Watch these predatory fish use rapid color changes to coordinate attacks
2024-02-26
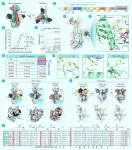
(Press-News.org) Striped marlin are some of the fastest animals on the planet and one of the ocean’s top predators. When hunting in groups, individual marlin will take turns attacking schools of prey fish one at a time. Now a new study reported in the journal Current Biology on February 5 helps to explain how they might coordinate this turn-taking style of attack on their prey to avoid injuring each other. The key, according to the new work, is rapid color changes.
“We documented for the first time rapid color change in a group-hunting predator, the striped marlin, as groups of marlin hunted schools of sardines,” says Alicia Burns of Humboldt University in Berlin, Germany. “We found that the attacking marlin 'lit up' and became much brighter than its groupmates as it made its attack before rapidly returning to its 'non-bright' coloration after its attack ended.”
Burns and her colleagues, including Jens Krause, explained that the use of drones in their research has given them a new perspective of how marlins move and hunt. As they examined the video footage they’d captured via drone, they noticed something unexpected: the stripes on individual marlins got obviously brighter as a fish moved in for an attack. As they swam away, those stripes dimmed again. Were the fish changing colors to communicate with one another?
To explore this question in the new study, the researchers analyzed 12 high-resolution video clips, each containing two separate attacks on a school of sardines by two different marlin. They also quantified the contrast of the stripes on the two attacking marlins compared to a randomly chosen marlin that wasn’t attacking. Their analysis confirms that the predatory fish rapidly change color, suggesting that the color change might serve as a reliable signal of an individual’s motivation to go in for an attack.
“Color change in predators is rare, but especially so in group-hunting predators,” Burns said. “Although it is known that marlin can change color, this is the first time it's been linked to hunting or any social behavior.”
The discovery suggests that marlins have more complicated communication channels than had been suspected. The researchers propose that the color changes might even serve a dual purpose of confusing their prey.
They now hope to explore this idea, alongside other questions. For example, they want to find out whether marlins use their color-changing abilities in other contexts. They’re curious to know whether they still change color when hunting solo and how the changes affect their prey. They are also looking into similar color changes in other predatory species of fish.
“We already have footage of hunting behavior of sailfish and mahi mahi where we have seen even more pronounced and more variable color change than in the marlin,” Burns says.
####
Current Biology, Burns et al. “Rapid colour change in a group-hunting pelagic predator when attacking schooling prey” https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(23)01740-2
Current Biology (@CurrentBiology), published by Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that features papers across all areas of biology. Current Biology strives to foster communication across fields of biology, both by publishing important findings of general interest and through highly accessible front matter for non-specialists. Visit http://www.cell.com/current-biology. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-26
When a star like our Sun reaches the end of its life, it can ingest the surrounding planets and asteroids that were born with it. Now, using the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT) in Chile, researchers have found a unique signature of this process for the first time — a scar imprinted on the surface of a white dwarf star. The results are published today in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
“It is well known that some white dwarfs — slowly cooling embers of stars like our Sun — are ...
2024-02-26
About The Study: This survey study found that primary care pediatricians felt less prepared to manage adolescents’ opioid use disorder (OUD) than alcohol, cannabis, or e-cigarette use and were more likely to refer them to offsite care. These results reveal an opportunity for greater workforce training in line with a 2019 survey showing fewer than 1 in 3 pediatric residency programs included education on prescribing OUD medications.
Authors: Scott E. Hadland, M.D., M.P.H., M.S., of Mass General for Children in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The ...
2024-02-26
About The Study: The findings of this study of 8,988 preadolescent children suggest that the increased risk of suicide attempts, consistently reported for adolescents and adults who smoke cigarettes, extends to a range of emerging tobacco products and manifests among elementary school–aged children. Further investigations are imperative to clarify the underlying mechanisms and to implement effective preventive policies for children.
Authors: Phil H. Lee, Ph.D., of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To ...
2024-02-26
In the face of increasing temperatures globally, a new Monash-led study of 1.2 million births in Sydney over two decades has shown a strong association between the risk of pre-term birth and exposure to extreme hot temperatures in the third trimester of pregnancy. The data suggested that this association with extreme temperature might be reduced by the level of greenery in a pregnant person’s residential surrounds.
The findings suggest health services should consider preparing for an increase in preterm births as our climate warms.
The study, published in JAMA Pediatrics, looked at the relationship ...
2024-02-26
Sight loss in certain inherited eye diseases may be caused by gut bacteria, and is potentially treatable by antimicrobials, finds a new study in mice co-led by a UCL and Moorfields researcher.
The international study observed that in eyes with sight loss caused by a particular genetic mutation, known to cause eye diseases that lead to blindness, gut bacteria were found within the damaged areas of the eye.
The authors of the new paper, published in Cell and jointly led by researchers in China, say their findings suggest that the genetic mutation may relax the body’s defences, thus allowing harmful bacteria to reach the eye and cause blindness.
The gut contains trillions ...
2024-02-26
DCM is the leading cause of heart failure in patients with chronic diabetes. However, the underlying mechanisms of DCM are poorly understood, and treatment options are limited. Another mystery is the regulation of cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs) in the central nervous system. Moreover, the link between the gut microbiome, microbiota-derived metabolites, and the progression of AD remains unknown. In the December issue of JPA, three articles provide insights into the pathologies of DCM, hippocampal neurotoxicity, and AD, providing a comprehensive ...
2024-02-26
Electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) cells, characterized by their self-emissive nature, have gathered significant interest for prospective display applications due to their uncomplicated structure and straightforward fabrication process. These cells are created by sandwiching a solution-based emitting layer between two transparent electrodes. Nevertheless, when compared to other self-emissive devices like light-emitting diodes (LED) and organic LEDs, the luminescent performance of ECL cells ...
2024-02-26
Human herpesviruses comprise the alpha, beta, and gamma subfamilies and are a widely prevalent group of DNA-enveloped viruses, capable of establishing lifelong latent infections in humans and causing various diseases. Among them, herpes simplex virus (HSV) belongs to the alpha herpesvirus group and infects a wide population, causing symptoms like oral or genital herpes. As an enveloped virus, HSV possesses a series of glycoproteins involved in virus recognition, adhesion, and infection processes. Among these, gB serves as the viral fusion protein, mediating the fusion between the virus and host cell membranes, and ...
2024-02-26
As Canada’s flu season collides with record strep A cases and ongoing COVID-19 concerns, a new study is shedding light on our understanding of respiratory immune responses. Scholars from the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC) have discovered a surprising facet about a century-old vaccine for tuberculosis, Bacillus Calmette Guérin (BCG). The study, published in the journal Nature Immunology, uncovered a previously unknown mechanism that extends the vaccine’s shield to combat influenza A virus—the most prevalent flu strain.
“The immune interactions ...
2024-02-26
Fungi are frequently found both around and within plant tissues (especially in roots) and are involved in both plant nutrient acquisition and resistance to pathogens. Thus, characterizing the diversity and composition of plant-associated fungal communities has been a growing interest in recent years.
High-throughput sequencing (HTS), also called metabarcoding, has become a prominent tool to assess complex microbial communities from environmental samples. However, HTS applied to plant-associated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Watch these predatory fish use rapid color changes to coordinate attacks