(Press-News.org) A research team led by Professor Wang Cheng from the Department of Electrical Engineering (EE) at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) has developed a world-leading microwave photonic chip that is capable of performing ultrafast analog electronic signal processing and computation using optics.
The chip, which is 1,000 times faster and consumes less energy than a traditional electronic processor, has a wide range of applications, covering 5/6G wireless communication systems, high-resolution radar systems, artificial intelligence, computer vision, and image/video processing.
The team's research findings were published in the prestigious scientific journal Nature titled “Integrated Lithium Niobate Microwave Photonic Processing Engine”. It is a collaborative research with The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK).
The rapid expansion of wireless networks, the Internet of Things, and cloud-based services has placed significant demands on underlying radio frequency systems. Microwave photonics (MWP) technology, which uses optical components for microwave signal generation, transmission, and manipulation, offers effective solutions to these challenges. However, integrated MWP systems have struggled to simultaneously achieve ultrahigh-speed analog signal processing with chip-scale integration, high fidelity, and low power.
“To address these challenges, our team developed a MWP system that combines ultrafast electro-optic (EO) conversion with low-loss, multifunctional signal processing on a single integrated chip, which has not been achieved before,” explained Professor Wang.
Such performance is enabled by an integrated MWP processing engine based on a thin-film lithium niobate (LN) platform capable of performing multi-purpose processing and computation tasks of analog signals.
“The chip can perform high-speed analog computation with ultrabroad processing bandwidths of 67 GHz and excellent computation accuracies,” said Feng Hanke, PhD student of EE and the first author of the paper.
The team has been dedicated to researching the integrated LN photonic platform for several years. In 2018, colleagues at Harvard University and Nokia Bell labs developed the world's first CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor)-compatible integrated electro-optic modulators on the LN platform, laying the foundation for the current research breakthrough. LN is referred to as the “silicon of photonics” for its importance to photonics, comparable to silicon in microelectronics.
Their work opens up a new research field, i.e., LN microwave photonics, enabling microwave photonics chips with compact sizes, high signal fidelity, and low latency; it also represents a chip-scale analog electronic processing and computing engine.
The paper's first authors are Feng Hanke and Ge Tong (EE undergraduate). Professor Wang is the corresponding author. Other contributing authors include Dr Guo Xiaoqing, PhD graduate of EE; Dr Chen Zhaoxi, Dr Zhang Ke, Dr Zhu Sha (also at Beijing University of Technology), Dr Sun Wenzhao (now at CityUHK (Dongguan)), EE postdocs; and Zhang Yiwen, EE PhD student; and collaborators (Wang Benshan, Professor Huang Chaoran, and Professor Yuan Yixuan) from CUHK.
END
CityUHK develops world-leading microwave photonics chip for high-speed signal processing
2024-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The “switch” that keeps the immune system from attacking the body
2024-02-28
A microscopic battle rages in our bodies, as our cells constantly fend off invaders through our immune system, a complex system of cells and proteins designed to protect us from harmful pathogens. One of its central components is the enzyme cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS), which acts as a sentinel, detecting foreign DNA and initiating an immune response.
However, the immune system requires precise regulation to prevent cGAS from mistakenly attacking the body's own tissues, leading to autoimmune disorders, which now affect about 10% of the global population.
Previous studies have revealed a little of how this ...
Study unravels the earliest cellular genesis of lung adenocarcinoma
2024-02-28
HOUSTON ― Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center built a new atlas of lung cells, uncovering new cellular pathways and precursors in the development of lung adenocarcinoma, the most common type of lung cancer. These findings, published today in Nature, open the door for development of new strategies to detect or intercept the disease in its earliest stages.
Led by Humam Kadara, Ph.D., professor of Translational Molecular Pathology and Linghua Wang, M.D., Ph.D., associate professor of Genomic Medicine, the team generated an atlas of around 250,000 normal and cancerous ...
Change in gene code may explain how human ancestors lost tails
2024-02-28
A genetic change in our ancient ancestors may partly explain why humans don’t have tails like monkeys, finds a new study led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
Published online February 28 as the cover story of the journal Nature, the work compared the DNA of tail-less apes and humans to that of tailed monkeys, and found an insertion of DNA shared by apes and humans, but missing in monkeys. When the research team engineered a series of mice to examine whether the insertion, in a gene called TBXT, affected their tails, they found a variety of tail effects, including some mice born without tails. ...
Risk of hospital readmission after surgery is high for older Americans
2024-02-28
New Haven, Conn. — A new Yale study finds an increased risk of hospital readmission for older Americans within 180 days of undergoing major surgery — a risk that is particularly acute for individuals who are frail or have dementia.
The findings were published Feb. 28 in the journal JAMA Network Open.
Previous research by the same Yale team demonstrated that major surgery is a common event for older Americans and also demonstrated a heightened mortality risk within one year of major surgery for people who are age 65 and older. The new study is the first to describe both the short-term risk (within 30 days) and longer-term ...
How molecular “handedness” emerged in early biology
2024-02-28
LA JOLLA, CA—Molecules often have a structural asymmetry called chirality, which means they can appear in alternative, mirror-image versions, akin to the left and right versions of human hands. One of the great mysteries about the origins of life on Earth is that virtually all of the fundamental molecules of biology, such as the building blocks of proteins and DNA, appear in just one chiral form.
Scripps Research chemists, in two high-profile studies, have now proposed an elegant solution to this mystery, showing how this single-handedness or “homochirality” could have become established in biology.
The studies were published in the Proceedings ...
The James Webb Space Telescope reveals the central role of low-mass galaxies in the reionization process of the Universe
2024-02-28
PARIS, France and BEER-SHEVA, Israel, February 28, 2024 – The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)[1], developed by NASA and ESA, has just obtained the first spectra of very low-mass galaxies less than a billion years after the Big Bang. A technological feat made possible by the unique combination of JWST sensitivity and the gravitational lensing effect of the Abell 2744 cluster: nearby galaxies act like cosmic magnifiers, distorting space and amplifying the light of background galaxies. By demonstrating that small galaxies are very likely at the origin of the reionization of the universe, this discovery represents a major breakthrough in our knowledge of the cosmos.
The international research ...
Immunotherapy combination may benefit patients with transplanted kidneys and advanced skin cancers
2024-02-28
People who have had a kidney transplant are at high risk for developing skin cancers. New research directed by investigators from the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center is exploring the best combination of treatments to target skin cancers while preserving the transplanted organs.
Now, they report results from a clinical trial testing a novel drug combination designed to stimulate the immune system to fight advanced, potentially lethal skin cancers while not permanently damaging patients’ transplanted kidneys. The treatment included two immune-suppressing drugs ...
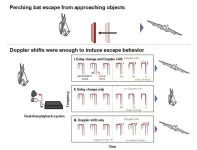
Nature’s sonar: Scientists reveal how Japanese horseshoe bats perceive moving objects
2024-02-28
Unlike most animals that rely on visual senses, bats navigate and locate prey or obstacles through echolocation. By emitting sounds and comparing them to the reflected echoes, bats can “visualize” movement in the environment. When sound waves encounter a moving object, they can undergo changes such as a Doppler shift in frequency or experience a delay, which the bat can sense. However, it is unclear which acoustic characteristics bats rely on to detect moving objects.
Japanese horseshoe bats (Rhinolophus ferrumequinum nippon) emit ultrasound pulses that are characterized ...
Dimensions Research GPT – evidence-based research insights for ChatGPT platform users
2024-02-28
Digital Science is pleased to announce the launch of two new products – Dimensions Research GPT and Dimensions Research GPT Enterprise – bringing the unmatched, trusted research coverage of Dimensions to the ChatGPT platform.
Users can get AI-generated answers to research-related questions on the GPT platform informed by Dimensions’ huge database, making ChatGPT more research-specific for topic exploration.
Available to users of both the free and paid Dimensions Analytics web application, Dimensions Research GPT and Dimensions Research GPT Enterprise help overcome ...
Calcium crystal deposits in the knee contribute to joint damage
2024-02-28
(Boston)— Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, affecting approximately 600 million people worldwide and 34 million people in the U.S. There are no treatments available that prevent its progression to date. Recommended pharmacological treatments for symptoms have either small-to moderate effects or short-term effects, often with side effects, and lifestyle behaviors such as exercise and weight loss are under-utilized.
Historically, intra-articular mineralization (IAM) or calcium crystal deposits in the joint, were thought to be of no clinical consequence, and perhaps just something that happens with older ...