also exist in cardiac arrest outcomes.
This scientific statement specifically identifies impact goals to achieve or exceed by 2030 to improve cardiac arrest for all people.
DALLAS, January 22, 2024 — Only 10% of people who experience a cardiac arrest survive.[1] In new challenge goals outlined in the American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care 2030 Impact Goals and Call to Action to Improve Cardiac Arrest Outcomes, the American Heart Association’s volunteer ...
Genetic alterations in thyroid cancer mediate resistance to BRAF inhibition and anaplastic transformation
2024-01-29
“An improved understanding of the molecular basis of thyroid cancer has led to the development of new targeted agents.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 29, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on January 24, 2024, entitled, “Genetic alterations in thyroid cancer mediating both resistance to BRAF inhibition and anaplastic transformation.”
In this new paper, researchers Mark Lee and Luc GT Morris from New York Presbyterian Hospital and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center discuss thyroid cancer. A subset of thyroid cancers present at advanced stage or with dedifferentiated histology and have limited response to standard therapy. ...
Psychology research: Women more sensitive to cocaine
2024-01-29
Previous studies focused on cocaine use have found that women are more likely than men to develop an addiction, try cocaine at a younger age, use larger amounts of the drug, and suffer from overdose.
Now, a new study from researchers at The University of Texas at Arlington in the journal Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior finally validates what scientists have long suspected: The female sex hormone estradiol (a synthetic version of the naturally occurring estrogen) is responsible for why women are more susceptible to cocaine addiction than men.
“For the first time, we have shown that estradiol enhances the cocaine-conditioned reward,” said Linda Perrotti, ...
When Chinese citizens are surveyed anonymously, support for party and government plummets
2024-01-29
By Ileana Wachtel January 29, 2024
Chinese citizens who rarely voice open criticism of their government reveal stronger negative views when they can answer questions anonymously, according to a new study published in The China Quarterly.
The study by researchers at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences shows an enormous drop in citizen support for the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and government policies when citizens are surveyed using a method that hides their identities and makes them feel more anonymous than a typical survey.
Why ...
Students are missing more school, and school nurses may be well-positioned to help
2024-01-29
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- School nurses are more than just health care heroes. They also play a key role in identifying students who are at risk for chronic absenteeism — a growing problem that diminishes academic success and can hurt students’ health and lead to a variety of negative long-term life outcomes.
A recent study by a University of Missouri researcher found that school nurses are often well-positioned to identify students at-risk for chronic school absenteeism. The finding could help schools implement assessments and interventions to ultimately better support students ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
[Press-News.org] Benchtop test quickly identifies extremely impact-resistant materialsHigh-speed experiments will help identify lightweight, protective “metamaterials” for spacecraft, vehicles, helmets, or other objects.