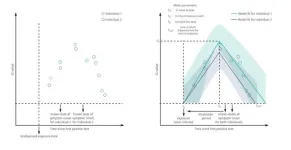
(Press-News.org) Scientists from Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and Northwestern University succeeded in regenerating fully functional urinary bladder tissue in a long-term study utilizing a non-human primate model. This unique model initially created by the Sharma Research Group explores long term bladder tissue regeneration at both anatomical and physiological levels. The Group used a novel biodegradable scaffold seeded with stem and progenitor cells from the animal’s own bone marrow, which demonstrated a higher degree of success than intestinal segments that are traditionally used to treat different types of bladder dysfunction. The regenerated bladder tissue was healthy after two years of monitoring and serves as a pre-clinical model for humans. Their findings were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) Nexus.
“Our results were fantastic and point to a new direction in the field,” said senior author Arun Sharma, PhD, Director of Pediatric Urological Regenerative Medicine at Manne Research Institute at Lurie Children’s and Research Associate Professor of Urology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “The likelihood that our innovative platform will be feasible in humans is very high and we anticipate launching a clinical trial soon.”
Patients with severe bladder dysfunction have very limited options for bladder tissue replacement which encompass a variety of adult and pediatric patients. Dr. Sharma and colleagues are targeting the pediatric spina bifida population with their bladder regeneration work. It has taken them over a decade to reach this milestone, which bears strong potential for translation to clinical practice. Their aim is to offer a better alternative to current bladder augmentation surgery for severe bladder disease. Currently, small intestine tissue is used to replace dysfunctional bladder tissue, but that increases the risk of numerous clinical complications.
“Our innovative approach is promising to make a great difference in the lives of children with spina bifida and others with end stage bladder dysfunction,” said Dr. Sharma. “Since we would be using the patient’s own bone marrow cells, there are no concerns with rejection and our scaffold is non-toxic and biodegradable. In our study, the bladder started working within a few months and demonstrated functionality throughout the course of the study. This is a major advance that will transform clinical practice.”
This work was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health.
Research at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago is conducted through Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute, which is focused on improving child health, transforming pediatric medicine and ensuring healthier futures through the relentless pursuit of knowledge. Lurie Children’s is a nonprofit organization committed to providing access to exceptional care for every child. It is ranked as one of the nation’s top children’s hospitals by U.S. News & World Report. Lurie Children’s is the pediatric training ground for Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine.
END
Functional bladder tissue regenerated using bone marrow cells
Major advance promises to transform clinical practice
2024-01-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tribal program takes addiction treatment on the road
2024-01-30
With the national opioid epidemic disproportionately affecting American Indians and Alaska Natives, a tribal confederation in Oregon decided to take matters into their own hands.
The Confederated Tribes of Grand Ronde not only opened Oregon’s first tribally owned opioid treatment program in Salem in 2021, but a year later, the tribe also began what is believed to be the nation’s first tribally operated mobile medication unit. The mobile bus runs a daily circuit from the tribal reservation in Grand Ronde to McMinnville to Salem, seeing patients and dispensing medications directly to tribal members struggling with an opioid use disorder.
The program appears ...
The emergence of successive SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern during 2020-22 created a need to understand the drivers of such growth
2024-01-30
The emergence of successive SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern during 2020-22 created a need to understand the drivers of such growth; this study uses a Bayesian model to reveal how a set of key covariates (the infecting variant, symptom status, age and number of prior exposures) affect viral kinetics at both individual and population levels
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002463
Article Title: Combined analyses of ...
Mutations in the Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase 1 gene SOD1 can cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (fALS) in a process that involves dissociation of the SOD1 dimer
2024-01-30
Mutations in the Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase 1 gene SOD1 can cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (fALS) in a process that involves dissociation of the SOD1 dimer; this study shows that a novel cyclic thiosulfinate cross-linker has favorable drug-like properties and can stabilize the SOD1 dimer in vivo, with therapeutic implications for fALS
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002462
Author ...
Prestigious NIH grant explores repetitive DNA sequences and cell dysfunction
2024-01-30
Dr. Jeannine Gerhardt, an assistant professor of stem cell biology in obstetrics and gynecology and in reproductive medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, has received a five-year, $2.1 million grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS), part of the National Institutes of Health, for the study of repetitive DNA and RNA sequences and the mechanisms by which they cause cell dysfunction and diseases.
The NIGMS Maximizing Investigators’ Research Award is intended to support recipients’ research more broadly and flexibly than standard project grants, which must specify proposed research thoroughly in advance.
“This award is particularly nice because ...
As cities grow, how will city trash, wastewater, and emissions rise?
2024-01-30
More than half of the world’s population—4.4 billion people—lives in cities, and that proportion will grow to two-thirds by the year 2050, according to the United Nations.
As the world’s population expands, and becomes increasingly urbanized, many have raised concerns about the impact of waste—from house trash to wastewater to greenhouse gas emissions—on the planet.
“We as a society tend to ignore the unpleasant side of our production,” says Mingzhen Lu, an assistant professor at New York University’s ...
A green alternative for treating Streptococcus iniae bacteria in hybrid striped bass
2024-01-30
Scientists at the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA)’s Agricultural Research Service (ARS) developed a green antibiotic alternative to treat the deadly pathogen Streptococcus iniae in hybrid striped bass, the fourth most farmed finfish in the United States, according to a recent study.
S. iniae is the causative agent of streptococcosis, a disease prevalent in aquaculture and causes a worldwide economic loss of $150 million annually. Disease outbreaks can bankrupt fish farms and ...
New research finds concerningly low levels of trust in fisheries institutions post-Brexit
2024-01-30
Peer-reviewed - Survey
Rebuilding trust in fisheries governance will be vital to create a sustainable industry post-Brexit England, according to new research.
Strong trust between managers and fishers is essential for achieving sustainable fisheries, but new research from the University of East Anglia has found worryingly low levels of trust in fisheries following the UK’s departure from the European Union.
The survey pioneered a methodology assessing different elements influencing trust. It revealed perceived incompetence, indifference to fishers' livelihoods, and inadequate consultation as major drivers of fishers' distrust towards fishery regulators.
Lead ...
Mapping cell behaviors in high-grade glioma to improve treatment
2024-01-30
PHOENIX — High-grade gliomas are cancerous tumors that spread quickly in the brain or spinal cord. In a new study led by Mayo Clinic, researchers found invasive brain tumor margins of high-grade glioma (HGG) contain biologically distinct genetic and molecular alterations that point to aggressive behavior and disease recurrence. The findings suggest insights into potential treatments that could modify the course of the disease.
The study published in Nature Communications, profiled 313 tumor biopsies from 68 HGG patients using genomics (study of genes), ...
Using vibrator found in cell phones, researchers develop 3D tumor spheroids to screen for anti-cancer drugs
2024-01-30
Depending on their location, cancer cells within a three-dimensional (3D) tumor structure can have different microenvironments. Cells in the core of the tumor receive less oxygen (hypoxia) and nutrients than those in the periphery. These varying conditions can drive differences in cell growth rates and drug sensitivities, highlighting the need to study 3D tumor models in lab settings. Until recently, conventional methods used to create such tumor spheroids were time-consuming, produced inconsistent results and involved high setup costs.
Investigators at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding ...
Research indicates nearly six million American women became pregnant from rape, sexual coercion, or both during their lifetimes
2024-01-30
Ann Arbor, January 30, 2024 – Experiencing a pregnancy from sexual violence is common in the United States, according to research conducted by investigators at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, published by Elsevier. Nearly six million women in the United States who were raped, sexually coerced (defined as non-physically forced unwanted penetration), or both became pregnant as a result. This equates to about one in twenty American ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
[Press-News.org] Functional bladder tissue regenerated using bone marrow cellsMajor advance promises to transform clinical practice