(Press-News.org) Image-sentence retrieval task aims to search images for given sentences and retrieve sentences from image queries. The current retrieval methods are all supervised methods that require a large number of annotations for training. However, considering the labor cost, it is difficult to re-align large amounts of multimodal data in many applications (e.g., medical retrieval), which results in unsupervised multimodal data.
To solve the problem, a research team led by Yang YANG published their new research on 15 Feb 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
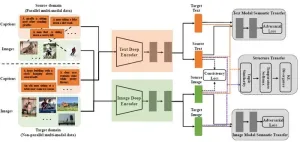
The team, strive to take a step towards non-parallel image-sentence retrieval by designing the alignment transfer, and propose a novel Alignment Efficient Image-Sentence Retrieval method (AEIR).
In the research, AEIR use other auxiliary parallel data with multimodal consistency as the source domain and non-parallel data with missing consistency as the target domain. Unlike unimodal transfer learning, AEIR transfers semantic representations and modal consistency relations together from the source domain to the target domain.
Firstly, AEIR learns cross-modal consistency representations using cross-modal parallel data in the source domain. Then AEIR jointly optimizes adversarial learning-based semantic transfer constraints and metric learning-based structural transfer constraints to learn cross-domain cross-modal consistency representations to achieve transfer of consistency knowledge from the source domain to the target domain. A large number of experimental experiments conducted in different transfer scenarios show that semantic transfer and structural transfer can effectively learn invariant features across modalities across domains. The proposed efficient alignment-based image-sentence retrieval network verifies that AEIR is more advantageous than current cross-modal retrieval methods, semi-supervised cross-modal retrieval methods and cross-modal transfer methods.
Future work can focus on the conduction of positive cross-modal transfer considering the domain discrepancy.
DOI: 10.1007/s11704-023-3186-6
END
Alignment efficient image-sentence retrieval considering transferable cross-modal representation learning
2024-02-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A novel deep learning modeling approach guided by mesoscience—MGDL
2024-02-23
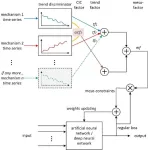
Deep learning modeling that incorporates physical knowledge is currently a hot topic, and a number of excellent techniques have emerged. The most well-known one is the physics-informed neural networks (PINNs). PINN integrates the residuals of the system’s governing partial differential equations (PDEs) and the initial value/boundary conditions into the loss function, thus the resulting model satisfies the constraints of the physical laws represented by the PDEs. However, PINN cannot work if equations among the key physical quantities of the system have not been established. To ...
Improving social symptoms of depression with a common anesthetic
2024-02-23
Osaka, Japan – Well-being is important for everyone, especially when we feel lonely or isolated. Depression is a serious challenge for many people and finding an effective solution is key.
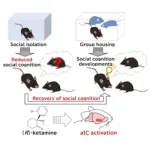
In a recent study published in Molecular Psychiatry, researchers from Osaka University used a mouse model of depression to reveal that one form of ketamine (a common anesthetic) in low doses can improve social impairments by restoring functioning in a specific brain region called the anterior insular cortex.
Ketamine is often used at low doses to treat depression, but its actions in the brain remain relatively unclear. Generally, ketamine refers to a mix of two different forms of ketamine: ...
Killer instinct drove evolution of mammals’ predatory ancestors
2024-02-23
The evolutionary success of the first large predators on land was driven by their need to improve as killers, researchers at the University of Bristol and the Open University suggest.
The forerunners of mammals ruled the Earth for about 60 million years, long before the origin of the first dinosaurs. They diversified as the top predators on land between 315–251 million years ago.
Researchers studied the jaw anatomy and body size of carnivorous synapsids, using these traits to reconstruct the likely feeding habits of these ancient predators and chart their ecological ...
Diversifying data to beat bias
2024-02-23
AI holds the potential to revolutionize healthcare, but it also brings with it a significant challenge: bias. For instance, a dermatologist might use an AI-driven system to help identify suspicious moles. But what if the machine learning model was trained primarily on image data from lighter skin tones, and misses a common form of skin cancer on a darker-skinned patient?
This is a real-world problem. In 2021, researchers found that free image databases that could be used to train AI systems to diagnose skin cancer contain very few images ...
Increased use of Paxlovid could cut hospitalizations, deaths and costs
2024-02-23
Increased use of Paxlovid, the antiviral drug used to treat COVID-19, could prevent hundreds of thousands of hospitalizations and save tens of billions of dollars a year, according to a new epidemiological model published by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin. In fact, epidemiologists found that treating even 20% of symptomatic cases would save lives and improve public health.
A 2023 National Institutes of Health study found that only about 15% of high-risk patients take Paxlovid when infected with COVID-19. Using a multiscale mathematical model based on ...
How to build your own robot friend: Making AI education more accessible
2024-02-23
From smart virtual assistants and self-driving cars to digital health and fraud prevention systems, AI technology is transforming almost every aspect of our daily lives—and education is no different. For all its promise, the rise of AI, like any new technology, raises some pressing ethical and equity questions.
How can we ensure that such a powerful tool can be accessed by all students regardless of background?
Inspired by this call to action, USC researchers have created a low-cost, accessible learning kit to help college and high school students build their own “robot friend.” Students can personalize the robot’s ...
Advances and future development of automated insulin delivery systems
2024-02-23
A special 13-article supplement to the peer-reviewed journal Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics (DTT) examines the “Development and Future of Automated Insulin Delivery (AID) Systems. Click here to read the supplement now.
Included in the supplement is the article titled “A Peek Under the Hood: Explaining the MiniMed™ 780G Algorithm with Meal Detection™ Technology", by Benyamin Grosman, PhD and his Medtronic algorithm team with co-authors Ohad Cohen, MD, and Robert Vigersky, MD, Chief Medical Officer at Medtronic. James Thrasher, MD “Early ...
Strategic grazing could boost conservation of ‘near-threatened’ sage-grouse
2024-02-23
RENO, Nev. – A multi-agency study, spearheaded by researchers from the University of Nevada, Reno’s College of Agriculture, Biotechnology & Natural Resources and the U.S. Department of Agriculture, underscores the impacts of strategic cattle grazing, particularly on restoring the declining population of the greater sage-grouse bird, a keystone species in the Great Basin region.
Amidst ongoing decline, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service acted by listing the sage-grouse for protection under the Endangered Species Act in 2011. This move prompted the Bureau of Land Management to develop a federal conservation plan for the species ...
Complement system response to AAV vector gene therapy
2024-02-23
Recent clinical trials utilizing high doses of adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors have highlighted a new challenge to AAV gene transfer – activation of the complement system. A new article in the peer-reviewed journal Human Gene Therapy describes how a convergence of AAV-specific, environmental, and patient-specific factors shaping complement responses likely contribute to differential outcomes seen in clinical trials. Click here to read the article now.
Complement responses may contribute to priming of the adaptive immune system or serious adverse events ...
Study suggests people in urban areas with more green space have better mental health
2024-02-23
By Ann Kellett, Texas A&M University School of Public Health
A new study from the Texas A&M University School of Public Health suggests that city dwellers who have more exposure to urban green spaces require fewer mental health services.
The study, published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, was conducted by Jay Maddock, Ph.D., Regents Professor of environmental and occupational health at Texas A&M, and colleagues from the Center ...