(Press-News.org) Scientists at The Universities of Manchester and Oxford have developed an AI framework that can identify and track new and concerning COVID-19 variants and could help with other infections in the future.
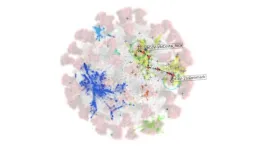
The framework combines dimension reduction techniques and a new explainable clustering algorithm called CLASSIX, developed by mathematicians at The University of Manchester. This enables the quick identification of groups of viral genomes that might present a risk in the future from huge volumes of data.
The study, presented this week in the journal PNAS, could support traditional methods of tracking viral evolution, such as phylogenetic analysis, which currently require extensive manual curation.
Roberto Cahuantzi, a researcher at The University of Manchester and first and corresponding author of the paper, said: “Since the emergence of COVID-19, we have seen multiple waves of new variants, heightened transmissibility, evasion of immune responses, and increased severity of illness.
“Scientists are now intensifying efforts to pinpoint these worrying new variants, such as alpha, delta and omicron, at the earliest stages of their emergence. If we can find a way to do this quickly and efficiently, it will enable us to be more proactive in our response, such as tailored vaccine development and may even enable us to eliminate the variants before they become established.”
Like many other RNA viruses, COVID-19 has a high mutation rate and short time between generations meaning it evolves extremely rapidly. This means identifying new strains that are likely to be problematic in the future requires considerable effort.
Currently, there are almost 16 million sequences available on the GISAID database (the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data), which provides access to genomic data of influenza viruses.
Mapping the evolution and history of all COVID-19 genomes from this data is currently done using extremely large amounts of computer and human time.
The described method allows automation of such tasks. The researchers processed 5.7 million high-coverage sequences in only one to two days on a standard modern laptop; this would not be possible for existing methods, putting identification of concerning pathogen strains in the hands of more researchers due to reduced resource needs.
Thomas House, Professor of Mathematical Sciences at The University of Manchester, said: “The unprecedented amount of genetic data generated during the pandemic demands improvements to our methods to analyse it thoroughly. The data is continuing to grow rapidly but without showing a benefit to curating this data, there is a risk that it will be removed or deleted.
“We know that human expert time is limited, so our approach should not replace the work of humans all together but work alongside them to enable the job to be done much quicker and free our experts for other vital developments.”
The proposed method works by breaking down genetic sequences of the COVID-19 virus into smaller “words” (called 3-mers) represented as numbers by counting them. Then, it groups similar sequences together based on their word patterns using machine learning techniques.
Stefan Güttel, Professor of Applied Mathematics at the University of Manchester, said: “The clustering algorithm CLASSIX we developed is much less computationally demanding than traditional methods and is fully explainable, meaning that it provides textual and visual explanations of the computed clusters.”
Roberto Cahuantzi added: “Our analysis serves as a proof of concept, demonstrating the potential use of machine learning methods as an alert tool for the early discovery of emerging major variants without relying on the need to generate phylogenies.
“Whilst phylogenetics remains the ‘gold standard’ for understanding the viral ancestry, these machine learning methods can accommodate several orders of magnitude more sequences than the current phylogenetic methods and at a low computational cost.”
END
Mathematicians use AI to identify emerging COVID-19 variants
2024-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cicadas’ unique urination unlocks new understanding of fluid dynamics
2024-03-11
Cicadas are the soundtrack of summer, but their pee is more special than their music. Rather than sprinkling droplets, they emit jets of urine from their small frames. For years, Georgia Tech researchers have wanted to understand the cicada’s unique urination.
Saad Bhamla, an assistant professor in the School of Chemical and Biochemical Engineering, and his research group hoped for an opportunity to study a cicada’s fluid excretion. However, while cicadas are easily heard, they hide in trees, making them hard to observe. As such, seeing a cicada pee is an event. Bhamla’s team had only watched the process on YouTube.
Then, ...
New research sets trap for potentially deadly sandfly
2024-03-11
Scientists have discovered the specific enzyme that a species of sandfly uses to produce a pheromone attractant, which could lead to the creation of targeted traps to control them and reduce the spread of the potentially fatal disease, Leishmaniasis.
The team from the University of Nottingham’s School of Chemistry analysed the genome of the Lutzomyia longipalpis, a species of sandfly native to Brazil and South America that can spread a disease called Leishmaniasis.
The study identified the enzyme, called a Terpene Synthase that is responsible ...
A new sensor detects harmful “forever chemicals” in drinking water
2024-03-11
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- MIT chemists have designed a sensor that detects tiny quantities of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) — chemicals found in food packaging, nonstick cookware, and many other consumer products.
These compounds, also known as “forever chemicals” because they do not break down naturally, have been linked to a variety of harmful health effects, including cancer, reproductive problems, and disruption of the immune and endocrine systems.
Using the new sensor technology, the researchers showed that they could detect PFAS levels as low as 200 parts per trillion in a water sample. The device they designed could offer a way ...
Robotic interface masters a soft touch
2024-03-11
The perception of softness can be taken for granted, but it plays a crucial role in many actions and interactions – from judging the ripeness of an avocado to conducting a medical exam, or holding the hand of a loved one. But understanding and reproducing softness perception is challenging, because it involves so many sensory and cognitive processes.
Robotics researchers have tried to address this challenge with haptic devices, but previous attempts have not distinguished between two primary elements of softness perception: cutaneous cues (sensory feedback ...
Tuberculosis bacteria also present in 90% of those with symptoms, who are not diagnosed with TB
2024-03-11
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the bacteria that causes a tuberculosis infection, is present in exhaled breath of 90% of those presenting with suspected tuberculosis. This includes those who were negative on conventional sputum testing and not diagnosed with TB. This raises the possibility that those who have tested negative may be unknowingly transmitting the infection. Researchers from the University of Cape Town and Amsterdam UMC analysed results from over 100 patients who presented themselves to clinics in South Africa. These findings are published today in PNAS.
“If ...
U of M-led study reveals shared blueprint in brain development across different functional areas
2024-03-11
In a new study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), researchers from the University of Minnesota Medical School investigated brain development to understand how different areas of the brain become specialized in handling information such as vision, sound, touch and planning.
The study found that different areas of the brain start with a similar organization rather than already being specialized in early development. This suggests that the brain might use a single shared blueprint to guide early development.
“Throughout life, the brain continually builds on the foundations set ...
Researchers solve crucial cold-induced sweetening problem in potato production
2024-03-11
Researchers have discovered a game changer for the potato industry.
According to a new study published in a leading international society journal published by the American Society of Plant Biologists, a small genetic element is the cause of a major production problem in potatoes.
“Our manuscript reveals the mystery of “cold-induced sweetening” (CIS), the most troublesome and expensive problem for the potato processing industry,” explained Jiming Jiang, Corresponding Author of “Molecular dissection of an intronic enhancer governing cold-induced expression ...
Developed by VHIO, a novel AI-based and non-invasive diagnostic tool enables accurate brain tumor diagnosis, outperforming current classification methods
2024-03-11
Developed by VHIO, a novel AI-based and non-invasive diagnostic tool enables accurate brain tumor diagnosis, outperforming current classification methods
Developed by VHIO’s Radiomics Group in close collaboration with researchers of the Neuroradiology Unit at the Bellvitge University Hospital (HUB), DISCERN is a deep learning tool that leverages information of magnetic resonance imaging and facilitates brain tumor classification to aid clinical decision making.
Currently, a definitive diagnosis often requires neurosurgical interventions that compromise the quality of life of patients.
Trained to differentiate between the three most ...
Natural history specimens have never been so accessible
2024-03-11
With the help of 16 grants from the National Science Foundation, researchers have painstakingly taken computed topography (CT) scans of more than 13,000 individual specimens to create 3D images of more than half of all the world's animal groups, including mammals, fishes, amphibians and reptiles.
The research team, made of members from The University of Texas at Arlington and 25 other institutions, are now a quarter of the way through inputting nearly 30,000 media files to the open-source repository MorphoSource. This will allow researchers ...
NRL research physicists explore fiber optic computing using distributed feedback
2024-03-11
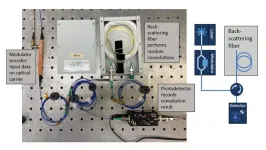
WASHINGTON – U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) researchers deliver novel contribution in fiber optics computing, Fiber Optic Computing Using Distributed Feedback paper recently published in Communications Physics journal, brings the Navy one step closer to faster, more efficient computing technologies.
Optical computing uses the properties of light, such as its speed and ability to carry large amounts of data, to process information more efficiently than traditional electronic computers.
In collaboration with Sandia National Laboratories and the University of Central Florida, NRL is aiming ...