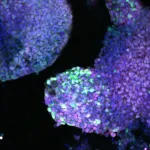
Fukuoka, Japan – In a collaborative study, researchers from Kyushu University and Harvard Medical School have identified proteins that can turn or “reprogram” fibroblasts — the most commonly found cells in skin and connective tissue — into cells with similar properties to limb progenitor cells. Publishing in Developmental Cell, the researchers’ findings have enhanced our understanding of limb development and have set the stage for regenerative therapy in the future.
Globally, close to 60 million people are living with limb loss. Amputations can result from various medical conditions such as tumors, infections, and birth defects, or due to trauma from industrial accidents, traffic accidents, and natural disasters such as earthquakes. People with limb injuries often rely on synthetic materials and metal prostheses, but many researchers are studying the process of limb development, with the aim of bringing regenerative therapy, or natural tissue replacement, one step closer as a potential treatment.
“During limb development in the embryo, limb progenitor cells in the limb bud give rise to most of the different limb tissues, such as bone, muscle, cartilage and tendon. It’s therefore important to establish an easy and accessible way of making these cells,” explains Dr. Yuji Atsuta, lead researcher who began tackling this project at Harvard Medical School and continues it as a lecturer at Kyushu University’s Graduate School of Sciences.
Currently, a common way to obtain limb progenitor cells is directly from embryos, which, in the case of human embryos, raises ethical concerns. Alternatively, they can be made using induced pluripotent stem cells — adult cells which are reprogrammed into an embryonic-like state, and which can later be coaxed into specific tissue types. The new method developed by Atsuta and colleagues, which directly reprograms fibroblast cells into limb progenitor cells and bypasses induced pluripotent stem cells, simplifies the process and reduces costs. It also mitigates the concern of cells turning cancerous, which often occurs with induced pluripotent stem cells.
In the initial phase of the study, the researchers looked at what genes were expressed in the early limb buds in mice and chicken embryos. Almost all cells in the body, including fibroblasts and limb progenitor cells, contain identical genomic DNA, but the different properties and functions of each cell type emerge during development due to changes in gene expression (in other words, which genes are active, and which proteins are produced by the cell). One way that gene expression is controlled in cells is by specific proteins, called transcription factors.
The research group identified 18 genes, mostly transcription factors, that are more highly expressed in the early limb bud compared to other tissues. They cultured fibroblasts from mouse embryos and introduced these 18 genes into the fibroblasts using viral vectors so that the cells produced these 18 protein factors. They found that the modified fibroblasts took on the properties and showed similar gene expression to naturally-occurring limb progenitor cells found in limb buds.
Next, over a series of experiments, the researchers narrowed down their selection and determined that only three protein factors were essential to reprogram mouse fibroblasts into limb progenitor-like cells: Prdm16, Zbtb16, and Lin28a. A fourth protein, Lin41, helped the cultured limb progenitor cells grow and multiply more rapidly.
The researchers not only confirmed that the reprogrammed limb progenitor cells had similar gene expression to natural limb progenitor cells, but also had similar ability. “These reprogrammed cells are not only molecular mimics; we have confirmed their potential to develop into specialized limb tissues, both in laboratory dishes (in vitro) and also in living organisms (in vivo),” says Atsuta. “Testing in vivo was particularly challenging, as we had to transplant the reprogrammed mouse cells into the limb buds of chicken embryos.”
In these experiments, the researchers used lentiviruses, which insert genes directly into the infected cells’ genome, raising the risk that the cells can become cancer. Instead, the team is considering other safer vectors, such as adeno-associated viruses or plasmids, which deliver genes to the cells without inserting genes into the genome.
Atsuta’s lab group is now trying to apply this method to human cells, for future therapeutic applications, and also to snakes, whose ancestors had limbs that were subsequently lost during evolution. “Interestingly, the reprogrammed limb progenitor cells generated limb bud-like organoids, so it seems possible to generate limb tissues in species that no longer possess them. The study of limbless snakes can uncover new pathways and knowledge in developmental biology.”
(By Negar Khalili)
###
For more information about this research, see "Direct reprogramming of non-limb fibroblasts to cells with properties of limb progenitors" Yuji Atsuta, Changhee Lee, Alan R. Rodrigues, Charlotte Colle, Reiko R. Tomizawa, Ernesto G. Lujan, Patrick Tschopp, Laura Galan, Meng Zhu, Joshua M. Gorham, Jean-Pierre Vannier, Christine E. Seidman, Jonathan G. Seidman, Marian A. Ros, Olivier Pourquié, Clifford J. Tabin, Developmental Cell, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2023.12.010
About Kyushu University
Founded in 1911, Kyushu University is one of Japan's leading research-oriented institutes of higher education, consistently ranking as one of the top ten Japanese universities in the Times Higher Education World University Rankings and the QS World Rankings. The university is one of the seven national universities in Japan, located in Fukuoka, on the island of Kyushu—the most southwestern of Japan’s four main islands with a population and land size slightly larger than Belgium. Kyushu U’s multiple campuses—home to around 19,000 students and 8000 faculty and staff—are located around Fukuoka City, a coastal metropolis that is frequently ranked among the world's most livable cities and historically known as Japan's gateway to Asia. Through its VISION 2030, Kyushu U will “drive social change with integrative knowledge.” By fusing the spectrum of knowledge, from the humanities and arts to engineering and medical sciences, Kyushu U will strengthen its research in the key areas of decarbonization, medicine and health, and environment and food, to tackle society’s most pressing issues.
END