(Press-News.org) About The Study: This study of emergency department visits for physical injuries from use of conducted energy devices, such as TASERs, by police departments found that most visits involved young Black and white males from low-income areas. Black individuals were overrepresented in the sample versus the U.S. population, consistent with research demonstrating increased risk of police violence in Black populations.
Authors: Kevin N. Griffith, Ph.D., of the Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.8012)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.8012?guestAccessKey=9a102890-741c-4fb5-9878-a036bbb19182&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=020524
END
Injuries from legal interventions involving conducted energy devices
JAMA Internal Medicine
2024-02-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Losing sleep over killings of unarmed Black individuals by police
2024-02-05
PHILADELPHIA – Black adults across the United States suffer from sleep problems following exposure to news about unarmed Black individuals killed by police during police encounters, according to new findings published today in JAMA Internal Medicine from researchers at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine. The issue, researchers said, may compound the risk factors that poor sleep already poses for many chronic and mental health conditions, from depression to post traumatic stress disorder.
Researchers conducted two separate analyses examining changes in sleep duration in the U.S. non-Hispanic Black population before and after exposure to such deaths ...
New technology unscrambles the chatter of microbes
2024-02-05
Researchers from University of California San Diego, as part of a large collaboration with scientists around the world, have developed a new search tool to help researchers better understand the metabolism of microorganisms. Microbes are key players in virtually all biological and environmental systems, yet limitations in current techniques used to study microbial metabolism make it difficult to decode their interactions and activities.
The new research, published February 5, 2023 in Nature Microbiology, directly addresses these limitations, which could ultimately transform our understanding of both human health and the environment.
“Humans are walking ecosystems in which microbes vastly ...
Pulmonary rehabilitation is difficult for millions of Americans to access
2024-02-05
New Haven, Conn. — Pulmonary rehabilitation, an essential component of care for patients with chronic respiratory conditions, is difficult for millions of Americans to access, a new Yale-led study reveals. The findings, researchers say, reveal geographic regions where this type of care is most lacking and illustrate the potential for telemedicine in helping to bridge this gap.
The study was published Feb. 5 in JAMA Network Open.
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a multidisciplinary program that incorporates exercise and strategic techniques to improve quality of life and overall health for patients with respiratory conditions like chronic ...
Bacterial test for raw, organic milk may require more precision
2024-02-05
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Cornell food scientists show that a standard quality test used for raw, organic milk is insufficient for distinguishing between specific groups of bacteria, suggesting that the criteria for determining milk quality at processing plants needs to be updated.
Their work was published Jan. 20 in the Journal of Dairy Science.
“Testing milk should not be one size fits all,” as tests should be used appropriately to give the best feedback to dairy producers, said lead author Renee Lee ’21, ...
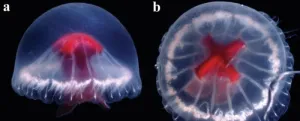
Brazilian researcher helps describe a novel species of jellyfish discovered in a remote location in Japan
2024-02-05
A gelatinous animal with a diameter of about 10 cm and a red stomach resembling the Cross of St George when seen from above. This is Santjordia pagesi, a newly described species of medusa. Medusae are a type of free-swimming, umbrella-shaped jellyfish with a reduced stalk.
The new species is described in an article published in the journal Zootaxa. The study was conducted by an international group of researchers that included a Brazilian scientist supported by FAPESP.
The scientist in question is André Morandini, last author ...
Small but mighty – study highlights the abundance and importance of the ocean’s tiniest inhabitants
2024-02-05
Tiny plankton – measuring less than 20µm (or 0.02mm) in diameter – make up the majority of plankton in the ocean and play a critical role in the planet’s health, according to new research.
However, scientists say challenges in identifying them have led to them becoming a silent majority that is currently being overlooked when it comes to global ocean policy.
The study is one of the first to explore the abundance and importance of these tiny ocean inhabitants around the UK coastline, with the technology capable of monitoring them only having been introduced in around 2010.
However, ...
Bullied teens’ brains show chemical change associated with psychosis
2024-02-05
Researchers have found that adolescents being bullied by their peers are at greater risk of the early stages of psychotic episodes and in turn experience lower levels of a key neurotransmitter in a part of the brain involved in regulating emotions. The finding suggests that this neurotransmitter — a chemical messenger that transmits nerve impulses for communication by a nerve cell — may be a potential target for pharmaceutical interventions aimed at reducing the risk of psychotic disorders.
Psychosis is a mental state characterized by loss of contact with reality, incoherent speech and behavior, and typically hallucinations and delusions seen in psychiatric disorders ...
Unlocking precision medicine for inflammatory bowel disease
2024-02-05
The prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), encompassing ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD), is rapidly increasing worldwide, affecting an estimated 6.8 million people. This surge brings significant economic burdens, with annual healthcare costs exceeding $12,000 and $7,000 for CD and UC patients, respectively. Tailored drug selection based on individual factors can potentially reduce these costs and improve patient outcomes.
Factors associated with a Western lifestyle such as urbanization, high animal protein intake, ultra-processed foods, and reduced fiber ...
High production of polyols using crude glycerol by wild-type safe yeasts
2024-02-05
Utilizing crude glycerol for the synthesis of high-value products offers a promising solution to counter the adverse effects of declining glycerol prices in the biodiesel sector. The prevalence of crude glycerol, a by-product of biodiesel production, across agriculture, biofuel, and industrial sectors is steadily rising. Recent advancements have demonstrated the effectiveness of both wild-type and mutant yeast strains as microbial cell factories capable of converting glycerol into a diverse array of valuable compounds, including microbial oils, sugar-alcohols (polyols), and organic acids. With the projected increase in biodiesel production, there is a need to explore integrated ...
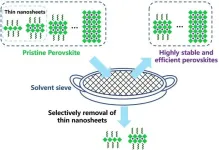
Solvent sieve method sets new record for perovskite light-emitting diodes
2024-02-05
Using a simple solvent sieve method, researchers from the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have taken the lead in developing highly efficient and stable perovskite light-emitting diodes (PeLEDs) with record performance.
The study was published in Nature Photonics.
Perovskites are one of the most promising optoelectronic materials due to their excellent optoelectronic performance and low preparation cost. Compared with traditional organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), PeLEDs have a narrower light-emitting spectrum and superior color ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
[Press-News.org] Injuries from legal interventions involving conducted energy devicesJAMA Internal Medicine