(Press-News.org)
When a recession takes a bite out of an entrepreneur’s personal stock portfolio, does that person’s business suffer more than those of older and larger competitors?
New research by Marius Ring, assistant professor of finance at Texas McCombs, finds a link between the wealth of small-business owners and the health of their companies during economic downturns. When their stock portfolios lose value, their businesses suffer ripple effects: less financing and curtailed hiring.
“Entrepreneurial wealth follows the ups and downs of economic cycles,” Ring says. “I show that for entrepreneurs whose stock portfolios take a hit, their businesses are adversely affected to a greater extent than established businesses.”
Such business constrictions are concentrated among younger companies, he noted, because older companies have more financial options.
Ring studied stock portfolios of entrepreneurs during the 2008-2009 financial crisis in Norway, where detailed income and investing data are available. He merged the data with information from education and employment registers to trace the crash’s impacts on investors, the businesses they own, and their employees.
He found that owners’ stock shortfalls hurt businesses in multiple ways, with fledgling companies faring worse.
Hiring Hiatuses. A stock loss of 10% reduced employment growth by an average 5 percentage points from 2007 to 2010. In younger companies, job levels still had not recovered five years after the crisis began.
Shrinking employment resulted not from firings, but from less hiring. Says Ring, “Investing in new employees is likely not a top priority in a recession.”
Investment Lessened. A 10% drop in the owner’s wealth led to cutbacks in capital available for business growth.
It reduced injections of outside equity 22%.
For younger companies, it meant an 84% decline in the two-year rate of investment in plants and property.
Why are younger businesses more sensitive to their owners’ investment setbacks? The answer, says Ring, is that “more mature firms seem to be able to substitute other sources of financing, such as banks.”
Mature companies, he found, took on more bank debt after an owner’s wealth shock. Younger ones, on the other hand, saw a decrease in bank debt.
An important policy question, says Ring, is whether reduced business activity is driven more by financial forces or by psychological ones, such as a decrease in entrepreneurs’ willingness to take risks.
His results suggest that financial constraints are more likely at play. That means government interventions, such as small-business lending subsidies, might help counter those constraints and help small businesses weather recessions.
“Small businesses are important in most economies, and most of these firms rely heavily on their owners for financing,” Ring says. “Owners can be a viable source of financing, but unfortunately, the owner’s personal wealth is likely to be hit at the same time as the firm is experiencing a downturn.”
“Entrepreneurial Wealth and Employment: Tracing Out the Effects of a Stock Market Crash” is published inThe Journal of Finance.
END
DURHAM, N.C. – Biomedical engineers at Duke University have uncovered a key link between the spread of antibiotic resistance genes and the evolution of resistance to new drugs in certain pathogens.
The research shows bacteria exposed to higher levels of antibiotics often harbor multiple identical copies of protective antibiotic resistance genes. These duplicated resistance genes are often linked to “jumping genes” called transposons that can move from strain to strain. Not only does this provide a mechanism for resistance to spread, having multiple copies of a resistance ...
BEAUFORT, N.C. – When it comes to protecting a crucial resource in the face of changing conditions, it’s important to know how the humans reliant on that resource have organized themselves. Especially if there isn’t a lot of government supervision.
A new study of small-scale fisheries in Mexico’s Gulf of California has found that the fishers’ response to a changing climate can be strongly influenced by what they fish for and how they’re organized. The work appears in the January 2024 issue of Global Environmental Change.
“When we ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Forests in the coolest, wettest parts of the western Pacific Northwest are likely to see the biggest increases in burn probability, fire size and number of blazes as the climate continues to get warmer and drier, according to new modeling led by an Oregon State University scientist.
Understanding how fire regimes may change under future climate scenarios is critical for developing adaptation strategies, said the study’s lead author, Alex Dye.
Findings were published today in JGR Biogeosciences.
Dye, ...
While the microchips inside electronic devices like cell phones and computers are incredibly small, transistors — the tiny electrical switches inside of microchips — are approaching the atomic level. Today’s microchips pack over 100 million transistors in an area the size of a pin head.
Despite their almost unimaginable size, the total number of such microelectronic devices consume an enormous amount of energy, which is growing exponentially. Predictions indicate that 20% of the world’s energy could be consumed ...
A Weill Cornell Medicine-led research team has been awarded a 2024 Top 10 Clinical Research Achievement Award from the Clinical Research Forum in recognition of an influential 2023 New England Journal of Medicine study on early-stage lung cancer resection.
The award is one of 10 given annually by the Clinical Research Forum for highly innovative and clinically translatable research with the potential to provide major benefits to patients. The Washington, D.C.-based organization is an influential advocate for government funding of clinical research and the interests of American clinical research institutions generally. The winners will present their award-winning ...
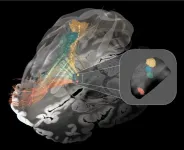
When certain connections in the brain do not function correctly, disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, dystonia, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and Tourette’s syndrome may result. Targeted stimulation of specific areas in the brain can help alleviate symptoms. To pinpoint the exact therapeutic target areas of the brain, a team led by researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin and Brigham and Women’s Hospital analyzed data from patients across the globe who had undergone implantation of tiny electrodes to stimulate ...
Join Gunther Eysenbach, the founder, CEO, and executive editor of JMIR Publications, in this new video as he reflects on the company's 25th anniversary and its remarkable journey in the scholarly publishing industry. Eysenbach discusses the inception of the Journal of Medical Internet Research and the driving forces behind creating an open access eHealth journal. He emphasizes the significance of innovation both in content and form, highlighting the company's early adoption of internet-based technologies ...
URBANA, Ill. – Black Americans experience racial discrimination as a chronic stressor that influences their quality of life. But it exists in conjunction with other social factors that may modify the impact in various ways. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign explores how discrimination, gender, and social class affect individual well-being and relationship quality for Black Americans.
“It’s well documented that discrimination negatively impacts individual quality of life, but research on how it affects relationships is mixed. Some studies find it has a negative effect, others that it has no effect, and some even find a positive effect, ...
Compound vital for all life likely played a role in life’s origin
A chemical compound essential to all living things has been synthesised in a lab in conditions that could have occurred on early Earth, suggesting it played a role at the outset of life, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The compound, pantetheine, is the active fragment of Coenzyme A. It is important for metabolism - the chemical processes that maintain life. Earlier studies failed to synthesise pantetheine effectively, leading to suggestions that it was absent at life’s origin.
In the new ...
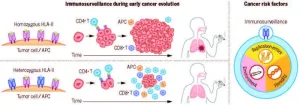
New York, NY (February 22, 2024)—Recent developments in cancer research have highlighted the vital role of the immune system, particularly in the notable successes of cancer immunotherapy.
Now, a paradigm-shifting study led by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York in collaboration with the University of Helsinki and Massachusetts General Hospital sheds light on how variations in immune genetics influence lung cancer risk, potentially paving the way for enhanced prevention strategies and screening.
The findings were described in the February 22 online issue of Science [DOI number: 10.1126/science.adi3808].
The investigators ...