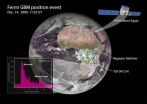
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON -- Scientists using NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope have detected beams of antimatter produced above thunderstorms on Earth, a phenomenon never seen before.
Scientists think the antimatter particles were formed in a terrestrial gamma-ray flash (TGF), a brief burst produced inside thunderstorms and shown to be associated with lightning. It is estimated that about 500 TGFs occur daily worldwide, but most go undetected.
"These signals are the first direct evidence that thunderstorms make antimatter particle beams," said Michael Briggs, a member of Fermi's Gamma-ray Burst Monitor (GBM) team at the University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH). He presented the findings Monday, during a news briefing at the American Astronomical Society meeting in Seattle.
Fermi is designed to monitor gamma rays, the highest energy form of light. When antimatter striking Fermi collides with a particle of normal matter, both particles immediately are annihilated and transformed into gamma rays. The GBM has detected gamma rays with energies of 511,000 electron volts, a signal indicating an electron has met its antimatter counterpart, a positron.
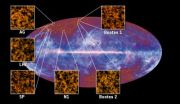
Although Fermi's GBM is designed to observe high-energy events in the universe, it's also providing valuable insights into this strange phenomenon. The GBM constantly monitors the entire celestial sky above and the Earth below. The GBM team has identified 130 TGFs since Fermi's launch in 2008.
"In orbit for less than three years, the Fermi mission has proven to be an amazing tool to probe the universe. Now we learn that it can discover mysteries much, much closer to home," said Ilana Harrus, Fermi program scientist at NASA Headquarters in Washington.
The spacecraft was located immediately above a thunderstorm for most of the observed TGFs, but in four cases, storms were far from Fermi. In addition, lightning-generated radio signals detected by a global monitoring network indicated the only lightning at the time was hundreds or more miles away. During one TGF, which occurred on Dec. 14, 2009, Fermi was located over Egypt. But the active storm was in Zambia, some 2,800 miles to the south. The distant storm was below Fermi's horizon, so any gamma rays it produced could not have been detected.
"Even though Fermi couldn't see the storm, the spacecraft nevertheless was magnetically connected to it," said Joseph Dwyer at the Florida Institute of Technology in Melbourne, Fla. "The TGF produced high-speed electrons and positrons, which then rode up Earth's magnetic field to strike the spacecraft."
The beam continued past Fermi, reached a location, known as a mirror point, where its motion was reversed, and then hit the spacecraft a second time just 23 milliseconds later. Each time, positrons in the beam collided with electrons in the spacecraft. The particles annihilated each other, emitting gamma rays detected by Fermi's GBM.
Scientists long have suspected TGFs arise from the strong electric fields near the tops of thunderstorms. Under the right conditions, they say, the field becomes strong enough that it drives an upward avalanche of electrons. Reaching speeds nearly as fast as light, the high-energy electrons give off gamma rays when they're deflected by air molecules. Normally, these gamma rays are detected as a TGF.
But the cascading electrons produce so many gamma rays that they blast electrons and positrons clear out of the atmosphere. This happens when the gamma-ray energy transforms into a pair of particles: an electron and a positron. It's these particles that reach Fermi's orbit.
The detection of positrons shows many high-energy particles are being ejected from the atmosphere. In fact, scientists now think that all TGFs emit electron/positron beams. A paper on the findings has been accepted for publication in Geophysical Research Letters.
"The Fermi results put us a step closer to understanding how TGFs work," said Steven Cummer at Duke University. "We still have to figure out what is special about these storms and the precise role lightning plays in the process."
INFORMATION:
NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope is an astrophysics and particle physics partnership. It is managed by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. It was developed in collaboration with the U.S. Department of Energy, with important contributions from academic institutions and partners in France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Sweden and the United States.
The GBM Instrument Operations Center is located at the National Space Science Technology Center in Huntsville, Ala. The team includes a collaboration of scientists from UAH, NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in Germany and other institutions.
For more Fermi information, images and animations, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/fermi
NASA's Fermi catches thunderstorms hurling antimatter into space
2011-01-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Benefit of brachytherapy in patients with early-stage prostate cancer is still unclear
2011-01-12
It remains an unresolved issue as to whether interstitial brachytherapy has advantages compared to other therapy options in men with localized prostate cancer, nor do newer studies provide proof in this respect. This is the result of a report published by the Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) on 11 January 2011. In this report IQWiG examined whether newer studies challenged the findings of research already completed in 2007. However, it was shown that no relevant new evidence could be obtained from the recent studies. The conclusions of the final ...
Targeting nicotine receptors to treat cognitive impairments in schizophrenia
2011-01-12
Smoking is a common problem for patients with schizophrenia. The increased tendency of patients diagnosed with this disorder is to not only smoke, but to do so more heavily than the general public. This raises the possibility that nicotine may be acting as a treatment for some symptoms of schizophrenia.
Nicotine acts through two general classes of brain receptors, those with high and low affinity for nicotine. The low affinity class of nicotinic receptors contains the alpha-7 subunit, which is present in reduced numbers in people with schizophrenia.
Two papers published ...
Planck unveils wonders of the Universe
2011-01-12
The first scientific results from Europe's Planck spacecraft featuring the coldest objects in the Universe have today been released.
Astronomers at The University of Manchester's Jodrell Bank Observatory played a key role in the worldwide teams searching for an exciting variety of astronomical finds, from massive galaxy clusters to new, unidentified objects.
Ranging from within our Galaxy to the most distant reaches of space, Planck is a flagship mission of the UK Space Agency, which funds the UK's involvement in both of Planck's scientific instruments.
Astronomers ...
The Starbucks effect: Committed customers don't like logo redesigns, research finds
2011-01-12
The negative reaction to Starbucks' redesigned logo by the company's self-described most loyal customers may be attributable to the strong connection Starbucks' consumers feel toward the brand, according to research co-authored by a professor at Penn State's Smeal College of Business.
Karen Winterich, assistant professor of marketing at Smeal, and researchers Michael Walsh of West Virginia University and Vikas Mittal of Rice University recently examined how consumers react to logo redesigns. They found that consumers who are strongly committed to a brand tend to react ...
UT researcher discovers water on moon originated from comets
2011-01-12
Researchers at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, continue to chip away at the mysterious existence of water on the moon -- this time by discovering the origin of lunar water.
Larry Taylor, a distinguished professor in the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, was the one last year to discover trace amounts of water on the moon. This discovery debunked beliefs held since the return of the first Apollo rocks that the moon was bone-dry.
Then, he discovered water was actually pretty abundant and ubiquitous -- enough so a human settlement on the moon is not ...
Study details how protein made by HPV teams up on and thwarts protective human protein
2011-01-12
BETHESDA, Md., Jan. 11, 2011 – An international team of researchers is reporting that it has uncovered new information about human papillomavirus that one day may aid in the development of drugs to eliminate the cervical-cancer-causing infection.
Led by researcher Per Jemth of Uppsala University in Sweden, the collaborators from four institutions detail in the Journal of Biological Chemistry how an offensive protein generated by the sexually transmitted virus handicaps a defensive protein made by the human body.
Co-author Neil Ferguson, a biophysicist at University ...
Planck's new view of the cosmic theater
2011-01-12
VIDEO:
This animation illustrates the position on the sky of all compact sources detected by Planck during its first all-sky survey and listed in the Early Release Compact Source Catalogue (ERCSC)....
Click here for more information.
The first scientific results from ESA's Planck mission were released at a press briefing today in Paris. The findings focus on the coldest objects in the Universe, from within our Galaxy to the distant reaches of space.
If William Shakespeare ...
Planck space observatory releases first data
2011-01-12
The first scientific results from Europe's Planck spacecraft were released at a press briefing today in Paris. The findings, focusing on the coldest objects in the Universe - both within our galaxy and also out to the most distant reaches of space - include an exciting variety of astronomical finds, from massive galaxy clusters to new, unidentified objects. Planck is a flagship mission of the UK Space Agency, which funds the UK's involvement in both of Planck's scientific instruments. Astronomers from around the UK are now heavily involved in the operation of Planck's ...
Family, friends, social ties influence weight status in young adults
2011-01-12
PROVIDENCE, RI – Does obesity tend to "cluster" among young adults? And if so, what impact does it have on both their weight and weight-related behaviors? That's what researchers from The Miriam Hospital's Weight Control and Diabetes Research Center set out to answer to better understand how social influences affect both weight status and weight loss intentions in this difficult-to-reach age group.
According to the study, published online by the journal Obesity, overweight and obese young adults between the ages of 18 and 25 were more likely to have overweight romantic ...
Revealed: Secret businesses which aimed to exploit vaccine fears
2011-01-12
Andrew Wakefield, the disgraced doctor who claimed a link between MMR and autism, planned secret businesses intended to make huge sums of money, in Britain and America, from his now-discredited allegations.
The Wakefield scheme is exposed today in the second part of a BMJ series of special reports, "Secrets of the MMR scare", by investigative journalist Brian Deer. Last week we revealed the scientific fraud behind the appearance of a link between the vaccine and autism. Now Deer follows the money.
Drawing on investigations and documents obtained under the Freedom of ...