(Press-News.org) Indiana University researchers in the College of Arts and Sciences in Bloomington have identified a missing link that can help protect the brain from aging.
Hui-Chen Lu, professor and director of the Linda and Jack Gill Center for Biomolecular Science at IU, alongside graduate students Sen Yang and Zhen Xian Niou, found that nicotinamide nucleotide adenylyl transferase 2, or NMNAT2, provides energy to axons independent of the mitochondria. It does this by propelling glycolysis, a process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy. This gives axons enough energy to carry out nerve impulses to the brain and other parts of the body, keeping them healthy and functional. The enzyme can play a critical role in fending off neurodegenerative diseases like ALS, Alzheimer’s, Huntington’s and Parkinson’s as people age.
The study can be found in Molecular Neurodegeneration.
Axons are long, thin fibers that connect nerve cells and allow them to communicate with each other. Axons are typically one micrometer in diameter — several times thinner than a human hair — making them vulnerable and easily damaged by inflammation, trauma, reduced blood flow to the brain and infection. Often, axon damage is the first sign of neurodegenerative disease, but their protection can delay neurodegeneration.
Axons quickly convey information throughout the entire body, a process of traveling long distances within an extremely short time scale that requires significant amounts of energy. However, the mitochondria, widely known as the cellular powerhouse, are in relatively sparse density in axons.
NMNAT2 is a vital provider of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide for the brain. NAD has been studied intensively for its regenerative properties and is sometimes referred to as the “fountain of youth.”
“This new finding showcases the importance of neuron-intrinsic glycolysis in supporting axonal transport, essential for the establishment and maintenance of neuronal circuitry,” Lu said. “With this information, the next step could be designing drugs to target NMNAT2 to boost its expression or activity in pre-symptomatic stages of neurodegeneration.”
Lu’s laboratory has studied NMNAT2 extensively, publishing research in 2017 which found that caffeine, along with 23 other compounds, can increase the body’s production of NMNAT2. In 2016, Lu published a study that found those with higher levels of NMNAT2 had greater resistance to cognitive decline as they aged.
END
Researchers find enzyme plays much larger role in preventing neurodegenerative diseases
2024-01-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CU Anschutz researchers identify new biomarker in quality of blood donations
2024-01-31
AURORA, Co. (January 31, 2024) - A collaborative cohort of researchers, led by University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus professor Angelo D’Alessandro, have identified kynurenine as a critical new biomarker in the quality of stored red blood cells (RBCs), a crucial step in the development of more personalized transfusions. Study results published today in the journal Blood.
The transfusion of RBCs is one of the most common in-hospital medical procedures second only to vaccination. The blood supply is dependent on altruistic blood donors, and donated RBCs are stored ...
38% of surveyed Danish owners put their dogs on unlicensed cannabinoids
2024-01-31
In a new study, 38 percent of dog owners surveyed in Denmark reported giving their pups cannabinoids, particularly cannabidiol or CBD. Pernille Holst and colleagues at the University of Copenhagen, Denmark present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on January 31.
Cannabis has become popular for recreational and medical use in humans, and many cannabis-based products are also available for pets. But because cannabis is not legal for veterinary use in countries such as Denmark, pet owners are using it without a prescription. To understand how common unlicensed cannabinoid use for pets is in Denmark, Holst and colleagues distributed an anonymous ...
After big shocks such as the pandemic lockdowns and the invasion of Ukraine, happiness levels may return to normal in as little as 2-3 weeks, per sentiment analysis of tweets in ten countries
2024-01-31
After big shocks such as the pandemic lockdowns and the invasion of Ukraine, happiness levels may return to normal in as little as 2-3 weeks, per sentiment analysis of tweets in ten countries
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295896
Article Title: Reactions to macro-level shocks and re-examination of adaptation theory using Big Data
Author Countries: South Africa, New Zealand
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Non-invasive wearable devices might be able to predict preterm birth by monitoring changes in maternal heart rate variability
2024-01-31
Non-invasive wearable devices might be able to predict preterm birth by monitoring changes in maternal heart rate variability
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295899
Article Title: Wearable-derived maternal heart rate variability as a novel digital biomarker of preterm birth
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Childhood vitamin D deficiency was likely prevalent during industrialization in England
2024-01-31
Evidence from teeth reveals that vitamin D deficiency during childhood was likely a major issue in industrialized England, according to a study published January 31, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Anne Marie Snoddy of the University of Otago, New Zealand and colleagues.
The 18th and 19th centuries AD were a period of industrialization and urbanization in England. This was also a time of increasing incidence of health issues like vitamin D deficiency (VDD) and associated conditions like rickets, potentially linked to changing social practices ...
Archaeological evidence of seasonal vitamin D deficiency discovered
2024-01-31
Rickets ran rife in children following the Industrial Revolution, but University of Otago-led research has found factory work and polluted cities aren’t entirely to blame for the period’s vitamin D deficiencies.
In a Marsden funded study, just published in PLOS One, researchers from Otago, Durham University, University of Edinburgh, University of Brighton, and University of Queensland, sampled teeth from a cemetery site in industrial era England, looking for microscopic markers of nutritional disease.
Lead author Dr Annie Sohler-Snoddy, Research ...
Jennifer J. Raab named President and CEO of The New York Stem Cell Foundation
2024-01-31
NEW YORK, NY (January 31, 2024) – The New York Stem Cell Foundation (NYSCF) announced today that, following a nationwide search, its Board of Directors has named Hunter College President Emerita Jennifer J. Raab as its next President and Chief Executive Officer, effective this month.
NYSCF is one of the world’s leading nonprofit stem cell organizations, raising and investing more than $450 million since its founding in 2005 to accelerate cures for the major diseases of our time through stem cell research. The foundation conducts its own pioneering research at the NYSCF Research Institute laboratories in Manhattan, informs and convenes scientists and ...
A new way to visualize brain cancer
2024-01-31
Brigham and MIT researchers uncovered never-before-seen details in human brain tissue with new, inexpensive microscopy technology.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Researchers have developed a new microscopy technology called decrowding expansion pathology (dExPath) to analyze brain tissue.
By pulling proteins apart with dExPath, researchers can stain proteins in tissue that could not be accessed before, highlighting nanometer sized structures or even cell populations that were previously hidden.
This “super-resolution imaging” technology ...
AI can predict brain cancer patients’ survival
2024-01-31
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can predict whether adult patients with brain cancer will survive more than eight months after receiving radiotherapy treatment.
The use of the AI to successfully predict patient outcomes would allow clinicians to be better informed for planning the next stage of treatment and refer patients to potentially life-saving treatment quicker.
This is the first use of AI to predict short-term and long-term survivors within eight-months of radiotherapy.
The paper published recently in Neuro-Oncology shows how researchers ...
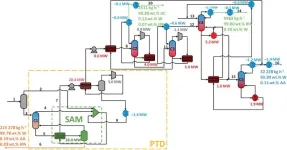
Fermentation revolution? Trash becomes treasure as bio-waste yields valuable acetone and isopropanol
2024-01-31
In a major stride towards sustainable industrial fermentation, a team of researchers at Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) in The Netherlands, has unveiled pioneering advancements in the purification of isopropanol and acetone from the fermentation of waste gases. The study, published in SCI's Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, introduces novel processes that promise to elevate the efficiency and viability of large-scale production.
Isopropanol and acetone have a combined global market of $10 billion. Both chemicals are important industry solvents and isopropanol ...