(Press-News.org) Asian Americans are less likely than their white peers to participate in health research involving MRIs and addressing this hesitancy could improve research, according to a Rutgers Health-led study.
Findings by the researchers, published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions, a journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, surveyed older adults about their experiences and perceptions of MRI brain imaging scans, their desire to learn results of scans and their attitudes related to dementia and overall research participation.
According to the study, South Asian older adults – those 65 and older – are less likely than older white adults to believe that healthy people should participate in research studies when it may not benefit them. South Asian and East Asian older adults also have less desire to learn about findings from an MRI brain scan – commonly used in clinical research studies – than older white adults.
“Addressing hesitancy toward participation may improve representation of a group that does not usually take part in research studies,” said Karthik Kota, an assistant professor of medicine and a geriatrician at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School and lead author of the study.
Asian Americans represent the fastest-growing racial group in the United States and the fastest-growing group of adults over 65. As age is the biggest risk factor for dementia, this group is at higher risk for dementia. In a prior pilot study, Rutgers Health researchers encountered unexpected hesitancy from these groups related to MRI scans.
In the latest study, 256 respondents answered what type of MRI results they wanted to learn of – including receiving serious findings without treatment options or benign ones common with aging – and questions on research and brain health attitudes. Researchers found similarly low desire to learn of MRI results in South Asians and East Asians despite the groups showing differing support for research participation and future dementia or stroke worries.
Researchers said the findings reinforce the need to separate different Asian American subgroups when conducting health-related research.
“Understanding concerns older Asian adults have about MRI brain findings could allow for more culturally appropriate return of scan results,” Kota said. “Progress in this area will not only affect how researchers recruit for studies, but also the expectations that the public may have when interacting with researchers.”
Research was supported by the Resource Center for Alzheimer’s and Dementia Research in Asian and Pacific Americans at the Rutgers Institute for Health, Health Care Policy and Aging Research (IFH), as well as the South Asian Total Health Initiative and the RWJBarnabas Health Chinese Medical Program.
Coauthors of the study include Alice Dawson, Julia Papas, Victor Sotelo and William Hu of the Department of Neurology at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School and the Center for Healthy Aging at IFH; and Guibin Su, Mei-Ling Li, Woowon Lee, Jaunis Estervil, Melissa Marquez, Shromona Sarkar and Lisa Lanza of IFH.
END
Certain older Americans show hesitation around brain scan research
2024-02-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Migration solves exoplanet puzzle
2024-02-09
Ordinarily, planets in evolved planetary systems, such as the Solar System, follow stable orbits around their central star. However, many indications suggest that some planets might depart from their birthplaces during their early evolution by migrating inward or outward. This planetary migration might also explain an observation that has puzzled researchers for several years: the relatively low number of exoplanets with sizes about twice as large as Earth, known as the radius valley or gap. Conversely, there are many exoplanets smaller and larger than this size.
“Six years ago, a reanalysis of data from the Kepler space telescope revealed a shortage of exoplanets with sizes around ...
New adhesive tape picks up and sticks down 2D materials as easily as child’s play
2024-02-09
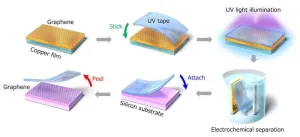
Fukuoka, Japan – Materials just atoms in thickness, known as two-dimensional (2D) materials, are set to revolutionize future technology, including in the electronics industry. However, commercialization of devices that contain 2D materials has faced challenges due to the difficulty in transferring these extremely thin materials from where they are made onto the device.
Now, a research team from Kyushu University, in collaboration with Japanese company Nitto Denko, have developed a tape that can be used to stick 2D materials to many different surfaces, in an ...
Researchers discover cosmic dust storms from Type Ia supernova
2024-02-09
Cosmic dust—like dust on Earth—comprises groupings of molecules that have condensed and stuck together in a grain. But the exact nature of dust creation in the universe has long been a mystery. Now, however, an international team of astronomers from China, the United States, Chile, the United Kingdom, Spain, etc., has made a significant discovery by identifying a previously unknown source of dust in the universe: a Type Ia supernova interacting with gas from its surroundings.
The study was published in Nature Astronomy on Feb. 9, and was led by Prof. WANG Lingzhi from the South America Center for Astronomy of the Chinese Academy ...
New fossil site of worldwide importance uncovered in southern France
2024-02-09
Nearly 400 exceptionally well-preserved fossils dating back 470 million years have been discovered in the south of France by two amateur paleontologists. This new fossil site of worldwide importance has been analyzed by scientists from the University of Lausanne, in collaboration with the CNRS and international teams. This discovery provides unprecedented information on the polar ecosystems of the Ordovician period.
Paleontology enthusiasts have unearthed one of the world's richest and most diverse fossil sites from the Lower Ordovician period (around 470 million ...
Global study: Wild megafauna shape ecosystem properties
2024-02-09
For millions of years, a variety of large herbivores, or megafauna, influenced terrestrial ecosystems. Among many others, these included elephants in Europe, giant wombats in Australia, and ground sloths in South America. However, these animals experienced a wave of extinctions coinciding with the worldwide expansion of humans, leading to dramatic but still not fully understood changes in ecosystems. Even the survivors of these extinctions strongly declined, and many are currently threatened with extinction.
While there are many case studies as well as theories about the effects of large animals, formal attempts to quantitatively synthesize their effects and establish ...
Towards A Better Way of Releasing Hydrogen Stored in Hydrogen Boride Sheets
2024-02-09
The looming threat of climate change has motivated scientists worldwide to look for cleaner alternatives to fossil fuels, and many believe hydrogen is our best bet. As an environmentally friendly energy resource, hydrogen (H2) can be used in vehicles and electric power plants without releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
However, storing and transporting H2 safely and efficiently remains a challenge. Compressed gaseous hydrogen poses a significant risk of explosion and leakage, whereas liquid hydrogen must be maintained at extremely low temperatures, ...
Language barriers could contribute to higher aggression in people with dementia
2024-02-09
Immigrants living with dementia were more likely to present with agitation and aggression compared with their non-immigrant counterparts, a new study by Edith Cowan University (ECU) in collaboration with The Dementia Centre, HammondCare, found.
Researchers from ECU’s Centre for Research in Aged Care and HammondCare’s The Dementia Centre noted that behaviours and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD), such as agitation and aggression, are common; however, its presentation may be influenced by the cultural background of the person.
A study investigated differences in clinical and demographics characteristics ...
Conversion process turns greenhouse gas into ethylene
2024-02-09
Engineers at the University of Cincinnati created a more efficient way of converting carbon dioxide into valuable products while simultaneously addressing climate change.
In his chemical engineering lab in UC’s College of Engineering and Applied Science, Associate Professor Jingjie Wu and his team found that a modified copper catalyst improves the electrochemical conversion of carbon dioxide into ethylene, the key ingredient in plastic and a myriad of other uses.
Ethylene has been called ...
Predicting psychosis before it occurs
2024-02-09
The onset of psychosis can be predicted before it occurs, using a machine-learning tool which can classify MRI brain scans into those who are healthy and those at risk of a psychotic episode. An international consortium including researchers from the University of Tokyo, used the classifier to compare scans from over 2,000 people from 21 global locations. About half of the participants had been identified as being clinically at high risk of developing psychosis. Using training data, the classifier was 85% accurate at differentiating between people ...
New research shows students' knowledge and perceptions of active learning declined during pandemic-era teaching
2024-02-09
Students’ knowledge and perceptions of active learning declined significantly during COVID-induced remote teaching and have not recovered to pre-pandemic levels, according to new research from Chapman University Assistant Professor Jeremy Hsu.
Hsu says the benefits of active learning – exercises like group projects, problem-solving and class discussions – are well documented, but he emphasizes that students’ understanding and perceptions of the practice can affect their level of engagement and investment. If students have limited exposure or are hesitant to participate in active learning practices, resistance could ...