Mutation solves a century-old mystery in meiosis
2024-03-08
(Press-News.org) Movies such as ‘X-Men,’ ‘Fantastic Four,’ and ‘The Guardians,’ which showcase vibrant mutant heroes, have captivated global audiences. Recently, a high-throughput genetic screening of meiotic crossover rate mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana garnered the interest of the academic community by unraveling a century-old mystery in the life sciences.
A research team, consisting of Professor Kyuha Choi, Dr. Jaeil Kim, and PhD candidate Heejin Kim from the Department of Life Sciences at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), has achieved a remarkable feat by unveiling the molecular mechanism responsible for crossover interference during meiosis, a biological pattern at the chromosome level. The findings of this research were published on February 20 in Nature Plants, an international journal in the field of life sciences.
In sexually reproducing organisms, individuals resemble their parents or siblings. Despite the striking similarities, it's crucial to recognize that absolute identicalness is unattainable. This variation is attributed to the process of meiosis, which generates reproductive cells like sperm and eggs in animals or pollen and ovules in plants. Unlike somatic cell division, which duplicates and divides the genome identically, meiosis creates genetically diverse reproductive cells through a mechanism known as crossover.
Meiosis and crossover play pivotal roles in biodiversity and have significant implications in breeding where the selection and cultivation of superior traits in crops occur. Typically, most animal and plant species exhibit a minimum of one and a maximum of three crossovers per a pair of homologous chromosomes. The ability to control the number of these crossovers could lead to cultivating crops with specific desired traits. However, achieving such control has been challenging due to the ‘phenomenon of crossover interference.’ Crossover interference, where one crossover inhibits the formation of another crossover nearby along the same chromosome, was initially identified by fruit fly geneticist Hermann J. Muller in 1916. Despite researchers' persistent efforts over the past century since its discovery, it is only recently that the mechanisms underlying crossover interference have started to unveil their secrets.
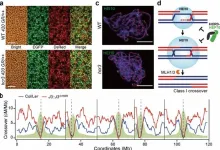
In this research, the team utilized a high-throughput fluorescent seed scoring method to directly measure crossover frequency in Arabidopsis plants. Through a genetic screen, they identified a mutant named hcr3 (high crossover rate3) that exhibited an increased crossover rate at the genomic level. Further analysis revealed that the elevated crossovers in hcr3 was attributed to a point mutation in the J3 gene, which encodes a co-chaperone related to HSP40 protein. This research demonstrated that a network involving HCR3/J3/HSP40 co-chaperone and the chaperone HSP70 controls crossover interference and localization by facilitating the degradation of the pro-crossover protein, HEI10 ubiquitin E3 ligase. The application of genetic screen approaches to uncover the crossover interference and inhibition pathway successfully addressed a century-old puzzle in the life sciences.
POSTECH Professor Kyuha Choi stated, "Applying this research to agriculture will enable us to rapidly accumulate beneficial traits, thereby reducing breeding time." He expressed optimism by saying, "We hope this research will contribute to the breeding of new varieties and identification of useful natural variations responsible for desirable traits such as disease and environmental stress resistance, improved productivity, and high-value production."
The research was conducted with support from the Basic Research Program in Science and Engineering and the Mid-Career Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program of the Rural Development Administration, the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, and the Samsung Science & Technology Foundation.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-08
A University of Colorado Department of Medicine faculty member says she and her colleagues have identified the means in which bacteria in the digestive system can break down tryptophan in the diet into an inflammatory chemical that primes the immune system towards arthritis.
The research was co-authored by Kristine Kuhn, MD, PhD, Scoville Endowed Chair and head of the CU Division of Rheumatology. Several of her division colleagues collaborated on the paper, which was published in February in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid found in many protein-rich foods, including meats, fish, dairy products, and certain seeds and nuts. It has many uses in the ...
2024-03-08
Adults who had amblyopia (‘lazy eye’) in childhood are more likely to experience hypertension, obesity, and metabolic syndrome in adulthood, as well as an increased risk of heart attack, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
In publishing the study in eClinicalMedicine, the authors stress that while they have identified a correlation, their research does not show a causal relationship between amblyopia and ill health in adulthood.
The researchers analysed data from more than 126,000 participants aged 40 to 69 years old from the UK Biobank cohort, who had undergone ocular examination.
Participants ...
2024-03-08
A new psychological treatment for children with epilepsy, developed by a UCL-led team of scientists, has been shown to reduce mental health difficulties compared to standard care, a new study finds.
Mental health problems such as worries, low mood and behaviour problems are more common in children and young people with brain conditions such as epilepsy, than in the general population – with up to 60% of those with epilepsy having associated mental health disorders and many having more than one mental ...
2024-03-08
Is obesity passed down the generations? Individuals are much more likely to be living with obesity in middle age if their parents were living with obesity, Norwegian research finds
Embargo: 2301H UK time Thursday 7 March
*This is an early press release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) Venice 12-15 May. Please credit the Congress if using this material*
Individuals have six times the odds of living with obesity in middle age if both their parents lived with obesity at that age, ...
2024-03-07
Waltham — February 21, 2024 — African American patients with carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) are less likely to receive surgical treatment, reports the March issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Our study shows significant race- and gender-related differences in treatment choices among Medicaid beneficiaries with CTS," comments ASPS Member Surgeon Rachel C. Hooper, MD, of University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. ...
2024-03-07
Waltham — February 21, 2024 — For women undergoing autologous breast reconstruction – reconstruction using the patient's own tissues, rather than implants – the risks of overall and specific complications are increased at higher body mass index (BMI) levels, reports the March issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Our study clarifies the impact of high BMI as a risk factor for adverse outcomes of autologous breast reconstruction," comments senior author Merisa Piper, MD, of ...
2024-03-07
Waltham — March 7, 2024 — In caring for transgender and gender diverse (TGD) people, psychiatrists should focus on alleviating the sequelae of gender minority stress, with the goal of promoting resilience, according to a review published in Harvard Review of Psychiatry, part of the Lippincott portfolio from Wolters Kluwer.
"We envision a role for psychiatry that goes beyond gatekeeping gender-affirming hormone therapy and surgeries," says Alex Keuroghlian, MD, MPH, Michele and Howard J. Kessler Chair and Director of the Division of Public and Community Psychiatry at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, and ...
2024-03-07
The Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation awarded researchers at the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson a $2.7 million grant for clinical testing of a novel, oxygen-enabled, implantable pouch containing pancreatic cell clusters that produce insulin.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body makes insufficient insulin, a hormone produced in the pancreas that regulates blood glucose levels. The disease is currently treated with supplemental insulin delivered by manual injection ...
2024-03-07
FRANKFURT. Bettina Stark-Watzinger, Germany’s Federal Minister of Education and Research, emphasizes: "The rapid and successful development of active substances against the SARS-CoV-2 virus illustrated the importance of good and trusting international cooperation among scientists, especially in the field of integrated structural biology. Exchanging information at an international level is crucial, especially when it comes to using specialist infrastructures. There are many advantages to us joining Instruct-ERIC, which ...
2024-03-07
The nationwide baby formula shortage two years ago forced many parents to involuntarily switch brands or types. A recent survey from researchers at the University of California, Davis, highlights how these substitutions led to undesirable effects for babies, including vomiting. The study was published in the journal Nutrients.
In an online survey of 178 parents whose infants were under six months of age during the May 2022 shortage, 81% of respondents switched formulas, with 87% of those switching because they could not find the formula ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Mutation solves a century-old mystery in meiosis


