(Press-News.org) The genetic material, in the form of DNA, contains the information that is crucial for the correct functioning of every human and animal cell. From this information repository, RNA, an intermediate between DNA and protein, the functional unit of the cell, is generated. During this process, the genetic information must be tailored for specific cell functions. Information that is not needed (introns) is cut out of the RNA and the important components for proteins (exons) are preserved. A team of researchers led by Professor Dr Mirka Uhlirova at the University of Cologne’s CECAD Cluster of Excellence in Aging Research has now discovered that if the processing of this information no longer works properly, a protein complex (C/EBP heterodimer) is activated and directs the cell towards a dormant state, known as cellular senescence. The results have appeared under the title ‘Xrp1 governs the stress response program to spliceosome dysfunction’ in Nucleic Acids Research.
All eukaryotes (i.e. organisms in which DNA is enclosed within the cell nucleus) have a spliceosome. This is a machine that performs ‘splicing’, the removal of introns and linking exons to form messenger RNA (mRNA). Malfunctions in the spliceosome lead to diseases known as spliceosomopathies, which may affect many different tissues, and manifest as retinal degeneration or myelodysplastic syndrome, a group of bone marrow diseases affecting the blood.
In the study, the Uhlirova lab used the model organism Drosophila melanogaster, a fruit fly, to investigate how cells within a developing organism respond to spliceosome malfunction. The scientists used a combination of genomics and functional genetics to determine the role of individual genes and interactions among them. The study showed that cells suffering from a defective spliceosomal U5 snRNP (U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle) activate a stress signalling response and cellular behaviours that are characteristic of cellular senescence. The senescence programme changes crucial functions of the cells. It prevents cells from dividing while stimulating their secretion. Senescence is triggered to preserve cells that are damaged, as their immediate elimination would cause more harm than good. However, senescent cell accumulation can have a negative impact on a tissue as well as the whole organism. Therefore, these cells are ultimately eliminated.
Uhlirova’s team identified the C/EBP-heterodimer protein complex, Xrp1/Irbp18, as the critical driver of the stress response programme caused by faulty splicing. Upregulation of Xrp1/Irbp18 in damaged cells led to increased protein production and induced a senescence-like state. “Senescence is a double-edged sword,” said Uhlirova. One advantage of senescent cells is that they are not all eliminated by cell death at the same time, thus maintaining the integrity of the tissue. After all, partially intact tissue is better than none at all. However, these cells create problems in the long term, as their accumulation promotes disease and ageing.
“A functioning spliceosome is a basic prerequisite for healthy cells, tissue and the entire organism,” she concluded. “Additional investigation of the stress signalling programme we have identified will be important to further unpack the complex responses triggered by defects in the essential machines controlling gene expression - and how we can influence them.” In future, the results could contribute to the development of therapeutic approaches to treat diseases that are caused by malfunctions of the spliceosome.
END
Mechanism discovered that protects tissue after faulty gene expression
2024-02-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Proteins suggest a path to reduce drug resistance in a form of cancer
2024-02-02
RICHLAND, Wash.—Doctors have nearly a dozen new targeted drugs to treat patients with acute myeloid leukemia, or AML, yet three of four patients still die within five years. Some patients succumb within just a month or two, despite the battery of drugs used to treat the aggressive blood disease, where blood cells don’t develop properly.
A new study draws on a field of science known as proteogenomics to try to improve the outlook. In a paper published Jan. 16 in Cell Reports Medicine, scientists report new ...
Unveiling Oxidation-induced Super-elasticity in Metallic Glass Nanotubes
2024-02-02
Oxidation can degrade the properties and functionality of metals. However, a research team co-led by scientists from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently found that severely oxidized metallic glass nanotubes can attain an ultrahigh recoverable elastic strain, outperforming most conventional super-elastic metals. They also discovered the physical mechanisms underpinning this super-elasticity. Their discovery implies that oxidation in low-dimension metallic glass can result in unique properties for ...
Ambitious workers park the office politics when employer is struggling, study suggests
2024-02-02
One of the study authors, Professor Hans Frankort, Professor of Strategy at Bayes Business School, City, University of London, said: “Sports – particularly motorsports – can be a good proxy for several other industries as they are extremely competitive: if you don’t perform and progress you may be out. Workers in sectors such as consultancy and financial services face similar pressures.”
The peer reviewed paper, which has been published on the website of the Academy of Management Journal, found that riders systematically adjusted their internal ...
Speech Accessibility Project begins recruiting people who have had a stroke
2024-02-02
The Speech Accessibility Project has begun recruiting U.S. and Puerto Rican adults who have had a stroke.
Those interested can sign up online.
Funded by Big Tech companies Amazon, Apple, Google, Meta, and Microsoft, the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign aims to train voice recognition technologies to understand people with diverse speech patterns and disabilities. The project is also recruiting adults with Parkinson’s disease, Down syndrome, cerebral palsy, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
“A stroke can cause big changes, including changes to your ability to speak,” said Mark Hasegawa-Johnson, the project’s ...
Urgent need to address health equity at intersection of American Heart Month and Black History Month 2024
2024-02-02
DALLAS, Feb. 2, 2024 — Black Americans have the highest incidence of cardiac arrest outside of the hospital and are significantly less likely to survive.[1] Cardiac arrest in Black neighborhoods is associated with alarmingly low treatment and survival rates and recent studies have shown lower rates of both bystander CPR and bystander AED use in these neighborhoods. Recognizing the unique intersection of American Heart Month and Black History Month, the American Heart Association, celebrating 100 years of service saving lives, marks the occasion by honoring ...
NRG Oncology selects Health Equity Fellows for 2024
2024-02-02
PHILADELPHIA, PA – NRG Oncology (NRG), a National Cancer Institute (NCI) National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN) group, recently announced that they have named two health equity fellows as a part of the organization’s Health Equity Fellowship Program. Fellowship awardees include Dr. Onyinye Balogun and Dr. Stephanie Rieder.
NRG’s Health Equity Fellowship Program was established by Joan Walker, MD, of the University of Oklahoma and an NRG NCI Community Oncology Research Program (NCORP) Principal Investigator, to train selected ...
Neptune-like exoplanets can be cloudy or clear — new findings suggest the reason why
2024-02-02
LAWRENCE — The study of “exoplanets,” the sci-fi-sounding name for all planets in the cosmos beyond our own solar system, is a pretty new field. Mainly, exoplanet researchers like those in the ExoLab at the University of Kansas use data from space-borne telescopes such as the Hubble Space Telescope and Webb Space Telescope. Whenever news headlines offer findings of “Earth-like” planets or planets with the potential to support humanity, they’re talking about exoplanets within our own Milky Way.
Jonathan Brande, a doctoral candidate in the ExoLab at the University of Kansas, has just published findings in the open-access ...
nTIDE January 2024 Jobs Report: Despite minor shifts, employment for people with disabilities remains near historic highs
2024-02-02
East Hanover, NJ – February 2, 2024 – Labor market indicators showed slight declines over the last two months for both people with and without disabilities, according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE), issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD). These declines may reflect the end of seasonal employment and the impact of the Federal Reserve’s anti-inflationary measures aimed at minimizing the risk of recession. ...
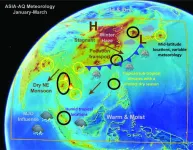
NRL joins Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ)
2024-02-02
WASHINGTON – U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) meteorologists, in partnership with NASA, will join a team of international scientists to participate in the Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ) experiment beginning on February 2.
NRL’s collaborators, David Peterson, Ph.D., meteorologist, Theodore McHardy, Ph.D., American Society for Engineering Education postdoctoral researcher, Nicholas Gapp, Science Applications International Corporation ...
New drug could prevent diabetic eye and kidney disease in people with diabetes
2024-02-02
New research has shown a new type of inhibitor drug could prevent microvascular diabetic complications, such as diabetic eye and kidney disease. The University of Bristol-led research is published in Cardiovascular Diabetology.
Diabetes, a disease which results in uncontrolled blood glucose levels, is estimated to affect one in 11 adults worldwide. Even when managed, this common disease can result in life-altering complications, impacting the small blood vessels of the body, known as the microvasculature.
While treatments ...