Data science approach to identifying thermal conductivity-related structural factors in amorphous materials
A breakthrough in metastable materials research
2024-03-04
(Press-News.org)
1. Using data science techniques, a NIMS–Tohoku University research team has discovered that different thermal conductivities exhibited by an amorphous material with the same composition are attributable to the sizes of atomic rings in its atomic structure. This is one of the first studies demonstrating that the structural features of amorphous materials can be correlated with their physical properties.
2. It is already feasible to synthesize amorphous materials with the same compositions but different thermal conductivities. However, the structural factors responsible for differences in thermal conductivity had yet to be identified due to a lack of appropriate analytical methods.
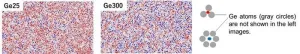
3. It had been impossible to identify structural differences between amorphous germanium (Ge) materials with different thermal conductivities based only on high-resolution transmission electron microscope (TEM) observation. This research team analyzed amorphous Ge material TEM images using data science techniques—topological data analysis and principal component analysis—and identified structural differences between the materials. The team found that the atomic structures of thin film specimens deposited at lower temperatures tended to be dominated by smaller atomic rings (Ge25 in Figure 1) while specimens deposited at higher temperatures contained higher proportions of larger atomic rings (Ge300 in Figure 1).
4. Larger atomic rings had been shown theoretically to be associated with higher thermal conductivity. This study found that Ge300 had higher thermal conductivity than Ge25—results consistent with the theoretical evidence.
5. The data science techniques developed in this research project can be used to identify metastable phases in materials—a task impossible to achieve using conventional structural analysis techniques. These techniques are therefore expected to be useful in developing metastable phase-integrated thermal control materials. They may also be useful in identifying structural features associated with the mechanical, electrical and other properties of amorphous materials in addition to their thermal properties.
***
6. This research was carried out by a research team consisting of Yibin Xu (Leader, Data-driven Inorganic Materials Group, Center for Basic Research on Materials, NIMS) and Kazuto Akagi (Associate Professor, Advanced Institute for Materials Research, Tohoku University). This work was conducted as part of a JST CREST Exploring Unknown Materials project (research supervisor: Professor Hiroshi Kitagawa, grant number: PMJCR21O2). It was also funded by JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Transformative Research (A) (project number: 22H05109) and Scientific Research (A) (project number: 20H00119).
7. This research was published in the December 6, 2023 issue of the International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer (vol. 221).
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-04
Male breast cancer has distinct alterations in the tumor genome that may suggest potential treatment targets, according to a study by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators. They have conducted the first whole genome sequencing analysis of male breast cancer, which looked at the complete DNA landscape of tumor samples from 10 patients.
This is an important step in viewing breast cancer in men, which represents less than 1 percent of all breast cancer cases each year, as a unique disease. Though most research has focused on women with breast cancer, the incidence in men has increased at a much faster rate than in women over the last 40 years. Also, ...
2024-03-04
According to the CDC, the suicide rate among young people ages 10‒24 increased 62% from 2007 through 2021. The CDC’s Youth Risk Behavior Summary reports that in 2021, 22% of high school students seriously considered attempting suicide during the year and 18% made a suicide plan. These statistics indicate a mental health crisis facing our youth. How can we identify children in crisis? Who is being missed?
The Brain & Behavior Research Foundation (BBRF) is hosting a free webinar, “Detection of Suicide-Related Emergencies Among ...
2024-03-04
Madhavi Venkatesan, PhD, Editor-in-Chief of the peer-reviewed journal Sustainability and Climate Change and founder of Sustainable Practices, has been named USA TODAY Woman of the Year for the state of Massachusetts in recognition of her outstanding efforts to eliminate single-use plastic bottles across Cape Cod and the Islands.
With economics and sustainability at the forefront, Venkatesan established Sustainable Practices in 2016, aiming to address pressing environmental issues through innovative solutions. Since then, she and her nonprofit team have spearheaded ...
2024-03-04
In the predawn hours of Sept. 5, 2021, engineers achieved a major milestone in the labs of MIT’s Plasma Science and Fusion Center (PSFC), when a new type of magnet, made from high-temperature superconducting material, achieved a world-record magnetic field strength of 20 tesla for a large-scale magnet. That’s the intensity needed to build a fusion power plant that is expected to produce a net output of power and potentially usher in an era of virtually limitless power production.
The test was immediately declared ...
2024-03-04
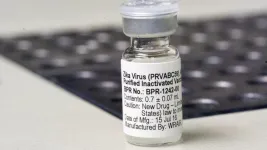
A vaccine against Zika virus is safe and effective when administered both before and during pregnancy, according to new research published in npj Vaccines.
The purified, inactivated Zika vaccine (ZPIV) candidate, developed by Walter Reed Army Institute of Research (WRAIR), is being evaluated in animal models at Texas Biomedical Research Institute (Texas Biomed) in collaboration with WRAIR and Trudeau Institute in New York.
The vaccine candidate has previously been shown to effectively block prenatal Zika virus transmission when given to nonhuman primates ...
2024-03-04
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Childhood lead exposure, primarily from paint and water, is a significant health concern in the United States, but a new study has identified a surprising additional source of lead exposure that may disproportionately harm children: firearms.
A team led by researchers at Brown University found an association between household firearm ownership and elevated lead levels in children’s blood in 44 states, even when controlling for other major lead exposure ...
2024-03-04
The role of African women and young people engaged in agricultural service provision has been investigated in a new CABI-led study published in the CABI Agriculture and Bioscience journal.
By combining a literature review with ongoing action research in Kenya, the scientists provide insights into the main characteristics, benefits, and shortfalls of business models for engaging women and young people in agricultural service provision in Africa.
‘Not a panacea to the challenges faced’
The findings show that the engagement of African women and young people in agricultural service provision is ‘not a panacea to the challenges they face’ such as limited ...
2024-03-04
The Redox Medicine Society (RMS) is pleased to announce the 26th International Conference of the Redox Medicine, taking place from June 27 to June 28, 2024, in Paris, France. Redox Medicine 2024 will gather the world’s leading experts in redox biology, signaling pathways, and their impact on medicine, promising to highlight the current and future state of Redox Medicine.
The influence of redox processes, redox biology, and redox signaling pathways extends across a broad spectrum of physiological and pathological phenomena. A deeper comprehension of the cellular and molecular mechanisms driving these redox interactions is pivotal for the development of innovative ...
2024-03-04
If you’ve driven the mostly flat stretch of I-25 in Colorado from Pueblo to Trinidad, you’ve seen them: the Spanish Peaks, twin mountains that soar into the sky out of nowhere, reaching altitudes of 13,628 and 12,701 feet above sea level.
In a new study, geologists from the University of Colorado Boulder have laid out a timeline for the emergence of these majestic but isolated mountains. The team’s findings could bring scientists closer to answering one of the most enduring puzzles in Colorado geology: What made ...
2024-03-04
Looking deeply into space and time, two teams using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have studied the exceptionally luminous galaxy GN-z11, which existed when our 13.8 billion-year-old universe was only about 430 million years old.
Initially detected with NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, this galaxy — one of the youngest and most distant ever observed — is so bright that it is challenging scientists to understand why. Now, GN-z11 is giving up some of its secrets.
Vigorous Black Hole Is Most Distant Ever Found
A team studying ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Data science approach to identifying thermal conductivity-related structural factors in amorphous materials
A breakthrough in metastable materials research