Last chance to get hotel discounts for the world’s largest physics meeting
Book your hotel by Feb. 9 to receive the discount
2024-02-06
(Press-News.org) Next month, scientists from around the world will convene to share new results from across the physical sciences in nearly 11,000 individual presentations. The American Physical Society’s (APS) March Meeting will be held in person in Minneapolis and online everywhere March 3-8.
Discounted hotel rates are available for in-person attendees at select Minneapolis hotels near the Minneapolis Convention Center. Book your hotel by Feb. 9 to receive the discount.
Press Registration
News media with valid APS press credentials may register for the meeting at no cost. To request press credentials, visit APS’s online newsroom. Registration will remain open throughout the meeting.
Scientific Program
The scientific program will include nearly 900 sessions and 11,000 individual presentations on new research in climate science, medicine, biological physics, quantum information, superconductivity, condensed matter, and more. For more information, search the scientific program. All times are in Central time.
Press Program
The press program will be announced soon. Press releases, tip sheets, and other press materials about newsworthy presentations will be available in the March Meeting press kit ahead of the meeting. A press room will be available for news media attending in person.
Hybrid Format
The March Meeting will have both in-person and online experiences. The in-person meeting will be at the Minneapolis Convention Center. It will include scientific sessions, exhibits, networking events, receptions, and more. In-person registration (excluding daily registration) includes access to the online meeting.
The online meeting will be held simultaneously, but it is geared toward remote attendees’ needs. It will feature select live streamed sessions from the in-person meeting, live and interactive presentations, a virtual poster session, and more. Select content from the scientific sessions at the in-person meeting will be available for on-demand viewing one week after the meeting concludes.
Content on the online meeting platform will be available to all attendees (excluding daily registrants) for 90 days after the online meeting concludes.
# # #
The American Physical Society is a nonprofit membership organization working to advance and diffuse the knowledge of physics through its outstanding research journals, scientific meetings, and education, outreach, advocacy, and international activities. APS represents more than 50,000 members, including physicists in academia, national laboratories, and industry in the United States and throughout the world.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-06
The search for habitable exoplanets involves looking for planets with similar conditions to the Earth, such as liquid water, a suitable temperature range and atmospheric conditions. One crucial factor is the planet's position in the habitable zone, the region around a star where liquid water could potentially exist on the planet's surface. NASA's Kepler telescope, launched in 2009, revealed that 20–50% of visible stars may host such habitable Earth-sized rocky planets. However, the presence of liquid water alone does not guarantee a planet’s habitability. On Earth, ...
2024-02-06
Over the past two decades, microfluidic devices, which use technology to produce micrometer-sized droplets, have become crucial to various applications. These span chemical reactions, biomolecular analysis, soft-matter chemistry, and the production of fine materials. Furthermore, droplet microfluidics has enabled new applications that were not possible with traditional methods. It can shape the size of the particles and influence their morphology and anisotropy. However, the conventional way of generating droplets in a single microchannel structure is often slow, ...
2024-02-06
The city you live in could be making you, your family, and your friends more unconsciously racist. Or, your city might make you less racist. It depends on how populous, diverse, and segregated your city is, according to a new study that brings together the math of cities with the psychology of how individuals develop unconscious racial biases.
The study, published in the latest issue of Nature Communications, presents data and a mathematical model of exposure and adaptation in social networks that can help explain why there is more unconscious, or implicit, racial bias ...
2024-02-06
6 February 2024
The Geological Society of America
Release No. 24-01
Contributed by Arianna Soldati, GSA Science Communication Fellow
Boulder, Colo., USA: Earth is a stressed planet. As plates move, magma rises, and glaciers melt—just to mention a few scenarios—rocks are subject to varying pressure and compressional and extensional forces. The effect of these stresses on rock mineralogy and texture is of great interest to the tectono-metamorphic community. Yet the link between process and outcome remains elusive.
There are two possible states of stress: either all principal ...
2024-02-06
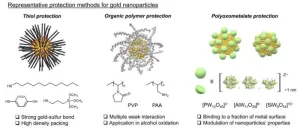
For the first time, researchers including those at the University of Tokyo discovered a way to improve the durability of gold catalysts by creating a protective layer of metal oxide clusters. The enhanced gold catalysts can withstand a greater range of physical environments compared to unprotected equivalent materials. This could increase their range of possible applications, as well as reduce energy consumption and costs in some situations. These catalysts are widely used throughout industrial settings, including chemical synthesis and production of medicines, these industries could benefit from improved gold catalysts.
Everybody loves gold: athletes, pirates, bankers — everybody. ...
2024-02-06
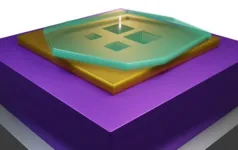
In a significant leap forward for quantum nanophotonics, a team of European and Israeli physicists, introduces a new type of polaritonic cavities and redefines the limits of light confinement. This pioneering work, detailed in a study published today in Nature Materials, demonstrates an unconventional method to confine photons, overcoming the traditional limitations in nanophotonics.
Physicists have long been seeking ways to force photons into increasingly small volumes. The natural length scale of the photon is the wavelength and when a photon is forced into a cavity much smaller than ...
2024-02-06
Promising trial results indicate that a new type of cell therapy could improve the prognosis of those who are critically ill with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) resulting from severe Covid-19.
Published in the journal Nature Communications, Professor Justin Stebbing of Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) is the joint senior author of the new study investigating the use of agenT-797, MiNK Therapeutic’s allogeneic, unmodified invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cell therapy.
The iNKT cell therapy has the effect of rescuing exhausted T cells and prompting an anti-inflammatory cytokine response, potentially activating anti-viral immunity to ...
2024-02-06
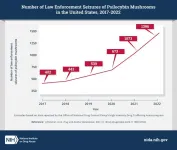
Law enforcement seizures of “magic mushrooms” or “shrooms” containing the psychoactive component psilocybin increased dramatically in the United States between January 2017 and December 2022, according to a new study funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, part of the National Institutes of Health. The number of law enforcement seizures increased from 402 seizures in 2017 to 1,396 in 2022. In addition, the total weight of psilocybin mushrooms seized by law enforcement increased ...
2024-02-06
Seizures by law enforcement officials of psilocybin, a compound found in psychedelic mushrooms, have increased by 369% since 2017, a new study shows. The authors say their findings may signal growing availability and public awareness of the hallucinogenic drug, along with possible heightened risks associated with recreational and unsupervised use of the drug.
The study was led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and other members of the National Drug Early Warning System, an organization that conducts surveillance of shifting drug trends. Their analysis of national and state-level trafficking data ...
2024-02-06
Decidious and evergreen forests dominate the limestone karst formations of the northwestern highlands of Thailand. A vast number of caves and rock shelters intersperses the mountains. In over 40 such caves in Mae Hong Son province, large wooden coffins mounted on stilts, dating between 2,300 and 1,000 years ago, can be found. During the Iron Age period, each of these up to several-meter-long coffins was crafted from a single teak tree and features refined carvings of geometric, animal- or human-like shapes at the handles ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Last chance to get hotel discounts for the world’s largest physics meeting
Book your hotel by Feb. 9 to receive the discount