Scientists try out stone age tools to understand how they were used
Used stone edges might help illuminate timber use by early humans
2024-02-17
(Press-News.org)
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University crafted replica stone age tools and used them for a range of tasks to see how different activities create traces on the edge. They found that a combination of macroscopic and microscopic traces can tell us how stone edges were used. Their criteria help separate tools used for wood-felling from other activities. Dated stone edges may be used to identify when timber use began for early humans.
For prehistoric humans, improvements in woodworking technology were revolutionary. While Paleolithic (early stone age) artifacts point to the use of wood for simple tools such as spears or throwing sticks, later Mesolithic and Neolithic artifacts reflect far more sophisticated uses, for building houses, canoes, bows, and wells. This is underscored by the availability of tools that let people craft more and more complex wooden instruments, particularly polished stone axes.
But while developed wood-processing technology is generally believed to be associated with a way of life seen in the Neolithic age of the Holocene, starting approximately 10,000 years ago, ground stone axes have been found from periods significantly before this. In sites around Australia and Japan, many ground edge artifacts from Marine Isotope Stage 3 (about 60,000 - 30,000 years ago) have been recovered. The important question becomes what they were used for at such an early stage.
To address this, a team led by Assistant Professor Akira Iwase from Tokyo Metropolitan University have tried to establish what kinds of traces might be left on ground stone edges when they are used for different activities. They took a hands-on approach, and crafted replicas of tools that might have been used in the Early Upper Paleolithic age (about 38,000 - 30,000 years ago). Edges were crafted and polished using knapping and grinding techniques which would have been available at the time. Though hafts have not been recovered from Japanese sites of the period, they adopted methods from Irian Jaya to attach a handle to the stone edges to create adzes, axes, and chisels.
The team then got to work using the tools for 15 different activities, including tree-felling, hide-processing, and butchering, as well as “non-use” events like carrying them around and trampling them. Edges were then examined in depth for both macroscopic and microscopic traces of their history. They found that impacts like those required for cutting down trees leave distinctive, macroscopic fractures on the stone; friction at the micron-scale between the stone edge and wood also form microscopic traces which may be used for diagnosis. While fractures alone cannot tell us what they were used for, they found that combining both macroscopic and microscopic evidence can help us make reliable conclusions about whether the edges were used to fell trees.
The team believe that if similar traces are found on the edges of real artifacts from Marine Isotope Stage 3 sites, this would mean that humans had honed woodworking technology from significantly earlier times than is currently believed. This would change our understanding of stone tool use by Ice Age humans, and how such technology was spread into different environments.
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers 15K16874, 18H03596, 20K13235, 23H04840, and 23H00009.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-17
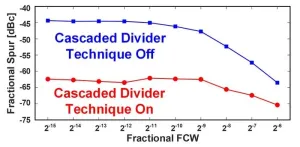
Two innovative design techniques lead to substantial improvements in performance in fractional-N phase locked loops (PLLs), report scientists from Tokyo Tech. The proposed methods are aimed to minimize unwanted signals known as fractional spurs, which typically plague PLLs used in many modern radar systems and wireless transceivers. These efforts could open doors to technological improvements in wireless communication, autonomous vehicles, surveillance, and tracking systems in beyond 5G era.
Many emerging and evolving technologies, such as self-driving vehicles, target tracking systems, and remote sensors, rely on the high-speed and error-free operation ...
2024-02-17
DENVER — Young physician investigators interested in research careers in pulmonology, allergy and immunology, pediatric and related programs, are encouraged to submit basic science or clinical research abstracts by June 3, 2024, to be considered for participation in the 20th Annual Respiratory Disease Young Investigators’ Forum. This year’s Forum will take place October 17-20, 2024, in Denver.
The annual event provides career development and research opportunities for fellows and early career faculty. The Forum is a celebration of talent and ingenuity in respiratory medicine. Physician-scientists in fellowship ...
2024-02-16
In an article published in the Journal of Pediatrics, researchers based in Brazil describe the case of a nine-year-old boy admitted to hospital with multiple symptoms and overlapping conditions that made diagnosis difficult, such as short stature, thin tooth enamel (dental enamel hypoplasia), moderate mental deficiency, speech delay, asthma, mildly altered blood sugar, and a history of recurring infections in infancy.
The team used exome sequencing, in which only the protein-coding portion of the genome is analyzed, to look for genetic mutations, and found them in GCK and BCL11B. ...
2024-02-16
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Feb. 15, 2024) – Prominent oncologist and researcher Damian Green, M.D., will join Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University Miami Miller School of Medicine this spring to lead its transplantation and cellular therapy services.
Green will serve as chief of Sylvester’s Division of Transplantation & Cellular Therapy, as well as assistant director of Translational Research, beginning March 1. He joins Sylvester from Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle, where he built a distinguished track record in research and ...
2024-02-16
By Wynne Parry
WOODS HOLE, Mass. – Like humans struggling to get through the COVID-19 pandemic, bacterial cells need social distancing to thwart viruses. But in some situations, such as inside elevators or within the candy-colored bacterial structures known as “pink berries,” staying apart just isn’t feasible.
Looking like spilled Nerds or Pop Rocks, the communal, multicellular pink berries litter the submerged surface of salt marshes in and around Woods Hole. New research conducted at the Marine Biological ...
2024-02-16
Hospital-acquired acute kidney injury (HA-AKI) is a common complication in hospitalized patients that can lead to chronic kidney disease and is associated with longer hospital stays, higher health care costs and increased mortality. Given these negative consequences, preventing HA-AKI can improve hospitalized patient outcomes. However, anticipating HA-AKI onset is difficult due to a large number of contributing factors involved.
Researchers from Mass General Brigham Digital tested a commercial machine learning tool, the Epic Risk of HA-AKI predictive model, and found it was moderately successful at predicting risk of HA-AKI in recorded patient data. ...
2024-02-16
(Toronto, February 16, 2024) JMIR Publications is pleased to announce that JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology has passed the Scientific Quality Review by the US National Library of Medicine (NLM) for PubMed Central (PMC). This decision reflects the scientific and editorial quality of the journal. All articles published from 2022 onward will be found on PMC and PubMed after their technical evaluation.
Launched in 2020, JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology is a sister journal of Journal of Medical Internet Research ...
2024-02-16
Standard chemotherapy regimens, which are mostly based on testing in relatively young and healthy patients, may do more harm to older adults with cancer who often struggle with other health issues. New research, published yesterday in JAMA Network Open, shows that lowering the dose and adjusting the schedule of how chemotherapy is given to older adults with advanced cancer can make life better for patients, without compromising their treatment goals.
The study, which was led by researchers from the University of Rochester Medical Center’s Wilmot Cancer Institute, focuses on how well older people tolerate chemotherapy. More than 30 percent of patients benefitted from treatment regimen ...
2024-02-16
HOUSTON – (Feb. 16, 2024) – Rice University computer science researchers have found bias in widely used machine learning tools used for immunotherapy research.
Ph.D. students Anja Conev, Romanos Fasoulis and Sarah Hall-Swan, working with computer science faculty members Rodrigo Ferreira and Lydia Kavraki, reviewed publicly available peptide-HLA (pHLA) binding prediction data and found it to be skewed toward higher-income communities. Their paper examines the way that biased data input affects the algorithmic recommendations being ...
2024-02-16
A study co-led by Professor Kelly Metcalfe of the Lawrence Bloomberg Faculty of Nursing, and researchers at the Familial Breast Cancer Research Unit at Women’s College Hospital, finds risk-reducing mastectomies (RRM) in women with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 genetic variant, significantly reduces the risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer and lowers the probability of death.
The study, published in the British Journal of Cancer, examined how RRM affects the rate of death of women with a pathogenic variant but no cancer diagnosis. To date, there has been only one other study published by researchers in the Netherlands that examines the impact ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists try out stone age tools to understand how they were used
Used stone edges might help illuminate timber use by early humans