(Press-News.org) Today, a team of scientists from Trinity College Dublin and investigators from FutureNeuro announced a major discovery that has profound importance for our understanding of brain fog and cognitive decline seen in some patients with Long COVID.
In the months after the emergence of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV2 in late 2019 a patient-reported syndrome termed Long-COVID began to come to the fore as an enduring manifestation of acute infection.
Long COVID has up to 200 reported symptoms to date, but in general patients report lingering symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, problems with memory and thinking and joint/muscle pain. While the vast majority of people suffering from COVID-19 make a full recovery, any of these symptoms that linger for more than 12 weeks post infection can be considered Long COVID.
Long COVID has now become a major public health issue since the outbreak of the pandemic in 2020. While international incidence rates vary, it is estimated to affect up to 10% of patients infected with the SARS-CoV2 virus. Of these patients suffering from Long-COVID, just under 50% of them report some form of lingering neurological effect such as cognitive decline, fatigue and brain fog.
Now, the findings reported by the Trinity team in the top international journal Nature Neuroscience showed that there was disruption to the integrity of the blood vessels in the brains of patients suffering from Long COVID and brain fog. This blood vessel “leakiness” was able to objectively distinguish those patients with brain fog and cognitive decline compared to patients suffering from Long-COVID but not with brain fog.
The team led by scientists at the Smurfit Institute of Genetics in Trinity’s School of Genetics and Microbiology and neurologists in the School of Medicine have also uncovered a novel form of MRI scan that shows how Long-COVID can affect the human brain’s delicate network of blood vessels.
“For the first time, we have been able to show that leaky blood vessels in the human brain, in tandem with a hyperactive immune system may be the key drivers of brain fog associated with Long COVID. This is critically important, as understanding the underlying cause of these conditions will allow us to develop targeted therapies for patients in the future,” said Prof. Matthew Campbell, Professor in Genetics and Head of Genetics at Trinity, and Principal Investigator at FutureNeuro.
This project was initiated by a rapid response grant funded by Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) at the height of the pandemic in 2020 and involved recruiting patients suffering from the effects of Long-COVID as well as patients who were hospitalised in St James’ Hospital.
“Undertaking this complicated clinical research study at a time of national crisis and when our hospital system was under severe pressure is a testament to the skill and resource of our medical trainees and staff. The findings will now likely change the landscape of how we understand and treat post-viral neurological conditions. It also confirms that the neurological symptoms of Long Covid are measurable with real and demonstrable metabolic and vascular changes in the brain,” said Prof. Colin Doherty, Professor of Neurology and Head of the School of Medicine at Trinity, and Principal Investigator at FutureNeuro.
Moving beyond COVID-19
In recent years, it has become apparent that many neurological conditions such as Multiple sclerosis (MS) likely have a viral infection as the initiating event that triggers the pathology. However, proving that direct link has always been challenging.
Prof. Campbell added: “Here, the team at Trinity was able to prove that every patient that developed Long-COVID had been diagnosed with SARS-CoV2 infection, because Ireland required every documented case to be diagnosed using the more accurate PCR-based methods. The concept that many other viral infections that lead to post-viral syndromes might drive blood vessel leakage in the brain is potentially game changing and is under active investigation by the team.”
Dr Chris Greene, Postdoctoral research fellow and first author of the study, added: “Our findings have now set the stage for further studies examining the molecular events that lead to post-viral fatigue and brain fog. Without doubt, similar mechanisms are at play across many disparate types of viral infection and we are now tantalisingly close to understanding how and why they cause neurological dysfunction in patients.”
END
Researchers discover underlying cause of “brain fog” linked with Long COVID
2024-02-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Carbon emissions from the destruction of mangrove forests predicted to increase by 50,000% by the end of the century
2024-02-22
The annual rate of carbon emissions due to the degradation of carbon stocks in mangrove forests is predicted to rise by nearly 50,000% by the end of the century, according to a new study published in IOP Publishing’s journal Environmental Research Letters. Mangroves in regions such as southern India, southeastern China, Singapore and eastern Australia are particularly affected.
Mangrove forests store a large amount of carbon, particularly in their soils, however human development in these areas has led to the degradation of these carbon ...
Cracking the code of neurodegeneration: New model identifies potential therapeutic target
2024-02-22
Scientists at the University of Zurich have developed an innovative neural cell culture model, shedding light on the intricate mechanisms underlying neurodegeneration. Their research pinpointed a misbehaving protein as a promising therapeutic target in the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD).
Neurodegenerative diseases cause some of the neurons in our brains to die, resulting in different symptoms depending on the brain region affected. In amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), neurons in the motor cortex and spinal ...
Former Dutch minister and renowned gastroenterologist joins NTU Singapore as Vice President of Research
2024-02-22
Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has appointed Professor Ernst Kuipers, a renowned gastroenterologist, healthcare executive, and former Minister of Health, Welfare and Sport for The Netherlands, as NTU Singapore’s new Vice President (Research).
Prof Kuipers will also be appointed to the tenured faculty rank of Distinguished University Professor, the highest faculty rank at NTU bestowed upon faculty members with extraordinary scholarly achievements that typically span multiple disciplinary boundaries.
Announcing this new appointment, NTU President Prof Ho Teck Hua said: “We warmly welcome ...
Biggest Holocene volcano eruption found by seabed survey
2024-02-22
A detailed survey of the volcanic underwater deposits around the Kikai caldera in Japan clarified the deposition mechanisms as well as the event’s magnitude. As a result, the Kobe University research team found that the event 7,300 years ago was the largest volcanic eruption in the Holocene by far.
In addition to lava, volcanos eject large amounts of pumice, ashes and gases as a fast-moving flow, known as “pyroclastic flow,” and its sediments are a valuable data source on past eruptions. For volcanoes on land, geologists understand the sedimentation mechanism of pyroclastic flows well, but the sediments themselves get lost easily ...
Generative AI used to create translatable pediatric care educational videos for hospitals in resource-poor countries
2024-02-22
Mass General Brigham pediatric clinicians created 45 videos on pediatric care topics including how-to for surgical procedures, best practices for intubation and intensive care, and translated them to Spanish through GPT-4 large language model.
Videos distributed to clinicians in Guatemala and Colombia
AI can offer health care professionals worldwide an inclusive resource for elevating pediatric standards of care, according to authors
A team of pediatric clinicians at Mass General Brigham have turned to generative artificial intelligence (AI) to tackle problems plaguing child medical care delivery in resource-poor countries that increase risk for poor outcomes and mortality.
The ...
New realistic computer model will help robots collect Moon dust
2024-02-22
A new computer model mimics Moon dust so well that it could lead to smoother and safer Lunar robot teleoperations.
The tool, developed by researchers at the University of Bristol and based at the Bristol Robotics Laboratory, could be used to train astronauts ahead of Lunar missions.
Working with their industry partner, Thales Alenia Space in the UK, who has specific interest in creating working robotic systems for space applications, the team investigated a virtual version of regolith, another name for Moon dust.
Lunar regolith is ...
Women in healthcare face significantly higher burnout rates compared to their male colleagues
2024-02-22
WASHINGTON (Feb. 22, 2024)--A new study finds women in healthcare occupations endure significantly more stress and burnout compared to their male counterparts. The analysis by researchers at the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences also found that job satisfaction and better work-life balance can protect women healthcare professionals from harmful stress.
“Human beings are not equipped to handle the combined, intense pressures in healthcare in part due to the pressure to not take time to care for yourself,” Leigh A. Frame, associate director of the GW Resiliency & Well-being Center, ...
New technique can quickly detect fentanyl and other opioids
2024-02-22
University of Waterloo researchers have developed a new blood testing method that can detect potent opioids much faster than traditional approaches and potentially save lives.
The method, the latest effort by Waterloo researchers and entrepreneurs to lead health innovation in Canada, can simultaneously analyze 96 blood samples that could contain opioids such as fentanyl in under three minutes – twice as quickly as other techniques.
"The difference between our blood testing method and traditional methods used in laboratories and hospitals is that we can do it faster ...
LHAASO discovers giant ultra-high-energy gamma-ray bubble, identifying the first super PeVatron
2024-02-22
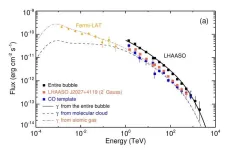
The Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory (LHAASO) has discovered a giant ultra-high-energy gamma-ray bubble structure in the Cygnus star-forming region, which is the first time that the origin of cosmic rays with energy higher than 10 Peta-Electronvolt (PeV, 1PeV=1015eV) has been discovered. This achievement was published in the form of a cover article in Science Bulletin on Feb. 26. The research was completed by the LHAASO Collaboration led by Prof. CAO Zhen as the spokesperson from the Institute of High Energy Physics of the ...
Method identified to double computer processing speeds
2024-02-22
Imagine doubling the processing power of your smartphone, tablet, personal computer, or server using the existing hardware already in these devices.
Hung-Wei Tseng, a UC Riverside associate professor of electrical and computer engineering, has laid out a paradigm shift in computer architecture to do just that in a recent paper titled, “Simultaneous and Heterogeneous Multithreading.”
Tseng explained that today’s computer devices increasingly have graphics processing units (GPUs), hardware accelerators for artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), or digital signal processing units as essential components. These components ...