2024 Carbon Future Young Investigator Award-Call for nominations
2024-03-05
(Press-News.org)
The call for the 2024 Carbon Future Young Investigator Award is open!
About The Award
Tsinghua University Press announces the 2024 Carbon Future Young Investigator Award. This award is intended to recognize and encourage outstanding early career researchers in the areas of carbon-related materials, catalysis, energy conversion and storage, as well as low carbon emission process and engineering. The award includes an honorarium of $1,000 for each awardee (up to 10 awardees).
Eligibility
The nominee must be a current PhD student or postdoctoral researcher.
The nominee’s research should align with the scope of Carbon Future (carbon-related materials, catalysis, low-carbon energy, or chemical engineering).
Nomination
The nomination should be made by the nominee’s PhD or postdoc advisor.
Required materials: CV of the nominee (less than 5 pages); 1-page research statement of the nominee; a nomination letter from the nominator commenting on the qualifications and accomplishments of the nominee as well as the significance and impact of his or her research.
All materials should be written in English or Chinese
IMPORTANT: Please email your full nomination to carbonfuture@tup.tsinghua.edu.cn by April 10, 2024.
Please supply the following words in your email: I hereby affirm that the information contained in the application is accurate and complete to the best of my knowledge.
Additional Information
The award is generously sponsored by Tsinghua University (and its Press).
We strive to ensure fair geographic distribution of awards, in keeping with Carbon Future’s status as an international journal.
Carbon Future will devote a special issue to feature the awardees and their research achievements. Therefore, if awarded, the nominee agrees to submit to Carbon Future, before August 1st, 2024, an article that introduces their research area and critically reviews their published work in the area.
If you have any questions, please contact us by email at carbonfuture@tup.tsinghua.edu.cn.
About The Journal:
Carbon Future (ISSN 2960-0561, https://www.sciopen.com/journal/2960-0561) is an open access, peer-reviewed, and international interdisciplinary journal sponsored by Tsinghua University (and its Press). It serves as a platform for researchers, scientists, and industry professionals to share their findings and insights on carbon-related materials and processes, including catalysis, energy storage and conversion, as well as low-carbon emission process and engineering. It features cutting-edge research articles, insightful reviews, perspectives, and news and views in the field (the article publishing charge is covered by the Tsinghua University Press).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-05
ST. LOUIS, MO, March 5, 2024 – The Donald Danforth Plant Science Center and the Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research (EIAR) have received a $4.9 million grant from The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation to build on previous advances in gene editing of tef for reduced height and lodging resistance in advanced, farmer preferred tef lines.
The grant will support research to validate the improved semi dwarf tef in Ethiopia under greenhouse and multi location field conditions and generate lodging resistance ...
2024-03-05
In a series of studies, a team of astronomers has shed new light on the fascinating and complex process of planet formation. The stunning images, captured using the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT) in Chile, represent one of the largest ever surveys of planet-forming discs. The research brings together observations of more than 80 young stars that might have planets forming around them, providing astronomers with a wealth of data and unique insights into how planets arise in different regions of our galaxy.
“This is really a shift in our field of study,” says Christian Ginski, a lecturer at the University of Galway, Ireland, ...
2024-03-05
A theoretical experiment characterized the network architecture of a species-rich ecosystem over 8 months. Predator–prey interaction networks play a key role in structuring ecosystems, but ecological research has often treated such networks as static, despite the broadly accepted understanding of ecosystems as dynamic. Hirokazu Toju and colleagues followed the complex food webs between 50 predatory spider species and 974 prey species, including midges, springtails, mosquitoes, and aphids, for eight months. The studied ecosystem is a warm-temperate grassland ...
2024-03-05
In the Japanese art of Kintsugi, an artist takes the broken shards of a bowl and fuses them back together with gold to make a final product more beautiful than the original.
That idea is inspiring a new approach to managing plasma, the super-hot state of matter, for use as a power source. Scientists are using the imperfections in magnetic fields that confine a reaction to improve and enhance the plasma in an approach outlined in a new paper in the journal Nature Communications.
“This approach allows you to maintain ...
2024-03-05
Researchers built a model that can predict with 73.5% accuracy when a person will experience aesthetic chills: shivers, goosebumps, or a feeling of cold down the neck or spine elicited by aesthetic stimuli, such as beautiful music or an inspirational speech. Felix Schoeller and colleagues surveyed 2,937 people from Southern California, through an online platform, gathering data on their personalities, demographic backgrounds, and emotional state. The authors then exposed survey respondents to 40 emotion-evoking audiovisual clips sourced from social media, selected because commenters had reported experiencing aesthetic chills while watching and listening. ...
2024-03-05
PULLMAN, Wash. – Bacteria can be tricked into sending death signals to stop the growth of their slimy, protective homes that lead to deadly infections, a new study demonstrates.
The discovery by Washington State University researchers could someday be harnessed as an alternative to antibiotics for treating difficult infections. Reporting in the journal, Biofilm, the researchers used the messengers, which they named death extracellular vesicles (D-EVs), to reduce growth of the bacterial communities by up to 99.99% in laboratory experiments.
“Adding the death extracellular vesicles to ...
2024-03-05
Text-to-image generative AI systems like Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, and DALL-E can produce images based on text prompts that, had they been produced by humans, would plausibly be judged as “creative.” Some artists have argued that these programs are a threat to human creativity. If AI comes to be relied on to produce most new visual works, drawing on what has been done before, creative progress could stagnate. Eric Zhou and Dokyun “DK” Lee investigated the impact of text-to-image AI tools on human creativity, seeking to understand ...
2024-03-05
Since its introduction, cryptocurrency governance has been one of the most controversial global financial topics. While some countries have established elaborate regulations for cryptocurrencies, many countries are still reluctant to oversee the markets, and some have outright banned them. Most studies suggest that public agencies naturally want to regulate markets and bring them into their purview. However, the significant differences in cryptocurrency regulation over the world call this view into question. Moreover, these differences cannot be explained by the development ...
2024-03-05
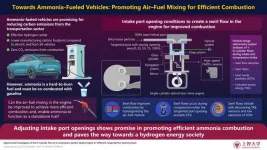
While the transportation sector has witnessed a dramatic shift toward electric vehicles (EVs), the idea of using hydrogen as a clean and efficient fuel for transportation has been explored for many decades. These vehicles emit water on combustion, and since they are based on the production of existing engine vehicles, they are expected to have a lower manufacturing carbon footprint than EVs. However, storing and transporting hydrogen requires high pressures and low temperatures, which are energy-intensive processes. To address this, ammonia has ...
2024-03-05
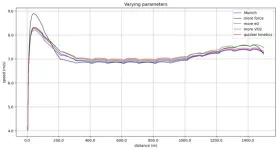
How to optimise running? A new mathematical model1 has shown, with great precision, the impact that physiological and psychological parameters have on running performance and provides tips for optimised training. The model grew out of research conducted by a French-British team including two CNRS researchers2, the results of which will appear on March 5th 2024 in the journal Frontiers in Sports and Active Living.
This innovative model was developed thanks to extremely precise data3 from the performances of Matthew Hudson-Smith (400m), Femke Bol (400m), and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 2024 Carbon Future Young Investigator Award-Call for nominations