(Press-News.org) Los Angeles, CA (February 14, 2024) — A new study published in the journal PLOS ONE explores the weight great fossil sites have on our understanding of evolutionary relationships between fossil groups—the lagerstätten effect—and for the first time, quantified the power these sites have on our understanding of evolutionary history. Surprisingly, the authors discovered that the wind-swept sand deposits of the Late Cretaceous Gobi Desert’s extraordinarily diverse and well-preserved fossil lizard record shapes our understanding of their evolutionary history more than any other site on the planet.
While famous as the region where Velociraptor was discovered, China and Mongolia’s Late Cretaceous Gobi Desert might have more of an impact on our understanding of ancient—and modern—life thanks to its rich record of fossil lizards.
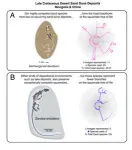
“What's so cool about these Late Cretaceous Gobi Desert deposits is that you're getting extremely diverse, exceptionally complete, three-dimensionally-preserved lizard skeletons,” said Dr. Hank Woolley, lead author and NSF Postdoctoral Research Fellow at the Dinosaur Institute. “You're getting many lineages on the squamate Tree of Life represented from this single unit, giving us this remarkable fossil signal of biodiversity in the rock record, something that stands out as a lighthouse in the deep dark chasms of squamate evolutionary history.”
More complete skeletons make it easier to trace relationships through time by making it easier to compare similarities and differences. The more complete a skeleton is, the more traits are preserved, and those traits translate into phylogenetic data—data that are used to construct the tree of life. “Where there’s exceptional preservation—hundreds of species from one part of the world at one period of very specific time—that doesn't necessarily give you a good idea of global signals,” said Woolley. “It's putting its thumb on the scale.”
To measure how impactful deposits of exceptional fossil preservation (known in the paleontology community by the German term “lagerstätten”) are on the broader understanding of evolutionary relationships through time, Woolley and co-authors including Dr. Nathan Smith, Curator of the Dinosaur Institute, combed through published records of 1,327 species of non-avian theropod dinosaurs, Mesozoic birds, and fossil squamates (the group of reptiles that includes mosasaurs, snakes, and lizards).
The Fossil Meta Narrative
When it came to squamates, the researchers found no correlation between the intensity of sampling and whether any given site impacted phylogenetic data on a global scale. Instead, they found a signal from depositional environments, the different kinds of sites where sediments accumulated preserved markedly different groups.
Because the squamate record from the Gobi Desert is so complete, it shapes our understanding of squamate evolution around the world and across time, a prime example of the “lagerstätten effect”—despite not being a typical lagerstätte. Traditional lagerstätten deposits come from marine chalks, salty lagoons, and ancient lake environments—not from arid sand dunes. The ancient environment shapes what gets preserved in the fossil record. “We were not expecting to find this detailed record from lizards in a desert sand dune deposit,” said Woolley.
“We often think of lagerstätten deposits as preserving soft tissues and organisms that rarely fossilize, or especially rich concentrations of fossils. What makes the Gobi squamate record unique, is that it includes both exceptionally complete skeletons, and a high diversity of species from across the group’s family tree,” said Smith.
“We're at this frontier between fields within paleontology that rarely overlap: assessing evolutionary relationships of fossil groups (phylogenetics) and assessing how things fossilize (taphonomy). Exploring this frontier will help to incorporate more of Earth’s extinct biodiversity in museum collections as we piece together the past.” said Woolley.
About the Natural History Museums of Los Angeles County (NHMLAC)
The Natural History Museums of Los Angeles County (NHMLAC) include the Natural History Museum in Exposition Park, La Brea Tar Pits in Hancock Park, and the William S. Hart Museum in Newhall. They operate under the collective vision to inspire wonder, discovery, and responsibility for our natural and cultural worlds. The museums hold one of the world’s most extensive and valuable collections of natural and cultural history—more than 35 million objects. Using these collections for groundbreaking scientific and historical research, the museums also incorporate them into on- and offsite nature and culture exploration in L.A. neighborhoods, and a slate of community science programs—creating indoor-outdoor visitor experiences that explore the past, present, and future. Visit NHMLAC.ORG for adventure, education, and entertainment opportunities.
About the Dinosaur Institute
The Dinosaur Institute (DI) houses NHMLAC’s collection of Mesozoic tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates), dating from 250 million to 65.5 million years ago. This collection includes fossils of dinosaurs spanning the Mesozoic Era, as well as fossils of other tetrapods that lived alongside the dinosaurs, such as flying and marine reptiles, crocodiles, turtles, amphibians, and early mammals. The DI maintains an active paleontological training program, supporting undergraduates, PhD students, and Postdoctoral fellows.
MEDIA CONTACTS
Amy Hood
213-763-3532
ahood@nhm.org
Josh Chesler
213-763-3580
jchesler@nhm.org
END
A lighthouse in the Gobi desert
A new study quantifies the impact of the world’s great fossil sites on our understanding of evolutionary relationships between fossil groups and discovers the key to understanding lizard evolutionary history in the Gobi Desert.
2024-02-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Paradigm Shift: How a risk-based program is changing health care use and outcomes for children with high-risk asthma
2024-02-14
Le Bonheur’s risk-based innovation program Changing High-Risk Asthma in Memphis through Partnership (CHAMP) significantly decreased health care use related to asthma by targeting barriers to asthma care, according to research published in the Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. After one year of enrollment in the program, results analyzing 945 children included a 48% reduction in Emergency Department (ED) visits, 68% reduction in inpatient and observation visits, 42% reduction in urgent care visits and 53% reduction in asthma exacerbations. Asthma exacerbations per patient significantly decreased from 2.97 to 1.4.
“Children ...
U of M research advances potential HIV cure strategy
2024-02-14
Published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases Oxford Academic, research led by the University of Minnesota Medical School offers a new avenue of hope in the fight against chronic human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection.
The researchers explored the use of Natural Killer (NK) cells aiming to restore their function for better infection control — an approach that could be used in a broader HIV cure strategy as multiple companies are working on mass production of healthy NK cells.
“HIV has really excellent therapies thanks to the unprecedented progress in developing antiretroviral therapy, ...
New review finds Indigenous people more likely to have a stroke
2024-02-14
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 14, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Indigenous people may be more likely to have a stroke than non-Indigenous people, according to a systematic review that looked at populations around the world. The review is published in the February 14, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
Researchers looked at countries with a very high Human Development Index, which measures average achievements in three areas: health, knowledge ...
UC Irvine-led research team creates novel rabies viral vectors for neural circuit mapping
2024-02-14
Irvine, Calif., Feb. 14, 2024 — A research team led by the University of California, Irvine has created 20 new recombinant rabies viral vectors for neural circuit mapping that offer a range of significant advantages over existing tools, including the ability to detect microstructural changes in models of aging and Alzheimer’s disease brain neurons.
The study published today online in the journal Molecular Psychiatry, introduced proof-of-concept data demonstrating the power of these new vectors, which express a range of improved ...
Broad Institute 2024 Media Boot Camp
2024-02-14
The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard is now accepting applications for its 2024 Media Boot Camp.
This annual program connects health/science journalists and editors with faculty from the Broad Institute, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Harvard University, and Harvard’s teaching hospitals for a two-day event exploring the latest advances in genomics and biomedicine. Journalists will explore possible future storylines, gain fundamental background knowledge, and build relationships with researchers. The program format ...
MEDIA ADVISORY: Mount Sinai doctors to present new research at 2024 SMFM Annual Pregnancy Meeting
2024-02-14
(New York, NY – February 9, 2024) – High-risk pregnancy specialists from the Mount Sinai Health System are presenting research at the Annual Pregnancy Meeting of the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM) in Fort Washington, MD from February 10-14. Mount Sinai experts are available for interview about their research findings, and can also provide commentary on other women’s health topics, breaking news, and studies.
PRESENTATIONS and POSTER SESSIONS
(*All abstracts are under embargo until the below listed times*)
Sunday, February 11, 2024
FGR prevention: Is there a role for aspirin, heparin, ...
Significantly fewer births on weekends and holidays than weekdays, data analysis of over 21 million births from 1979-2018 in Japan shows
2024-02-14
Significantly more babies were born on a weekday instead of weekend day or holiday, reveals a large-scale analysis of 21 million births in Japan over almost four decades published February 14, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Miho Sassa from the University of Tokyo, Japan, and colleagues.
Medical resources are generally stretched during holidays (including weekends) due to factors like staffing and hospital policies. This may amplify holiday effects: disparities and variations of health outcomes between holidays and weekdays. Dr. Sassa and colleagues studied this holiday effect with a focus on birth, especially high-risk births as measured by babies born preterm ...
Vittrup Man crossed over from forager to farmer before being sacrificed in Denmark
2024-02-14
Vittrup Man was born along the Scandinavian coast before moving to Denmark, where he was later sacrificed, according to a study published February 14, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Anders Fischer of the University of Gothenburg, Sweden and colleagues.
Vittrup Man is the nickname of a Stone Age skeleton recovered from a peat bog in Northwest Denmark, dating to between 3300-3100 BC. The fragmented nature of the remains, including a smashed skull, indicate that he was killed in a ritualistic sacrifice, a common practice in this region at this time. After a DNA study found Vittrup Man’s genetic ...
Some Pre-Roman humans were buried with dogs, horses and other animals
2024-02-14
Some people from an ancient community in what is now northern Italy were interred with animals and animal parts from species such as dogs, horses and pigs. The reasons remain mysterious, but might indicate an enduring companion relationship between these humans and animals, or religious sacrificial practices, according to a study published February 14, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Zita Laffranchi from the University of Bern, Stefania Zingale from the Institute for Mummy Studies, Eurac Research Bozen, ...
Reported marital harmony—or conflict—accounts for nearly ten percent of the variation in mental health self-assessments in a broad study of Australian adults
2024-02-14
Australian adults who report a good relationship that meets their original expectations tend to score higher in mental health, while adults who report loving their spouse but wished they had never entered the relationship and note relationship problems tend to score significantly lower in mental health, according to a survey of almost 7000 Australian adults published February 14, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Bernard Kwadwo Yeboah Asiamah-Asare and colleagues.
Many recent studies have examined the possible social determinants of mental health. In this study, Yeboah Asiamah-Asare and colleagues looked specifically at how one’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
[Press-News.org] A lighthouse in the Gobi desertA new study quantifies the impact of the world’s great fossil sites on our understanding of evolutionary relationships between fossil groups and discovers the key to understanding lizard evolutionary history in the Gobi Desert.