Lack of functional eyes does not affect biological clock in zebrafish
2024-03-07
(Press-News.org)
Functional eyes are not required for a working circadian clock in zebrafish, as a research team1 including CNRS scientists has now shown.
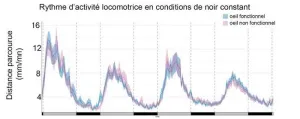
Though it is understood that the eye plays a key role in mammalian adaptation to day-night cycles, the circadian clock is most often studied in nocturnal vertebrates such as mice. The zebrafish, in contrast, is a diurnal vertebrate. Through observation of various zebrafish larvae lacking functional eyes,2 the team of scientists has demonstrated that the latter are not needed to establish circadian rhythms that remain synchronized with light-dark cycles in the laboratory. This suggests that, in some animal species, other neural circuits set the circadian clock.
In addition to molecular analyses, the researchers relied on video tracking of larval locomotion, the most reliable indicator in the study of the circadian clock. These findings, to be published in PLOS Genetics on 7 March, reveal major differences between organisms in the regulation of circadian rhythms.
Notes :
1 - Laboratories involved in the study include the Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology research unit (CNRS / Université Toulouse III–Paul Sabatier) and the Centre for Integrative Biology (CNRS/Université Toulouse Paul Sabatier).
2 - Larvae with mutated lak genes do not have functional retinal ganglion cells, which relay what is perceived by the eye to the brain: hence, the larvae cannot see.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-07
What’s in a name? A lot, actually.
For the scientific community, names and labels help organize the world’s organisms so they can be identified, studied, and regulated. But for bacteria, there has never been a reliable method to cohesively organize them into species and strains. It’s a problem, because bacteria are one of the most prevalent life forms, making up roughly 75% of all living species on Earth.
An international research team sought to overcome this challenge, which has long plagued scientists who study bacteria. Kostas Konstantinidis, Richard ...
2024-03-07
The University of Colorado Denver | Anschutz Medical Campus is listed as one of Forbes America’s Best Large Employers for 2024.
The 2024 list of “America’s Best Employers” was conducted by Forbes and market research firm Statista, the world-leading statistics portal and industry ranking provider.
“This ranking is meaningful to our organization because the people who work at CU Anschutz drive our success as a leading academic medical campus by providing unparalleled patient care services, being a premier national leader in research and innovation, and fostering a supportive learning ...
2024-03-07
As data from the Anti-Defamation League shows antisemitism growing on college campuses in recent years and spiking after the Hamas-Israel conflict, a New Jersey Institute of Technology researcher is doing her part to combat the trend by developing a training model that will help prepare mental health professionals who work with Jewish students.
Modern students are hearing people chant slogans without understanding the intentions behind the words, or finding swastikas and other anti-Jewish graffiti on their campuses, but they are not encountering suitably trained counselors and psychologists who understand their ...
2024-03-07
Becoming a parent comes with lots of bills. For new mothers, being able to afford the rent may help stave off postpartum depression.
“Housing unaffordability has serious implications for mental health,” said Katherine Marcal, an assistant professor at the Rutgers School of Social Work and author of a study published in the journal Psychiatry Research. “For mothers who rent their homes, the ability to make monthly payments appears to have a correlation to well-being.”
Housing hardship – missing rent or mortgage payments, moving in with others, being evicted ...
2024-03-07
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments at MD Anderson offer clinical insights into a novel treatment strategy for patients with relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML), molecular insights into Burkitt lymphoma development, a therapeutic target to overcome ...
2024-03-07
AUSTIN, Texas — Managers can do much to help their workers become more resilient to inevitable time disruptions in today’s workplace, says new research from The University of Texas at Austin.
With intricate supply chains and operations that sprawl across time zones, workplace time disturbances are only increasing. Such temporal disruptions aren’t just inconvenient, says David Harrison, Texas McCombs professor of management professor: They can carry tangible business costs, such as impaired health, increased mistakes, and reduced ...
2024-03-07
In the four years after the border wall height was increased from 17 feet to 30 feet along the US-Mexican border, drowning deaths of migrants in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego increased by 3200%, according to a new study published in JAMA. Co-authors Anna Lussier, M.D, Ph.D. student in the University of California San Diego School of Medicine, and Peter Lindholm, M.D., Ph.D., Gurnee Endowed Chair of Hyperbaric and Diving Medicine Research and professor in residence in the Department of Emergency Medicine at UC San Diego School of Medicine, ...
2024-03-07
Over half of the 60 countries holding national elections this year are experiencing a democratic decline, risking the integrity of the electoral process, as reported in the latest Democracy Report from the V-Dem Institute at the University of Gothenburg. The worsening election quality is concerning, given the pivotal role elections play in either reinforcing or mitigating the trend of autocratization.
The wave of democratic backsliding, or autocratization, continues to be noticeable, according to the report. 42 countries are autocratizing, and 71 percent of the world’s population now live in autocracies – up from 48 percent ten years ago. There ...
2024-03-07
The frequency and scale of mass mortality events — events where large numbers of organisms die in short periods of time — among farmed salmon have increased since 2012, according to a study published in Scientific Reports.
Gerald Singh and colleagues analysed salmon mortality data from Norway, Canada, the UK, Chile, Australia, New Zealand — countries that produced over 92% of the world’s farmed salmon in 2021 — between 2012 and 2022. They identified 865 million instances of salmon mortality during ...
2024-03-07
The cacao tree (Theobroma cacao), whose beans (cocoa) are used to make products including chocolate, liquor and cocoa butter, may have spread from the Amazon basin to the other regions of South and Central America at least 5,000 years ago via trade routes, suggests a paper published in Scientific Reports. These findings, based on residues in ancient vessels, reveal how different strains of cacao tree were bred and suggest that cacao products were more widely used among ancient South and Central American cultures than previously thought.
The modern cacao tree — whose scientific ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Lack of functional eyes does not affect biological clock in zebrafish


