(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this study involving 247,000 UK residents, habitual short sleep duration was associated with increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This association persisted even among participants who maintained a healthy diet. To validate these findings, further longitudinal studies are needed, incorporating repeated measures of sleep (including objective assessments) and dietary habits.
Authors: Christian Benedict, Ph.D., of Uppsala University in Uppsala, Sweden, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.1147)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.1147?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=030524
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Habitual short sleep duration, diet, and development of type 2 diabetes in adults
JAMA Network Open
2024-03-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Screen time, sociodemographic factors, and psychological well-being among young children
2024-03-05
About The Study: In this multiyear cross-sectional study of a representative sample of young children in the U.S., the increased prevalence of high screen time in 2020 returned to pre-pandemic levels in 2021; however, it remained elevated in children living in poverty. Two hours or more of daily screen time was associated with lower psychological well-being among preschool-aged children.
Authors: Soyang Kwon, Ph.D., of Northwestern University in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
Too little sleep raises risk of type 2 diabetes
2024-03-05
Adults who sleep only three to five hours a day are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This is demonstrated in a new study from Uppsala University, published in JAMA Network Open. It also shows that chronic sleep deprivation cannot be compensated by healthy eating alone.
“I generally recommend prioritising sleep, although I understand it’s not always possible, especially as a parent of four teenagers,” says Christian Benedict, Associate Professor and sleep researcher at the Department of Pharmaceutical Biosciences at Uppsala University and leading researcher behind the study.
He and a team of researchers have examined the link between type 2 ...
Toward understanding sperm quality
2024-03-05
A novel screening system developed at Kyoto University enables researchers to investigate sperm cell development and health at the molecular level. The new approach, published in Cell Genomics, promises breakthroughs in male contraception and infertility treatments.
The study, led by Professor Jun Suzuki of the Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS), addresses a critical gap by directly targeting genes within testicular cells inside living organisms. Utilizing a genetic tool called CRISPR, which can ...
Game-changing sensor unveiled for spotting chemical threats
2024-03-05
Scientists have unveiled a groundbreaking sensor that can wirelessly detect chemical warfare agents, marking a significant leap in public safety technology. This innovative device, capable of identifying substances like dimethyl methylphosphonate (DMMP), offers a new level of efficiency and reliability in monitoring and responding to chemical threats, without the need for direct power sources or physical connections.
The urgent need for advanced detection of chemical warfare agents (CWAs) to ensure global security has led to the development of a novel gas sensor. This sensor is distinguished ...
The many faces of a zinc anode: Configurations can make a difference in performance
2024-03-05
Sometimes the solution to a problem can be as simple as changing the way the components are structured
Researchers have proposed a reconfiguration of zinc anodes, a component of renewable energy sources, to help improve the battery and reduce the reliance society has on fossil fuels. The potential that different configurations of a zinc anode can have could reduce costs and side reactions while increasing the safety of the rechargeable zinc metal battery (RZMB) and, of course, improve its “green” rating.
The results were published in Energy Materials and Devices ...
Team successfully synthesizes atomically precise metal nanoclusters
2024-03-05
A research team has successfully synthesized a metal nanocluster and determined its crystal structure. Their study provides experimental evidence for understanding and designing nanoclusters with specific properties at the atomic level. Metal nanoclusters have wide-ranging applications in the biomedical field.
Their work is published in the journal Polyoxometalates on February 6, 2024.
Scientists have shown interest in ligand-protected atomically precise metal nanoclusters because they have definite atomic structures and exceptional ...
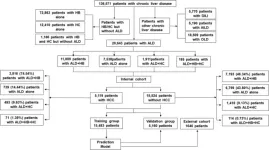
Rising alcohol-related liver cancer prompts new prediction tool
2024-03-05
Liver cancer, unfortunately, is the sixth most common cancer and the third most frequent cause of cancer-related death globally. However, its distribution and causes vary greatly across different regions. While areas like Eastern Asia and sub-Saharan Africa see the most cases, the reasons behind them differ significantly.
In high-income countries, liver cancer has been on the decline thanks to widespread newborn hepatitis B vaccination and antiviral drugs. Meanwhile, low-income countries witness a worrying rise, ...
Sprinting ‘like a jet’ will produce Premier League strikers of tomorrow
2024-03-05
Sprinting “like a jet plane taking off” will help produce Premier League star strikers of tomorrow, new research has revealed.
A University of Essex study of Tottenham Hotspur’s academy has shown that just a few words can instantly boost sprinting speed by 3 per cent over 20 metres.
It would normally take weeks of targeted training to achieve such a large increase.
These short bursts of acceleration are largely seen in goal-scoring situations and could be the difference in beating a defender and finding the net.
Dr Jason Moran, from the School of Sport, Rehabilitation and Exercise Sciences, discovered simple analogies increased ...
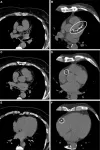
Coronary artery calcium score predictive of heart attacks, strokes
2024-03-05
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Coronary artery calcium scoring with CT can identify symptomatic patients with a very low risk of heart attacks or strokes, according to a new study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). Researchers said the findings may one day help some patients with stable chest pain avoid invasive coronary angiography.
Coronary artery calcium scoring with CT was developed to noninvasively measure the amount of calcium in the arteries of the heart. Higher scores are linked with atherosclerosis, a buildup of plaque in the arteries. A score of 1 to 399, for instance, suggests a moderate amount of plaque, while 400 ...
Harvard neuroscientist Haim Sompolinsky awarded Brain Prize
2024-03-05
Haim Sompolinsky, Professor in Residence in Harvard’s Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology and Department of Physics, has received the Brain Prize for his pioneering contributions to computational and theoretical neuroscience.
Considered the world’s most prestigious prize for neuroscience research, the Brain Prize 2024 is shared by Sompolinsky, Larry Abbott of Columbia University, and Terrence Sejnowski of the Salk Institute. All three scientists have helped uncover key principles governing the brain’s structure, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Habitual short sleep duration, diet, and development of type 2 diabetes in adultsJAMA Network Open