Five advances that could change heart health monitoring
2024-02-01
(Press-News.org) Chocolate valentines and candies with sweet sayings shouldn't be the only hearts you think about this February. It’s also American Heart Month, which puts a spotlight on cardiovascular health. According to the American Heart Association, heart disease is the leading cause of death for Americans, so it’s important to know the status of your own heart health. New methods for cardiac monitoring can be found in these five papers recently published in ACS journals. Reporters can request free access to these papers by emailing newsroom@acs.org.
Future electrocardiography (better known as ECG or EKG) monitoring could be done with self-powered electrodes. A study in ACS Applied Nano Materials details how a flexible heart rhythm sensor generates power from a person’s movements. Real-time heart rate and ECG signals were collected by flexible electrodes placed on a person’s chest, fingertip and wrist and transmitted wirelessly.
Proof-of-concept test strips could identify the severity of congestive heart failure in about 30 minutes. Reporting in ACS Sensors, researchers developed paper-based strips that measure blood serum for three known markers of heart failure. When combined with a smartphone-connected reader, the method accurately indicated the cardiac disease severity of 13 out of 14 people.
A soft implant to assess post-surgery heart function could dissolve in the body and avoid a follow up surgery to remove it. The flexible, biocompatible device has components that sense changes in levels of lactic acid and volatile organic compounds, as well as pH and pressure. Demonstrations on a beating, 3D-printed silicone heart model and 3D-printed cardiac tissue patches showed the device’s potential for cardiac monitoring, as published in ACS Sensors.
Next-generation implantable “smart” stents could wirelessly monitor blood flow and blood pressure. Authors report in ACS Sensors that the technology, which opens previously obstructed arteries, self-reports an unprecedented level of information on arterial function. In a 3D-printed system mimicking the beating of a human heart, the stent relayed systolic and diastolic pressures and detected blockages occupying up to 50% of a blood vessel.
Blood biomarkers could indicate brain inflammation and neuronal injury after cardiac arrest. Multiple circulating immune cells were identified as indicators from preclinical animal studies of cardiac arrest and resuscitation. Researchers say the biomarkers could be incorporated into blood tests to predict and improve neurological outcomes in cardiac arrest patients, as reported in ACS Chemical Neuroscience.
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-01
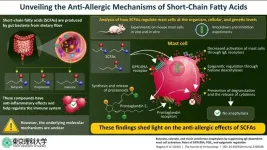
The intricate relationship that exists between humans and the gut microbiome has become a hot research topic, and scientists are constantly uncovering new reasons why a healthy diet can lead to a healthier life. Dietary fibers are a particularly important aspect of this connection. When we ingest these compounds, which are mainly found in plant-based foods, our gut bacteria break them down into small molecules, called short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Over the past few years, studies have revealed various important anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating effects of SCFAs.
One of the ways SCFAs interact with ...
2024-02-01
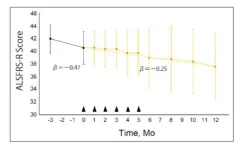
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive loss of motor functions, which eventually leads to death within 5 years of its onset. This disease causes weakness and atrophy of limbs and other muscles, which affect mobility speech, eating, and even breathing in patients. Some drugs, including riluzole, edaravone, and sodium phenylbutyrate/taurursodiol are used for treating ALS, but with limited therapeutic benefits. Therefore, novel, effective ALS treatments are the need of the hour.
Multilineage-differentiating stress-enduring (Muse) cells are pluripotent stem cells ...
2024-02-01
Researchers from Chalmers University of Technology, in Sweden, have discovered a change in what scientists already knew about global warming dynamics. It had been widely accepted since the 1950s that global temperature rises were not consistent throughout the day and night, with greater nighttime warming being observed. However, the recent study reveals a shift in dynamics: with greater daytime warming taking place since the 1990s. This shift means that the temperature difference between day and night is widening, potentially affecting all life on Earth.
The ...
2024-02-01
HOUSTON – (Feb. 1, 2024) – A team of Rice University researchers mapped out how flecks of 2D materials move in liquid ⎯ knowledge that could help scientists assemble macroscopic-scale materials with the same useful properties as their 2D counterparts.
“Two-dimensional nanomaterials are extremely thin ⎯ only several atoms thick ⎯ sheet-shaped materials,” said Utana Umezaki, a Rice graduate student who is a lead author on a study published in ACS Nano. “They behave very differently from materials we’re used to in daily life and can have really useful properties: They can withstand a lot of ...
2024-02-01
Previous studies have found less than 40% of patients with stable chest pain undergoing invasive coronary angiography are found to have obstructive coronary artery disease. Recent randomized clinical trials have demonstrated a benefit to using computed tomography angiography (CTA) first in evaluation of these patients, and a new study being presented at the American College of Cardiology Cardiovascular Summit lends credence to this strategy, finding that CT was associated with a higher likelihood of revascularization compared to other imaging modalities or no testing.
Stable angina ...
2024-02-01
A study led by UMass Chan Medical School viral immunologists Liisa Selin, MD, PhD, and Anna Gil, PhD, discovered similarities in immune system dysfunction as a potential biomarker among people living with long COVID and myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). The research also introduced a novel treatment and a method to track effective treatment interventions. The research was published online in Brain, Behavior & Immunity.
Dr. Selin, professor of pathology, ...
2024-02-01
Research Highlights:
Black women who develop high blood pressure before age 35 may have triple the odds of having a stroke, and those who develop high blood pressure before age 45 may have twice the risk of suffering a subsequent stroke.
The findings, from a study of 59,000 Black women in the U.S., are important for expanding high blood pressure screening and treatment in this high-risk population.
Researchers say health care professionals should be vigilant in high blood pressure screening and ...
2024-02-01
Research Highlights:
One month after hospital evaluation for stroke-like symptoms, people whose symptoms were attributed to another condition were 3 times more likely to have increased risk of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) than people diagnosed with a confirmed stroke.
Knowing that the experience of being evaluated for stroke can itself be traumatic may help health care professionals recognize PTSD symptoms and connect people quickly to the appropriate resources.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET, Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024
DALLAS, Feb. 1, 2024 — People with so-called stroke mimics may be even more likely to develop post-traumatic stress ...
2024-02-01
Research Highlights:
Lifetime exposure to different types of traumatic events or stress appears to reduce the chances for optimal recovery after a stroke.
A review of health records for U.S. stroke survivors found that sexual assault was consistently linked to worse physical functioning and poorer cognitive recovery measurements one year after a stroke.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET, Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024
DALLAS, Feb. 1, 2024 — Stressors and traumatic events experienced over the course of a lifetime may negatively impact subsequent stroke recovery; specifically, stroke survivors exposed to sexual assault at any point in their life had poorer physical functioning ...
2024-02-01
Research Highlights:
In a large population study conducted in Canada, the risk of dementia was nearly 3 times higher in the first year after a stroke, then fell to a 1.5-times increased risk by the 5-year mark and remained elevated 20 years later.
Having a stroke increased the risk of dementia by 80%, even after accounting for other dementia risk factors, such as high blood pressure, Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes and high cholesterol.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET, Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024
DALLAS, Feb. 1, 2024 — Having a stroke may significantly increase the risk of developing dementia. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Five advances that could change heart health monitoring