(Press-News.org) A team from Nagoya University in Japan has identified previously unidentified gene variants that are associated with the development of generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP). The team’s findings, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, offer hope for improving diagnosis and therapy.
GPP is rare, but its effects are often serious. People with GPP can experience recurrent flares of the disease, which include multiple erythematous lesions and sterile pustules over the whole body, often accompanied by fever and chills. This can lead to emergency treatment and even death.
Until now, researchers have reported six genes associated with GPP. Although these genes are widely used for diagnosis and treatment, there remain GPP patients who do not have any variants of these genes. This suggests unknown genetic factors associated with the development of GPP.
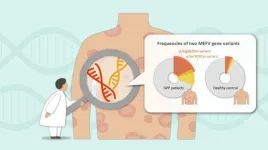
To address this problem, a group led by Prof. Masashi Akiyama, Takenori Yoshikawa, and Dr. Takuya Takeichi from the Department of Dermatology at Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine used next-generation sequencing to investigate the genes of Japanese patients with GPP. They found that higher frequencies of two MEFV gene variants, p.Arg202Gln and p.Ser503Cys, were associated with GPP. In particular, 21% of the patients carried the variant p.Arg202Gln variant and 13% carried the p.Ser503Cys variant.
Pyrin, the product of MEFV, regulates inflammatory pathways. But specific variants of pyrin induce excessive neutrophil migration to tissues, eventually triggering excessive inflammation. This finding, therefore, suggests a likely path for the disease.
The researchers believe that therapies targeting inflammatory pathways related to MEFV are a promising therapeutic strategy for patients with these variants. According to Yoshikawa, their findings suggest a new use for a commonly used drug to treat familial Mediterranean fever (FMF): “As these variants are associated with both FMF and GPP, treatments for FMF may also be effective for the treatment of patients with MEFV-associated GPP.”
END
Missing disease-related gene identified in generalized pustular psoriasis
2024-03-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Schisanhenol: A potential drug for the treatment of cytokine storm
2024-03-07
Background and objectives
Cytokine storm (CS) is an acute systemic inflammatory response with limited effective interventions up to now. The treatment experience of the COVID-19 pandemic suggests great potential in the intervention of CS by herbal medicine. This study aimed to investigate whether Schisanhenol (SSH), an active component of the Chinese herbal medicine Schisandra chinensis, has the potential to interfere with CS.
Methods
The effect of SSH on nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway activity ...
Revealing a hidden threat: Researchers show viral infections pose early heart risks
2024-03-07
In a potentially game-changing development, scientists with the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC have revealed a new understanding of sometimes fatal viral infections that affect the heart.
Traditionally, the focus has been on heart inflammation known as myocarditis, which is often triggered by the body’s immune response to a viral infection.
However, a new study led by James Smyth, associate professor at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute, sheds new light on this notion, revealing that the virus itself creates potentially dangerous conditions in the heart ...
Study reveals unexpected literacy in autistic people who cannot speak
2024-03-06
About one-third of autistic people are unable to communicate using speech, and most are never provided an effective alternative. However, a new study from scientists at the University of Virginia suggests that many of these individuals are literate, raising the possibility that they could learn to express themselves through writing.
The study published in the journal Autism, reports that five times more nonspeaking autistic teenagers and adults demonstrated knowledge of written language conventions than would be expected from previous estimates of their abilities. The finding has important implications for the millions of autistic ...
The sweet stuff: How insects tell sugars apart
2024-03-06
New Haven, Conn. — Whereas humans have one receptor on their tongues that can detect all sorts of sweet things, from real sugar to artificial sweeteners like aspartame, insects have many receptors that each detect specific types of sugars. Yale researchers have now uncovered one way insect receptors are able to be so selective, an insight they say will help us understand how animals decipher the chemical world and how we might mimic that ability in the future.
They reported their findings in a study published March 6 in Nature.
Sugar is important to animals ...
What are Hubble and Webb observing right now? NASA tool has the answer
2024-03-06
It’s not hard to find out what NASA’s Hubble and James Webb space telescopes have observed in the past. Barely a week goes by without news of a cosmic discovery made possible using images, spectra, and other data captured by NASA’s prolific astronomical observatories.
But what are Hubble and Webb looking at right this minute? A shadowy pillar harboring nascent stars? A pair of colliding galaxies? The atmosphere of a distant planet? Galactic light, stretched and distorted on a 13-billion-year journey across ...
Medical malpractice incidents are more severe during daylight saving time
2024-03-06
DARIEN, IL – Medical malpractice incidents are more severe during the months of the year when daylight saving time is observed in the U.S., according to a new study that examined three decades of malpractice claims.
Results show that both medical malpractice incident severity and payment decisions were higher during the months of daylight saving time compared with the months of standard time, after controlling for whether states observe daylight saving time. Payment decisions also were higher, but medical incidents were not more severe, during the one week following the spring transition to daylight saving time.
“The spring daylight saving shift ...
Airflow dynamics scrub classroom air
2024-03-06
If you’ve ever wondered why some folks never catch the office or school cold, where they’re sitting might be keeping them from the path of pathogens, according to new UBC Okanagan research.
Using a working UBCO classroom as their test lab, the team found that accounting for airflow dynamics reduced pathogens in the classroom by 85 per cent.
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, the advice was often just to increase ventilation to the maximum,” says Mojtaba Zabihi, a doctoral student in mechanical engineering ...
New product development shapes firms and the economy
2024-03-06
Understanding product life cycles plays an important role in the innovation arms race, helping to define firm growth and market competition.
Products experience a substantial decline in sales after an initial period of growth, a trend that is consistent across various industries and product types.
“By examining the life cycle of a wide cross-section of products, we can see the role product performance plays in shaping firm and economic growth,” said Munseob Lee, assistant professor of economics at the University of California San Diego School of Global Policy ...
People with essential tremor may have increased risk of dementia
2024-03-06
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 6, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Dementia may be three times more common among people with essential tremor, a movement disorder that causes involuntary shaking, than the general population, according to research released today, March 6, 2024. The study will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 76th Annual Meeting taking place April 13–18, 2024, in person in Denver and online.
Essential tremor is the most common tremor disorder, more common than Parkinson’s disease. In addition to arm and ...
Black people half as likely to be evaluated for genetic testing as white people
2024-03-06
MINNEAPOLIS – Genetic testing has become a more common way to diagnose and manage many neurologic conditions including dementia, Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy, but a new study has found not everyone may have the same level of access to these tests. Black people were half as likely as white people to be evaluated for genetic testing, according to a study published in the March 6, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Genetic testing is crucial for identifying neurologic conditions and has potential to impact treatment and management of symptoms,” said study author Colin A. Ellis, ...