(Press-News.org) A molecule created at the University of Auckland is one step closer to becoming a treatment for an extremely rare and severely debilitating neurological disorder called Phelan-McDermid syndrome. Children with the disorder showed significant improvements in a phase two clinical trial in the US, Neuren Pharmaceuticals, which is listed on the Australian Securities Exchange, said in December.
Next steps would be a phase three trial and seeking approval from the US Food & Drug Administration. The molecule, NNZ-2591, comes from work years ago by Dr Jian Guan and Professor Sir Peter Gluckman at the Liggins Institute and Distinguished Professor Dame Margaret Brimble in her chemistry laboratory.
That’s the same group whose work led to the breakthrough drug Trofinetide, approved last year for treating Rett syndrome, another rare genetic neurological disorder. The treatment is marketed under the name Daybue.
Neuroprotective qualities of a peptide called cyclic glycine-proline (cGP) were investigated by Guan and Gluckman. In Brimble’s lab, Dr Paul Harris produced NNZ-2591, a synthetic analogue of cGP, which Neuren Pharmaceuticals hopes will become a Phelan-McDermid treatment. The University spun out a company to commercialise research, ultimately selling out.
Intellectual disability, low muscle tone, developmental delays and symptoms of autism can be among the features of Phelan-McDermid.
Neuren is also conducting Phase 2 clinical trials of NNZ-2591 in children with three other neurodevelopmental disorders – Pitt Hopkins syndrome, Angelman syndrome and Prader-Willi syndrome. Likewise, NNZ-2566, the Trofinetide/Daybue molecule, may eventually be used for disorders beyond Rett syndrome.
END
New molecule from University step closer to treatment for rare disease
A molecule created at the University of Auckland is one step closer to becoming a treatment for an extremely rare and severely debilitating neurological disorder called Phelan-McDermid syndrome.
2024-02-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Machine learning to battle COVID-19 bacterial co-infection
2024-02-02
University of Queensland researchers have used machine learning to help predict the risk of secondary bacterial infections in hospitalised COVID-19 patients.
The machine learning technique can help detect whether antibiotic use is critical for patients with these infections.
Associate Professor Kirsty Short from the School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences said secondary bacterial infections can be extremely dangerous for those hospitalised with COVID-19.
“Estimates of the incidents of secondary bacterial infections in COVID-19 ...
Some tumors ‘grow bad’: Why a dangerous subtype of Wilms tumor is so resistant to chemotherapy
2024-02-02
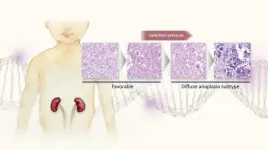
An international team, led by researchers at Nagoya University in Japan, may have determined why the diffuse anaplasia (DA) subtype of Wilms tumor (WT) resists chemotherapy. This subtype grows even when it has a high burden of DNA damage and increases the mutation rate of tumor protein 53 (TP53), a gene that plays a critical role in the regulation of cell growth and division. The team’s findings, published in Modern Pathology, suggest new ways to treat this subtype.
WT, also known as nephroblastoma, is the most common childhood cancer originating in the kidney. Fortunately, the survival rate of adolescents ...
Disrupted cellular function behind type 2 diabetes in obesity
2024-02-02
Disrupted function of “cleaning cells” in the body may help to explain why some people with obesity develop type 2 diabetes, while others do not. A study from the University of Gothenburg describes this newly discovered mechanism.
It is well known that obesity increases the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. It is also well known that some people who gain weight suffer from the disease and others do not. The reasons for these differences are not clear, but they are related ...
USC launches School of Advanced Computing
2024-02-02
USC President Carol Folt launched the university’s first new school in more than a decade: the USC School of Advanced Computing, a cornerstone of her $1 billion advanced computing initiative. The school seeks to educate all students, regardless of their major, in the ethical use of computing technology as part of the president’s Frontiers of Computing initiative.
Gaurav Sukhatme — a professor of computer science and electrical and computer engineering, and executive vice dean of the USC Viterbi School of ...
A clutch stretch goes a long way
2024-02-02
Kyoto, Japan -- Cell biology has possibly never jumped to the next level in the same way.
In multicellular organisms, cell migration and mechanosensing are essential for cellular development and maintenance. These processes rely on talin, the key focal adhesion -- or FA -- protein, central in connecting adjacent cellular matrices and enabling force transmission between them.
Talins are commonly considered fully extended at FAs between actin filaments -- or F-actin -- and the anchor-like integrin receptor.
Yet, a research ...
Psychological care delivered over the phone is an effective way to combat loneliness and depression, according to a major new study
2024-02-02
The study, led by a team based at the University of York and Hull York Medical School and at Tees, Esk and Wear Valleys NHS Foundation Trust, found levels of depression reduced significantly and the benefits were greater than those seen for antidepressants.
Participants in the study reported their levels of emotional loneliness fell by 21% over a three-month period and the benefits remained after the phone calls had ceased, suggesting an enduring impact.
The Behavioural Activation in Social ...
Insulin prices in US are more than twice as high as in other wealthy nations
2024-02-02
The gross price of insulin in the U.S. is more than nine times higher than in 33 high-income comparison nations, according to a new RAND report.
Although the cost differences of insulin between the U.S. and other nations varied depending on the comparison country and the type of insulin, U.S. prices were always higher -- often five to 10 times higher -- than those in other countries. The new report updates findings from earlier RAND work about U.S. insulin prices.
After accounting for rebates and other discounts often offered by drug ...
My love language is peer-reviewed research
2024-02-02
Feb. 1, 2024, TORONTO – From the Five Love Languages to the concept of “Happy Wife, Happy Life,” popular culture is riddled with ideas of how sex and relationships are supposed to work, but does the science back these ideas up? According to Faculty of Health Assistant Professor and Research Chair in Relationships and Sexuality Amy Muise, the answer is frequently no.
Ahead of Valentine’s Day, Muise, also director of the Sexual Health and Relationship (SHaRe) Lab, can offer alternative theories that are supported by her research and other literature in the ...
Husker researchers using metabolic model to study temperature stress on corn
2024-02-02
A research team led by Nebraska scientists has built the largest-ever metabolic model of corn to study how temperature stress affects the plant and how a certain fungus can help alleviate the problem.
The research is an expansion of earlier work with a metabolic model of corn roots that the same team used to study the plant’s nitrogen-use efficiency under nitrogen stress conditions, said Rajib Saha, Richard L. and Carol S. McNeel associate professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering and principal investigator. Saha and ...
New prescription drugs typically sold first in US
2024-02-01
Most new prescription drugs are sold first in the U.S. before they reach other nations, but ultimately important medications are sold across most wealthy nations within about a year of first sale, according to a new RAND report.
Researchers say the study’s findings have implications for the debate over whether efforts to reduce high prescription costs in the U.S. could hurt patients’ access to the newest drug treatments.
“Other wealthy nations -- all of which have much lower drug prices compared ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] New molecule from University step closer to treatment for rare diseaseA molecule created at the University of Auckland is one step closer to becoming a treatment for an extremely rare and severely debilitating neurological disorder called Phelan-McDermid syndrome.