(Press-News.org) People who eat a healthy, plant-based diet that is high in vegetables, fruit, whole grains and nuts are less likely to suffer with obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA), according to a study published today (Wednesday) in ERJ Open Research [1]. However, people eating an unhealthy plant-based diet, high in refined carbohydrates, sugary drinks, high-sugar and high-salt foods, are at a higher risk of OSA.
People with OSA often snore loudly, their breathing starts and stops during the night, and they may wake up several times. Not only does this cause tiredness, but it can also increase the risk of high blood pressure, stroke, heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
The new study is one of the first large-scale analyses to investigate the correlation between plant-based diets and OSA risk. Researchers say its findings suggest that eating a healthy, plant-based diet may help prevent or treat OSA.
The research was led by Dr Yohannes Melaku from Flinders University in Adelaide, Australia. He said: “Risk factors for obstructive sleep apnoea may stem from genetics or behaviour, including diet. Previous research has primarily focused on the impact of calorie restriction, specific dietary elements and weight loss. There's a gap in our knowledge of how overall dietary patterns affect OSA risk. With this study, we wanted to address that gap and explore the association between different types of plant-based diets and the risk of OSA.”
The research included data on 14,210 people who were taking part in the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Participants were asked to explain everything they had eaten over the last 24 hours. Researchers categorised this information according to whether people were eating a healthy plant-based diet (including whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes, tea and coffee) or a diet high in animal foods (including animal fat, dairy, eggs, fish or seafood and meat). They also looked at whether people were eating an unhealthy, plant-based diet (including refined grains, potatoes, sugar-sweetened drinks, sweets, desserts and salty foods).
Participants also answered a questionnaire designed to gauge whether they are likely to be suffering from OSA.
People with diets highest in plant-based food were 19% less likely to be suffering with OSA, compared with those eating diets lowest in plant-based food. Those eating a largely vegetarian diet were also at a lower risk. However, people eating a diet high in unhealthy plant-based foods were at a 22% higher risk, compared to those eating low amounts of these foods.
The researchers also found differences in the risks for women and men, with a plant-based diet having a stronger correlation with OSA risk for men and an unhealthy plan-based diet having a bigger increase on women’s risk.
Dr Melaku said: “These results highlight the importance of the quality of our diet in managing the risk of OSA. It's important to note these sex differences because they underscore the need for personalised dietary interventions for people with OSA.
“This research doesn’t tell us why diet is important, but it could be that a healthy plant-based diet reduces inflammation and obesity. These are key factors in OSA risk. Diets rich in anti-inflammatory components and antioxidants, and low in harmful dietary elements, can influence fat mass, inflammation, and even muscle tone, all of which are relevant to OSA risk.”
The researchers now plan to investigate the links between eating ultra-processed food and OSA risk in the same group of people. They also intend to study the interaction between diet and OSA risk over the longer term.
Professor Sophia Schiza is Head of the European Respiratory Society’s assembly on sleep disordered breathing, based at the University of Crete, Greece, and was not involved in the research. She said: “Obstructive sleep apnoea is a frequently occurring condition, and a significant number of individuals remain unaware of their own diagnosis despite the associated risks. There are treatments available for OSA, and patients can also take certain steps to improve their condition. This involves refraining from smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying physically active.
“The findings of this study propose that modifying our diet might be beneficial in managing or avoiding OSA. Being aware that incorporating a wide variety of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains into our diet while minimizing the consumption of unhealthy foods and sugary drinks can greatly improve our overall health. We need to make it as easy as possible for everyone to adopt a healthy diet.”
END
People who a eat healthy, plant-based diet are less likely to suffer with dangerous snoring
2024-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
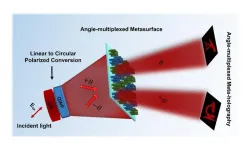
Angle-dependent holograms made possible by metasurfaces
2024-02-21
The expression "flawless from every angle" is commonly used to characterize a celebrity's appearance. This doesn't simply imply that they appear attractive from a specific viewpoint, but rather that their appeal remains consistent and appealing from various angles and perspectives. Recently, a research team from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has employed metasurface to fabricate angle-dependent holograms with multiple functions, capturing significant interest within ...
These tiny power converters run on vibrational energy
2024-02-21
University of California San Diego and CEA-Leti scientists have developed a ground-breaking piezoelectric-based DC-DC converter that unifies all power switches onto a single chip to increase power density. This new power topology, which extends beyond existing topologies, blends the advantages of piezoelectric converters with capacitive-based DC-DC converters.
The power converters the team developed are much smaller than the huge, bulky inductors currently used for this role. The devices could eventually be used for any type of DC-DC conversation, ...
Ochsner Health Hospitals accredited as Surgical Review Corporation Centers of Excellence
2024-02-21
NEW ORLEANS, La – Ochsner Medical Center – New Orleans achieved accreditation as a Center of Excellence in Robotic Surgery, and Ochsner Baptist – A Campus of Ochsner Medical Center, inclusive of Ochsner Medical Center and Ochsner Medical Complex- Clearview, received accreditation as a Center of Excellence in Continence Care for Women by SRC (Surgical Review Corporation). This accreditation recognizes Ochsner Health’s commitment to a high standard of quality patient care delivery and safety.
“Robotic ...
$2 million grant from The Roe Green Foundation catalyzes multidisciplinary research building in Uganda
2024-02-21
CLEVELAND--For the past 38 years, Case Western Reserve University (CWRU) and University Hospitals (UH) have worked closely with a variety of institutions in Uganda to advance medical research and education across a range of fields.
Their facilities have remained scattered across the campuses of local partners but now, the collaboration will have a permanent home.
A $2 million gift from The Roe Green Foundation, jointly awarded to CWRU and UH, will advance global health initiatives from each institution and establish a state-of-the-art research hub and gathering ...
SFU researchers develop AI that can understand light in photographs
2024-02-21
Despite significant progress in developing AI systems that can understand the physical world like humans do, researchers have struggled with modelling a certain aspect of our visual system: the perception of light.
“Determining the influence of light in a given photograph is a bit like trying to separate the ingredients out of an already baked cake.” explains Chris Careaga, a PhD student in the Computational Photography Lab at SFU. The task requires undoing the complicated interactions between light and surfaces in a scene. This problem is referred to as intrinsic decomposition, and has been ...
Minority ethnic NHS staff more likely to face workplace discrimination during pandemic than White colleagues
2024-02-21
Minority ethnic NHS staff were more likely to face workplace harassment, discrimination, and unavailability of personal protective equipment (PPE) than their White British colleagues during the pandemic, reveals research published online in the journal Occupational & Environmental Medicine.
Urgent action is needed to redress ongoing race inequalities in the health service, insist the researchers, who call for the inclusion of diversity and inclusion training in professional development, and the expansion of the NHS Workforce Race Equality Standard.
Staff from minority ethnic groups make up nearly ...
J-shaped curve apparent between dietary thiamine and worsening mental acuity
2024-02-21
There seems to be a J-shaped curve between dietary thiamine (vitamin B1) and worsening mental acuity among cognitively healthy older people, suggests research published in the open access journal General Psychiatry.
The sweet spot seems to be a daily intake of 0.68 mg, below which there is relatively little impact. But higher daily intake was strongly associated with cognitive decline, with the optimal maintenance dose 0.6 to less than 1 mg/day, the findings show.
Thiamine is an essential water-soluble B vitamin involved in energy metabolism and brain neurotransmitter activity. Good dietary sources include whole grains, fortified ...
Adopting healthy lifestyle strongly linked to lower irritable bowel syndrome risk
2024-02-21
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is strongly linked to a lower risk of irritable bowel syndrome or IBS for short, finds research published online in the journal Gut.
Of the big 5 healthy behaviours, not smoking, a high level of vigorous physical activity, and getting enough sleep were independently associated with keeping the condition at bay.
Characterised by abdominal pain, bloating, and abnormal bowel habit, IBS is thought to affect up to 1 in 10 people worldwide. Exactly what causes IBS isn’t fully understood, but disordered functioning of the gut–brain ...
Avid appetite in childhood linked to later eating disorder symptoms
2024-02-21
An enthusiastic response to food in early childhood may be linked to a higher likelihood of experiencing eating disorder symptoms in adolescence, according to a new study led by researchers at UCL and Erasmus University Rotterdam.
The study, published in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health, looked at survey data from 3,670 young people in the UK and the Netherlands to investigate how appetite traits in early childhood might relate to the likelihood of developing eating disorder symptoms up to 10 years later.
The researchers found that a particularly high food responsiveness, defined as the urge to eat when you see, smell ...
Red light can reduce blood glucose levels, says study
2024-02-21
The researchers found that 670 nanometres (nm) of red light stimulated energy production within mitochondria, the tiny powerhouses within cells, leading to increased consumption of glucose. In particular, it led to a 27.7% reduction in blood glucose levels following glucose intake, and it reduced maximum glucose spiking by 7.5%.
While the study was conducted in healthy individuals, the non-invasive, non-pharmacological technique has the potential to have an impact on diabetes control after meals, as it can reduce damaging fluctuations of blood glucose in the body that contribute to ageing.
The study also highlights the significant long-term consequences for human health, including ...