(Press-News.org)
“The findings validate the combined PROX1/α-SMA gene set as a prospective prognostic biomarker and a central regulator in CRC progression and its TME.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 7, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 2, entitled, “PROX1 interaction with α-SMA-rich cancer-associated fibroblasts facilitates colorectal cancer progression and correlates with poor clinical outcomes and therapeutic resistance.”
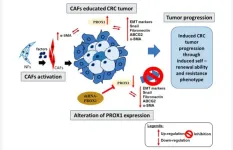
The tumor microenvironment (TME) plays a vital role in tumor progression through intricate molecular interactions. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), notably those expressing alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) or myofibroblasts, are instrumental in this context and correlate with unfavorable outcomes in colorectal cancer (CRC). While several transcription factors influence TME, the exact regulator causing CAF dysregulation in CRC remains elusive. Prospero Homeobox 1 (PROX1) stands out, as its inhibition reduces α-SMA-rich CAF activity. However, the therapeutic role of PROX1 is debated due to inconsistent study findings.
In this new study, researchers Shiue-Wei Lai, Yi-Chiao Cheng, Kee-Thai Kiu, Min-Hsuan Yen, Ying-Wei Chen, Vijesh Kumar Yadav, Chi-Tai Yeh, Kuang-Tai Kuo, and Tung-Cheng Chang from Taipei’s National Defense Medical Center, Taipei Medical University, Taipei Medical University Shuang-Ho Hospital, and National Taitung University used the ULCAN portal and noted an elevated PROX1 level in advanced colon adenocarcinoma, linking to a poor prognosis. Their assays determined the impact of PROX1 overexpression on CRC cell properties, while co-culture experiments spotlighted the PROX1-CAF relationship. Molecular expressions were validated by qRT-PCR and Western blots, with in vivo studies further solidifying the observations.
“Our study emphasized the connection between PROX1 and α-SMA in CAFs.”
Elevated PROX1 in CRC samples correlated with increased α-SMA in tumors. PROX1 modulation influenced the behavior of specific CRC cells, with its overexpression fostering invasiveness. Kaplan-Meier evaluations demonstrated a link between PROX1 or α-SMA and survival outcomes. Consequently, PROX1, alone or with α-SMA, emerges as a CRC prognostic marker. Co-culture and animal experiments further highlighted this relationship.
PROX1 appears crucial in modulating CRC behavior and therapeutic resistance within the TME by influencing CAFs, signifying the combined PROX1/α-SMA gene as a potential CRC prognostic marker. The concept of developing inhibitors targeting this gene set emerges as a prospective therapeutic strategy. However, this study is bound by limitations, including potential challenges in clinical translation, a focused exploration on PROX1/α-SMA potentially overlooking other significant molecular contributors, and the preliminary nature of the inhibitor development proposition.
“As we advance in this field, the development and clinical validation of small-molecule inhibitors targeting PROX1/α-SMA become imperative, paving the way to refine and optimize CRC therapeutic interventions.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205447
Corresponding Author: Tung-Cheng Chang
Corresponding Email: 09432@s.tmu.edu.tw
Keywords: colorectal cancer, prognosis, biomarker, PROX1 α-SMA, cancer-associated fibroblast, metastasis
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Facebook
X, formerly Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Rocks once buried deep in ancient subduction zones — where tectonic plates collide — could help scientists make better predictions of how these zones behave during the years between major earthquakes, according to a research team from Penn State and Brown University.
Clues from rock formations in Alaska and Japan allowed the scientists to develop a new model to predict the pressure solution activity in subduction zones, the researchers reported in the journal Science Advances. ...
The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research has chosen MUSC as one of four sites for the Black and African American Connections to Parkinson’s Disease (BLAAC PD) research study, a part of the Global Parkinson’s Genetics Program.
BLAAC PD will explore the genetic basis of Parkinson’s disease (PD) in the Black community by genotyping more than 150,000 people worldwide, setting the stage for the development of targeted treatments. According to the Parkinson’s Foundation, approximately 36,265 people with ...
The American Society of Heating, Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning Engineers, or ASHRAE, selected Jason DeGraw, a researcher with the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, as one of 23 members elevated to Fellow during its 2024 winter conference.
A thermal-fluid scientist and mechanical engineer in the Thermal Energy Storage group, DeGraw was recognized for making substantial contributions in heating, ventilation, air-conditioning and refrigeration, and the built environment. He contributes education, research, engineering design and consultation, publications, presentations and mentoring to ASHRAE. At ORNL, DeGraw works with the Building Technologies ...
(Memphis, Tenn. – February 7, 2024) St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital today announced Sara M. Federico, MD, has been named director of the institution’s Solid Tumor Division within the Department of Oncology. Federico is an internationally recognized leader in pediatric oncology whose contributions have defined the landscape of treatment for high-risk childhood solid tumors, such as neuroblastoma.
“Dr. Federico’s experience will pave the way for new discoveries that will help advance cure rates for patients with high-risk cancers by identifying, testing and optimizing novel therapeutic strategies,” said Julie R. ...
INDIANAPOLIS – Pioneering cancer researcher Craig B. Thompson, MD, has been named the 2024 winner of the August M. Watanabe Prize in Translational Research.
Awarded by the Indiana University School of Medicine, the Watanabe Prize is one of the nation's largest and most prestigious awards recognizing individuals focused on shepherding scientific discoveries into new therapies for patients. The prize is awarded to a senior investigator who has made a significant contribution to the field of translational science.
Thompson is the former president and chief executive officer ...
Generative artificial intelligence platforms, from ChatGPT to Midjourney, grabbed headlines in 2023. But GenAI can do more than create collaged images and help write emails — it can also design new drugs to treat disease.
Today, scientists use advanced technology to design new synthetic drug compounds with the right properties and characteristics, also known as “de novo drug design.” However, current methods can be labor-, time-, and cost-intensive.
Inspired by ChatGPT’s popularity and wondering if this approach could speed up the drug design process, scientists in the Schmid ...
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 7, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – The drugs used to treat erectile dysfunction may also be associated with a reduced risk of Alzheimer’s disease, according to a study published in the February 7, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that erectile dysfunction drugs reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. It only shows an association.
Erectile dysfunction drugs, which work by dilating blood vessels to allow more blood ...
Imagine a coffee cup sitting on a table. Now, imagine a book partially obscuring the cup. As humans, we still know what the coffee cup is even though we can't see all of it. But a robot might be confused.
Robots in warehouses and even around our houses struggle to identify and pick up objects if they are too close together, or if a space is cluttered. This is because robots lack what psychologists call "object unity," or our ability to identify things even when we can't see all of them.
Researchers at the University of Washington ...
“[...] the results of the studies presented in this review will hopefully provide the impetus for conducting additional preclinical and clinical studies to evaluate RUX in the setting of MM as well as other types of cancer.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 7, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on February 5, 2024, entitled, “Preclinical and clinical evaluation of the Janus Kinase inhibitor ruxolitinib in multiple myeloma.”
In this new paper, researchers Ashley Del Dosso, Elizabeth Tadevosyan, and James ...
Research Highlights:
Although giving blood thinners along with clot-busting medication may help in treating heart attacks, it did not improve 90-day outcomes in people with clot-caused strokes.
Enrollment in a large clinical trial, which had been planned to include more than 1,200 patients with ischemic stroke (clot-caused stroke), was halted after an independent data and safety monitoring board found no indication of benefit among the first 500 patients.
The data analysis for the 500 enrolled participants found giving blood thinners along with clot-busting medication did not increase the risk of bleeding into the brain.
Embargoed ...