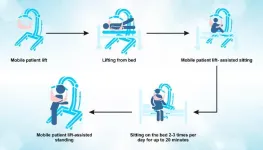
Mobile patient lifts help ICU patients recover
Mobile patient lift-assisted early mobilization in ventilated ICU patients achieved earlier standing in a randomized controlled trial
2024-02-06
(Press-News.org)
Tokyo, Japan – A recent randomized controlled trial in Tokyo, Japan, has unveiled the positive impact of early mobilization, assisted by mobile patient lifts, on the recovery of ventilated intensive care unit (ICU) patients. The debate surrounding the efficacy of early mobilization in ICU has persisted for an extended period.
The treatment of critically ill patients in ICUs, often involving prolonged limb immobilization or restricted mobility, is acknowledged as a risk factor for diminished physical strength and diminished quality of life post-recovery, commonly termed as post-intensive care syndrome (PICS) or ICU-acquired weakness (ICU-AW). While early mobilization, the initiation of physical activity in the early stages of ICU treatment, has been suggested as a preventive measure for ICU-AW, its impact on outcomes has been highly controversial. This new study aimed to investigate whether a more proactive approach to early mobilization, assisted by mobile patient lifts, could facilitate mobilization compared to usual rehabilitation.
The study enrolled 80 patients who received ventilation for a minimum of 48 hours. The intervention group underwent assistance in sitting, standing, transfers, and walking using a mobile patient lift. The researchers observed that the use of mobile lifts led to earlier standing (on day 1, compared to day 3 in the control group after the initiation of rehabilitation). Furthermore, the intervention group exhibited higher Functional Status Score for the Intensive Care Unit scores (FSS-ICU) at ICU discharge, physical function during ICU stay. This study underscores the benefits of early mobilization for mechanically ventilated ICU patients when combined with the use of mobile patient lifts. Given the historical controversy surrounding the effectiveness of early mobilization, these findings may contribute to our understanding of the recovery process in ICU patients.
"We anticipate that proactive early mobilization, with the assistance of mobile patient lifts, will play a pivotal role in preventing post-intensive care syndrome. To draw conclusive evidence for the advantages of early mobilization, further studies should accumulate supportive data," remarked Dr. Ginga Suzuki, the lead author of the study.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-06
Rates of re-excision after initial breast-conserving surgery in women with breast cancer remain high across the United States, leading to an increased cost of care and a higher risk of postoperative complications, according to new research from UTHealth Houston.
The study, led by first author Youngran Kim, PhD, assistant professor; and senior author Trudy Krause, PhD, professor, was published today in Annals of Surgical Oncology. Both are with the Center for Health Care Data in the Department of Management, Policy ...
2024-02-06
Our genomes provide the instructions for proper growth and development. Millions of genomic switches, known as enhancers, control the location and timing of gene expression, which in turn ensures the correct proteins are made in the right cells at the right time throughout our lives. New research from University of California San Diego Assistant Professor Emma Farley’s lab shows how we can now predict which single base-pair changes to the DNA within our genomes will alter these instructions and disrupt development, causing extra digits and hearts.
We now ...
2024-02-06
One of the most common add-ons to IVF procedures undertaken in Australia and globally by infertile couples may be a waste of time as well as expensive and invasive, and maye even reduce the chances of success, according to a new report in The Lancet.
The research, by Monash University’s Professor Ben Mol in Australiaa and Dr. Rui Wang and colleagues in China, found that intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) whereby a single sperm is injected directly into a mature egg – originally developed in 1992 for couples with severe male infertility but which has since expanded ...
2024-02-06
Males born to obese women are more likely to be overweight at birth and develop metabolic complications in later life, including liver disease and diabetes.
The way that male sex hormones activate pathways in the developing liver is partly to blame.
That’s the finding from a new study led by University of South Australia (UniSA) researchers looking at the impact of maternal obesity on fetal liver androgen signalling.
Male fetuses of obese pregnant women have different signals that are activated by male sex hormones in the liver, which encourages them to prioritise growth at the expense of their health.
UniSA researcher Dr Ashley Meakin ...
2024-02-06
Understanding the responses of different rhizosphere microbial lineages to soil amendments during in situ remediation of Cd-contaminated soil is of great importance in the assessment of the restoration and crop health. This study demonstrates the distinct responses of rice rhizosphere microbial communities to soil amendment applications, highlighting the interactive associations between microbiomes, which is vital for enhancing our ability to develop effective strategies for sustainable soil management. The researchers' findings appeared December 4, 2023 in Soil Ecology Letters.
A series ...
2024-02-06
Pulmonary malignancy is one of the most frequent and fatal cancers in older patients. Studies have shown that lung cancer patients have a high incidence of lower respiratory tract infections. This is due to the fact that these patients usually have airway obstruction, sticky sputum that is not easy to cough up, destruction of mucosal surfaces, and treatment with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. When most patients are found to have lung cancer, they have already developed distal metastasis and lost the chance of surgery, therefore, they usually choose to be treated with radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted drugs. Radiotherapy and chemotherapy ...
2024-02-06
Researchers at the University of Queensland have revealed the crucial role of saturated fatty acids in the brain’s consolidation of memories.
Dr Isaac Akefe from UQ’s Queensland Brain Institute has uncovered the molecular mechanism and identified the genes underlying the memory creation process, opening the door to a potential treatment for neurodegenerative disorders.
“We’ve shown previously that levels of saturated fatty acids increase in the brain during neuronal communication, but we ...
2024-02-06
Deep learning has led to great improvements recently on a number of difficult tasks.
In CRYPTO 2019, Gohr innovatively integrated deep learning with differential cryptanalysis, specifically applied to Speck32/64, resulting in developing a neural distinguisher that outperforms the DDT-based distinguisher. Applying differential neural cryptanalysis methods to more cryptographic algorithms is an issue worth studying.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Liu ZHANG published their new research on 15 Dec 2023 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press ...
2024-02-06
Ottawa, ON, February 5, 2024 – Twenty-seven percent of individuals who had an emergency department visit for cannabis use developed a new anxiety disorder within three years, according to new research.
Led by researchers at the Bruyère Research Institute, University of Ottawa Department of Family Medicine, The Ottawa Hospital, and ICES, this is the largest study of the relationship between cannabis use and anxiety to date. The study published today in The Lancet’s open access journal eClinical Medicine included over 12 million individuals living in Ontario, Canada, between 2008 and 2019 who had never received a diagnosis or treatment for anxiety. The researchers ...
2024-02-06
A Doppler ultrasound that measures the blood flow of small unborn babies can reveal whether or not the placenta is working properly. In case of repeated deviations from these Doppler measurements, additional monitoring of the unborn baby is necessary. These deviations indicate a higher risk of oxygen deficiency and other health problems for the baby. This study by Amsterdam UMC in collaboration with UMC Groningen and 17 other Dutch hospitals is published today in the British Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology.
Around 10% of unborn babies are classed as small for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Mobile patient lifts help ICU patients recover
Mobile patient lift-assisted early mobilization in ventilated ICU patients achieved earlier standing in a randomized controlled trial