Defects engineering of layered double hydroxide-based electrocatalyst for water splitting
2024-02-29
(Press-News.org)
In the context of the gradual depletion of fossil fuels and the energy crisis, hydrogen energy has attracted widespread attention due to its ultra-high energy density and eco-friendly properties. However, most of the hydrogen production still relies on fossil fuels, with less than 1 million tonnes produced as low-emission hydrogen in 2021, which means it has limited benefits in mitigating the energy crisis and environmental degradation. Alternatively, hydrogen production via water electrolysis has the advantages of non-polluting products, sustainable regeneration, and abundant reactant storage, making it an attractive option for further development.
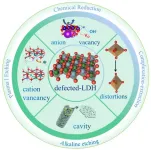
Since driving the water electrolysis requires overcoming a significant overpotential, it is essential to use efficient catalysts that can reduce the overpotential. Layered double hydroxide (LDH)-based materials are considered as promising electrocatalysts for water splitting due to the advantages of unique layered structure, flexible tunability, high specific surface area and distinct electron distribution.
However, the low conductivity and limited active sites hinder the industrial applications of LDH-based electrocatalysts. On the other hand, defect engineering is an effective strategy to tune the local surface microstructure and electronic structure, which can efficiently address the drawbacks of LDH.
Recently, Prof. Deli Wang’s team from Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China, reported the recent defect fabrication strategies on LDH and systematically discussed how defects affect the electrocatalytic behavior of LDH. To begin with, the fundamental mechanism of water electrolysis and the challenges faced by LDH as an electrocatalyst for water electrolysis are presented. And then, the superiority of defect engineering for improving the electrocatalytic performance of LDH is presented and a series of defect fabrication strategies on LDH are summarized and discussed in detail. Subsequently, the relationship among catalytic activity, stability, morphology, structure, composition and defect types are emphatically analyzed and discussed. Finally, the challenges and prospects of applying defect engineering on LDH are discussed. The review was published in Chinese Journal of Catalysis (https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(23)64557-7).
###
About the Journal
Chinese Journal of Catalysis is co-sponsored by Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Chemical Society, and it is currently published by Elsevier group. This monthly journal publishes in English timely contributions of original and rigorously reviewed manuscripts covering all areas of catalysis. The journal publishes Reviews, Accounts, Communications, Articles, Highlights, Perspectives, and Viewpoints of highly scientific values that help understanding and defining of new concepts in both fundamental issues and practical applications of catalysis. Chinese Journal of Catalysis ranks among the top one journals in Applied Chemistry with a current SCI impact factor of 16.5. The Editors-in-Chief are Profs. Can Li and Tao Zhang.
At Elsevier http://www.journals.elsevier.com/chinese-journal-of-catalysis
Manuscript submission https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/cjcatal
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-29
Researchers with the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, and Oak Ridge National Laboratory are hosting an international symposium focused on efforts to make urban and rural communities healthy and resilient to changes in climate, demographics, natural resources and ecosystems.
The “Food-Energy-Water Bioeconomies for Net-Zero Transition” international conference will be March 18-20 in Knoxville. The interdisciplinary conference is sponsored through a U.S. National Science Foundation grant awarded to a team led by Jie ...
2024-02-29
An innovative Oregon Health & Science University research program that enlists older Black adults to walk through and reminisce about historically Black neighborhoods in Portland — which now look very different after rapid change through gentrification — may help improve cognitive function, a new study finds.
The OHSU project has gained wide interest since its 2016 launch, with similar versions beginning to take root in Seattle and Oakland, California.
Now, newly published research suggests it may improve brain health in a population that’s disproportionately affected by Alzheimer’s disease. The study, published online ...
2024-02-29
Supported by a $2 million R01 grant from the National Institutes of Health, the Auerbach Lab at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology will examine how different genes associated with autism spectrum disorders may similarly impact our brain’s neurons, resulting in heightened sensitivity to sounds.
Autism spectrum disorders are genetically complex, and hundreds of genes are implicated in their development. As a result, some may conclude that autism is a collection of disconnected disorders with comparable symptoms. However, much like how roads converge as they approach a destination, at some level of brain function ...
2024-02-29
Medical University of South Carolina neuroscientist Bashar Badran, Ph.D., was one of only 10 investigators nationwide recognized for their research at the fifth annual scientific meeting of the National Institutes of Health – Helping to End Addiction Long-Term (NIH HEAL) Initiative in Bethesda, Maryland. Badran received an honorable mention for the NIH HEAL Initiative Trailblazer Award.
The NIH HEAL Initiative provides funding to encourage scientific research into opioid use and pain management to fast-track progress in the face of the country’s current opioid epidemic. Its Trailblazer ...
2024-02-29
A basic premise of how plants grow is that shoots grow up and roots grow down. A new study, published in Plant Physiology, a leading international society journal published by the American Society of Plant Biologists, reveals the answer to a fascinating question: why do weeping tree varieties defy this natural growth pattern?
Researchers identified a protein called WEEP that is missing from the Weeping Peach Tree. Their results show how a DNA deletion in just one gene completely changes the localization of the hormone auxin, which ...
2024-02-29
A new review has concluded that hospitals that are privatised typically deliver worse quality care after converting from public ownership. The study, led by University of Oxford researchers, has been published today in The Lancet Public Health (video summary available in the notes section)..
Lead author Dr Benjamin Goodair, postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Social Policy and Intervention at the University of Oxford, said: ‘This review challenges the justifications for healthcare privatisation and concludes that the scientific support for healthcare privatisation ...
2024-02-29
Consistent evidence shows that higher exposure to ultra-processed foods is associated with an increased risk of 32 damaging health outcomes including cancer, major heart and lung conditions, mental health disorders, and early death.
The findings, published by The BMJ today, show that diets high in ultra-processed food may be harmful to many body systems and underscore the need for urgent measures that target and aim to reduce dietary exposure to these products and better understand the mechanisms linking ...
2024-02-29
Many cancer drugs approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) between 1995 and 2020 lack proof of added benefit, particularly those approved through expedited (“fast track”) pathways, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
And despite pharmaceutical industry claims that high drug prices are needed to offset research and development (R&D) costs, the results show that more than half of these drugs, including those with minimal or no added benefit, recover R&D expenses within three years.
As such, the researchers call for better alignment between regulatory and reimbursement processes, particularly for drugs approved through expedited pathways, to promote development ...
2024-02-29
Peer-reviewed / Modelling study / People
The Lancet Public Health: Menu calorie labelling may reduce deaths from cardiovascular disease in England, modelling study suggests
The first estimates of the impact of the current calorie labelling legislation in England, which applies only to large out-of-home food businesses, suggests the policy could prevent or postpone about 730 deaths from cardiovascular diseases between 2022 to 2041.
Larger health benefits are estimated if the policy were to be implemented in all English out-of-home food businesses, with about 9,200 deaths from cardiovascular diseases potentially prevented over ...
2024-02-29
A new study conducted by researchers from Utrecht University sheds light on the dynamics of added benefit and revenues of oncology drugs approved by the EMA between 1995 and 2020. The findings, published today, reveal significant insights. The research team consisted of Francine Brinkhuis, Wim Goettsch, Aukje Mantel-Teeuwisse, and Lourens Bloem, affiliated with the Pharmacoepidemiology and Clinical Pharmacology division at Utrecht University.
The study aimed to evaluate the added benefit and financial outcomes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Defects engineering of layered double hydroxide-based electrocatalyst for water splitting