(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan – Throughout the world, it is common for threats to national sovereignty or territorial integrity to stir up strong emotions among the public. Now, researchers from Japan have found that the strength of the reaction to such threats can break down along political lines in interesting ways.
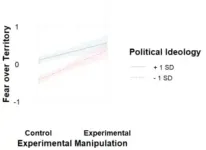
In a study published in Peace and Conflict: Journal of Peace Psychology, researchers from Osaka University have revealed that the Japanese public is highly sensitive to what are known as “collective ownership threats” (COT, i.e., fear of losing control of what is perceived as “ours”), as might be expected given Japan’s strongly collectivist and ethnically homogenous character. Interestingly though, Japanese individuals with politically liberal beliefs tend to show a higher degree of sensitivity to COT than conservatives.
Political scientists distinguish between COT and other types of potential threats to a nation, such as economic or symbolic threats. Although there may be some overlap between these types of threats, in the case of COT, the defining feature is the sense that something that is “ours” is being infringed upon by outsiders (such as a foreign nation).
“In Japan, the issue of the Senkaku Islands (known as the Diaoyu Islands in Chinese) is a matter of great public concern,” says lead author of the study Tomohiro Ioku. “Reports of threats to Japan’s territorial rights over the islands, such as when a Chinese Coast Guard ship recently entered nearby waters, can cause significant public anxiety.”
To investigate how the Japanese public reacts to such infringements, the researchers conducted an online survey of more than 800 Japanese adults in February 2022. As part of this survey, the respondents were shown a fictitious newspaper article depicting a threat from China to Japan’s collective ownership, economy, or culture and tradition.
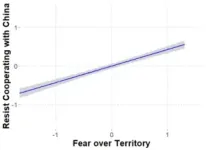
“Our findings suggest that the Japanese public is particularly sensitive to COT,” explains Eiichiro Watamura, senior author. “However, what is fascinating is that this sensitivity is even more pronounced among liberals than conservatives.”
This finding runs counter to conventional wisdom, which is that conservatives tend to react more strongly to issues involving territorial integrity and national sovereignty. Another interesting finding is that the fictitious examples of COT from China in the study had the result of reducing the participants’ willingness to cooperate with Chinese policies such as the Belt and Road Initiative.
This study underscores the psychological importance of collective ownership threats, potentially deterring countries from engaging in activities that infringe on the territorial integrity of others.
###
The article, “Cultural invariance and ideological variance of collective ownership threat in intergroup relations,” is published in Peace and Conflict: Journal of Peace Psychology at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1037/pac0000707
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
END
A threat to what is ours: How Japanese people react to perceived territorial infringements
Researchers from Osaka University find that Japanese liberals and conservatives react differently to perceived threats to national sovereignty and that there is less willingness to cooperate with the policies of countries perceived as threatening
2024-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Experiment captures why pottery forms are culturally distinct
2024-02-28
Potters of different cultural backgrounds learn new types differently, producing cultural differences even in the absence of differential cultural evolution. The Kobe University-led research has implications for how we evaluate the difference of archaeological artifacts across cultures.
Cultural artifacts differ between cultures but are relatively stable within cultures. This makes pottery, and in particular its form, an important archaeological indicator to determine the presence of different cultural groups in specific locations and how they influenced each other over time. But where do such culturally stable variations arise from? The typical explanation for this is through “selective ...
A liking for licking
2024-02-28
HONG KONG (28 Feb 2024) — Unique insights into the social lives of cattle revealed in a new study by scientists at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) can enhance our understanding of animal behaviour and welfare. The study suggests that sex and social status influence social grooming (where one animal licks another, also known as allogrooming) among free-ranging feral cattle in Hong Kong.
The CityUHK researchers found that feral cattle performed preferential grooming of certain individuals and, in particular, that more dominant females received more grooming. This asymmetrical distribution of licking also applied to whom male cattle decided to ...
Scientists provide first detailed estimates of how much sediment is supplied to coral islands from the reef system
2024-02-28
Scientists have produced the first detailed estimates of how much sediment is transported onto the shores of coral reef islands, and how that might enable them to withstand the future threats posed by climate change.
Coral reef islands are low-lying accumulations of sand and gravel-sized sediment deposited on coral reef surfaces.
The sediments are derived from the broken down remains of corals and other organisms that grow on the surrounding reef. Therefore, the rate of supply of sediment from reefs is a critical control on island formation and future change.
The international team of researchers used data available for 28 reef islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans, widely ...
Study details five cutting-edge advances in biomedical engineering and their applications in medicine
2024-02-28
Bridging precision engineering and precision medicine to create personalized physiology avatars. Pursuing on-demand tissue and organ engineering for human health. Revolutionizing neuroscience by using AI to engineer advanced brain interface systems. Engineering the immune system for health and wellness. Designing and engineering genomes for organism repurposing and genomic perturbations.
These are the five research areas where the field of biomedical engineering has the potential to achieve tremendous impact on the field of medicine, according to “Grand Challenges at the Interface of Engineering and Medicine,” a study published by a 50-person task force published ...
Traditional regression approach outperformed machine learning algorithms in predicting optimal surgical method in patients with submucosal tumors.
2024-02-28
Submucosal tumors (SMTs) are usually found in the stomach and esophagus during an upper endoscopy. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection (STER) and non-tunneling endoscopic resection (NTER) are the two most commonly used techniques in the treatment of gastric and esophageal SMTs. As novel technologies continue to shape the medical landscape, machine learning (ML) algorithms find increased application, demonstrating enhanced performance in various fields. Although some studies have evaluated the incremental value of flexible ML methods, comparisons with traditional logistic regression (LR) models are lacking.
To this end, a recent study by a team of researchers from China published in the ...
A survey on federated learning: A perspective from multi-party computation
2024-02-28
Federated learning (FL) has emerged as a popular machine learning paradigm which allows multiple data owners to train models collaboratively with out sharing their raw datasets. It holds potential for a wide spectrum of nalytics applications on sensitive data. For example, federated learning has been applied on medical big data analysis such as disease prediction and diagnosis without revealing the patients’ private medical information to thirdparty services. It has also been exploited by banks and insurance ...
New pediatric cancer marker, new hope for a treatment target
2024-02-28
Researchers have newly identified a universal, essential biomarker for the childhood cancer neuroblastoma – and a potential new target for treatment.
Neuroblastoma accounts for 15% of all pediatric cancer deaths and is the most common source of childhood tumors outside of brain cancer. The disease develops in early nerve tissue, usually in and around the adrenal glands, and typically affects children under age five. High-risk cases have a five-year survival rate of just 50%.
Led by UC San Francisco, researchers suspected the oncoprotein AF1q, which is known to play a role in leukemia and solid tumor progression, might be important in tumors of neural origin ...
Could we assess autism in children with a simple eye reflex test?
2024-02-28
Scientists at UC San Francisco may have discovered a new way to test for autism by measuring how children’s eyes move when they turn their heads.
They found that kids who carry a variant of a gene that is associated with severe autism are hypersensitive to this motion.
The gene, SCN2A, makes an ion channel that is found throughout the brain, including the region that coordinates movement, called the cerebellum. Ion channels allow electrical charges in and out of cells and are fundamental to how they function. Several variants ...
Researchers closer to understanding hydrogen's great challenge
2024-02-28
Why hydrogen causes steels to become brittle and crack is the great conundrum of engineers and researchers looking to develop large-scale transport and storage solutions for the hydrogen age – an era which Australia hopes to lead by 2030.
They may now be one step closer to understanding how hydrogen affects steels, thanks to new University of Sydney research. The researchers found adding the chemical element molybdenum to steel reinforced with metal carbides markedly enhances its ability to ...
Concerted efforts urgently needed to meet 2030 Global Alcohol Action Plan targets
2024-02-28
Concerted international efforts are urgently needed to meet the targets set out in the 2030 Global Alcohol Action Plan (GAAP) and avert “dire consequences” for low and middle income countries, where alcohol markets are expanding, warn health scientists in the open access journal BMJ Global Health.
A lack of progress on alcohol and health in the wake of the 2010 Global Strategy for Reducing the Harmful Use of Alcohol prompted the 75th World Health Assembly to initiate the Global Alcohol Action Plan 2022-30 and declare alcohol a public health priority, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
[Press-News.org] A threat to what is ours: How Japanese people react to perceived territorial infringementsResearchers from Osaka University find that Japanese liberals and conservatives react differently to perceived threats to national sovereignty and that there is less willingness to cooperate with the policies of countries perceived as threatening