(Press-News.org) (LOS ANGELES) – February 29, 2024 - The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) is pleased to announce their selection of Professor Nicholas A. Peppas of The University of Texas at Austin as the recipient of the 2024 Paul Terasaki Distinguished Scientist Innovation Award. The award will be presented at TIBI’s 2nd annual Terasaki Innovation Summit, to be held March 27-29, 2024, at the UCLA Meyer & Renee Luskin Conference Center.
The award was created in memory of Dr. Paul I. Terasaki, a pioneer in organ transplant research and innovation. It recognizes outstanding achievement in the field of biomedical innovation through research, education, industry, translation, or clinical practice. It also recognizes individuals who have demonstrated exemplary leadership skills and have successfully translated high-impact innovations to real-world solutions.
For over 40 years, Dr. Nicholas A. Peppas has made pioneering contributions to the various interdisciplinary fields of biomedical engineering. He was the first to introduce a theoretical framework and equations for analysis which could be applied to drug delivery systems, biomaterial transport, ionic hydrogels, and gel-tissue interactions. In so doing, he provided definitive and fundamental designs for polymer-based drug delivery, as well as a unified model for all drug delivery systems. This resulted in his being one of the world’s most highly cited scientists, with over 196,000 citations.
Dr. Peppas has applied his principles in several groundbreaking biomedical therapeutic innovations, including a novel freeze-thawing technique to produce non-toxic gels for cartilage regeneration and replacement of vocal cords, oxygen-permeable hard contact lenses for astigmatism and treating oxygen deficiencies in eye tissues, and temperature and bio-responsive devices that can be used for disease treatment. His laboratories have also created first-of-its-kind effective oral delivery systems for diabetics (eliminating the need for daily insulin injections), which also can be used to treat osteoporosis, multiple sclerosis, and cancer. These efforts have led to the formation of three multibillion-dollar medical product companies.
Dr. Peppas’ leadership skills have supported his sincere commitment to education, and he has trained a highly diverse pool of over 5,600 graduate and undergraduate students. He has even established a National Science Foundation-sponsored K-12 program for underrepresented high school students. He has also exhibited great leadership qualities in his roles as either president or chair of several bioengineering societies.
Said Ali Khademhosseini, Ph.D., TIBI’s Director and CEO, “We are very proud to honor Dr. Peppas for his many profound and far-reaching scientific contributions during a long and distinguished career. He is a true pioneer, from which all of us in the field of biomedical engineering have benefited.”
###
About the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation
The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation is accelerating the pace of translational research by supporting the world’s leading scientists with an open, entrepreneurial environment for bioengineering new materials, biological models, and advanced technologies to address critical challenges to the health of the planet and its people. The Institute’s worldwide collaborations with academic, clinical, and entrepreneurial partners provide a rich foundation for translating innovations to the real world.
Contact:
Stewart Han
President
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation
shan@terasaki.org
END
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation announces 2024 Paul Terasaki Award recipient
2024-02-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation announces 2024 Hisako Terasaki Award recipients
2024-02-29
(LOS ANGELES) – February 29, 2024 - The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) is pleased to announce their selections of Assistant Professors Amir Manbachi of Johns Hopkins University and Ritu Raman of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) as the recipients of the 2024 Hisako Terasaki Young Innovator Awards. The awards will be presented at TIBI’s 2nd annual Terasaki Innovation Summit, to be held March 27-29, 2024, at the UCLA Meyer & Renee Luskin Conference Center.
The award was created in memory of Hisako Terasaki, philanthropist, accomplished artist, and wife ...
Small dietary changes can cut your carbon footprint by 25%
2024-02-29
The latest Canada’s Food Guide presents a paradigm shift in nutrition advice, nixing traditional food groups, including meat and dairy, and stressing the importance of plant-based proteins. Yet, the full implications of replacing animal with plant protein foods in Canadians’ diets are unknown.
New research at McGill University in collaboration with the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine provides compelling evidence that partially substituting animal with plant protein foods can increase life expectancy and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. Importantly, ...
Uncertainty in measuring biodiversity change could hinder progress towards global targets for nature
2024-02-29
More than ever before, there is a growing interest in dedicating resources to stop the loss of biodiversity, as recently exemplified by the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) decided at COP15 in December 2022. The GBF focuses on understanding why biodiversity is declining and what actions are needed to reverse this trend. However, according to researchers at McGill University, implementing the plan is challenging because information about biodiversity changes is not evenly available everywhere, and is uncertain in many places.
With the available data, can the ...
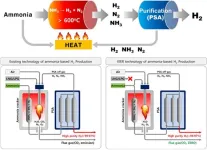
Zero emissions of carbon dioxide! Successful production of ammonia-based clean hydrogen
2024-02-29
Dr. Jung Unho's research team at the Hydrogen Research Department of the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) has developed Korea's first clean hydrogen production technology. This technology is based on ammonia decomposition and does not use fossil fuels. The team's breakthrough could pave the way for a more sustainable and eco-friendly energy source. This allows for the production of high-purity hydrogen that meets international standards for hydrogen-powered vehicles, without the carbon dioxide emissions produced by using fossil fuels.
Ammonia, a compound of hydrogen and nitrogen, has a hydrogen storage density 1.7 times ...
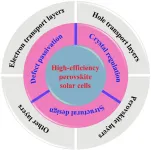
Guiding future research on ‘extraordinary potential’ of next-generation solar cells
2024-02-29
Today’s commercial solar panels can convert about 15% to 20% of the sunlight they absorb into electrical energy — but they could be much more efficient, according to researchers at Soochow University. The next generation of solar cells has already demonstrated 26.1% efficiency, they said, but more specific research directions are needed to make such efficiency the standard and expand beyond it.
They published their review of the current state of research on high-efficiency perovskite solar cells and their recommendations for future work in Energy Materials and Devices on February 4.
“Metal halide perovskite ...
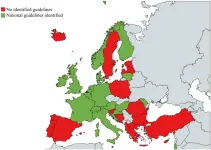
Urgent need for guidelines for the care of child victims of sexual abuse
2024-02-29
Only half of 34 surveyed European countries have national guidelines on how to provide clinical care and treatment to children who have experienced sexual abuse. This finding was revealed in a study led by researchers at Barnafrid, a national knowledge centre in the field of violence and other abuse against children, at Linköping University in Sweden. The consequences for the affected children can be severe, according to the researchers.
“Our findings suggest that children in Europe may not receive equal care. From a child rights perspective, this is unacceptable. ...
Overcoming barriers to conducting clinical trials in childhood rare disease research
2024-02-29
Using a novel methodology, researchers at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) are the first in paediatric research to use data from an international real-world cohort to overcome the barriers associated with conducting randomized clinical trials in children with rare diseases.
The gold standard for evaluating new therapeutics is through randomized clinical trials, where one group of individuals receives treatment while another does not. Unfortunately, conducting this type of clinical trial proves challenging for many rare conditions due to the limited number of individuals with the condition, making meaningful comparisons difficult. Additionally, ...
Faster and simpler point-of-care malaria test developed by Rice researchers
2024-02-29
Rice University researchers have developed a rapid, accurate test for diagnosing malaria that is significantly faster and easier to use than traditional tests. The advancement has the potential to improve patient outcomes, especially in rural regions with limited health care resources.
Malaria remains a significant global health challenge with an estimated 247 million cases and more than 600,000 deaths annually, the majority of which occur in sub-Saharan Africa. The most severe form, cerebral malaria, has a high mortality ...
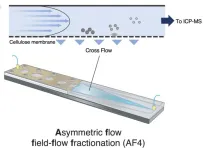
Investigating cell killers: Advanced system for size-dependent cytotoxicity analysis of silica
2024-02-29
Metal nanomaterials have become an indispensable part of industrial and medical fields due to their unique and versatile properties. Their size, which imparts them with the desired physiochemical properties, is also the reason for environmental and health concerns. The nano-sized particles in nanomaterials have shown high reactivity towards biomolecules and often even toxicity towards biological cells.
Scientists have attributed this behavior of metal nanoparticles in interaction with biomolecules to phenomena like inflammation or oxidative stress. However, to ensure the safe usage of metal nanoparticles, ...
Poor spatial navigation could predict Alzheimer’s disease years before the onset of symptoms
2024-02-29
People at risk of Alzheimer’s disease have impaired spatial navigation prior to problems with other cognitive functions, including memory, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The research, published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, used virtual reality to test the spatial navigation of 100 asymptomatic midlife adults, aged 43-66, from the PREVENT-Dementia prospective cohort study.
Participants had a hereditary or physiological risk of Alzheimer’s disease, due to either a gene (the APOE-ε4 allele) that puts them at risk of the condition, a family history of Alzheimer’s disease, ...