(Press-News.org) CAMBRIDGE, MA -- More than 20 million Americans undergo colonoscopy screenings every year, and in many of those cases, doctors end up removing polyps that are 2 cm or larger and require additional care. This procedure has greatly reduced the overall incidence of colon cancer, but not without complications, as patients may experience gastrointestinal bleeding both during and after the procedure.
In hopes of preventing those complications from occurring, researchers at MIT have developed a new gel, GastroShield, that can be sprayed onto the surgical sites through an endoscope. This gel forms a tough but flexible protective layer that serves as a shield for the damaged area. The material prevents delayed bleeding and reinforces the mechanical integrity of the tissue.
“Our tissue-responsive adhesive technology is engineered to interact with the tissue via complimentary covalent and ionic interactions as well as physical interactions to provide prolonged lesion protection over days to prevent complications following polyp removal, and other wounds at risk of bleeding across the gastrointestinal tract,” says Natalie Artzi, a principal research scientist in MIT’s Institute for Medical Engineering and Science, an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, and the senior author of the paper.
In an animal study, the researchers showed that the GastroShield application integrates seamlessly with current endoscopic procedures, and provides wound protection for three to seven days where it helps tissue to heal following surgery. Artzi and other members of the research team have started a company called BioDevek that now plans to further develop the material for use in humans.
Gonzalo Muñoz Taboada, CEO of BioDevek, and Daniel Dahis, lead scientist at BioDevek, are the lead authors of the study, which appears in the journal Advanced Materials. Elazer Edelman, the Edward J. Poitras Professor in Medical Engineering and Science at MIT and the director of IMES, and Pere Dosta, a former postdoc in Artzi’s lab, are also authors of the paper.
Adhesive gels
Routine colon cancer screenings often reveal small precancerous polyps, which can be removed before they become cancerous. This is usually done using an endoscope. If any bleeding occurs during the polyp removal, doctors can cauterize the wound to seal it, but this method creates a scar that may delay the healing, and result in additional complications.
Additionally, in some patients, bleeding doesn’t occur until a few days after the procedure. This can be dangerous and may require patients to return to the hospital for additional treatment. Other patients may develop small tears that lead the intestinal contents to leak into the abdomen, which can lead to severe infection and requires emergency care.
When tissue reinforcement is required, doctors often insert metal clips to hold tissue together, but these can’t be used with larger polyps and aren’t always effective. Efforts to develop a gel that could seal the surgical wounds have not been successful, mainly because the materials could not adhere to the surgical site for more than 24 hours.
The MIT team tested dozens of combinations of materials that they thought could have the right properties for this use. They wanted to find formulations that would display a low enough viscosity to be easily delivered and sprayed through a nozzle at the end of a catheter that fits inside commercial endoscopes. Simultaneously, upon tissue contact, this formulation should instantly form a tough gel that adheres strongly to the tissue. They also wanted the gel to be flexible enough that it could withstand the forces generated by the peristaltic movements of the digestive tract and the food flowing by.
The researchers came up with a winning combination that includes a polymer called pluronic, which is a type of block copolymer that can self-assemble into spheres called micelles. The ends of these polymers contain multiple amine groups, which end up on the surface of the micelles. The second component of the gel is oxidized dextran, a polysaccharide that can form strong but reversible bonds with the amine groups of the pluronic micelles.
When sprayed, these materials instantly react with each other and with the lining of the gastrointestinal tract, forming a solid gel in less than five seconds. The micelles that make up the gel are “self-healing” and can absorb forces that they encounter from peristaltic movements and food moving along the digestive tract, by temporarily breaking apart and then re-assembling.
“To obtain a material that adheres to the design criteria and can be delivered through existing colonoscopes, we screened through libraries of materials to understand how different parameters affect gelation, adhesion, retention, and compatibility,” Artzi says.
A protective layer
The gel can also withstand the low pH and enzymatic activity in the digestive tract, and protect tissue from that harsh environment while it heals itself, underscoring its potential for use in other gastrointestinal wounds at high risk of bleeding, such as stomach ulcers, which affect more than 4 million Americans every year.
In tests in animals, the researchers found that every animal treated with the new gel showed rapid sealing, and there were no perforations, leakages, or bleeding in the week following the treatment. The material lasted for about five days, after which it was sloughed off along with the top layer of tissue as the surgical wounds healed.
The researchers also performed several biocompatibility studies and found that the gel did not cause any adverse effects.
“A key feature of this new technology is our aim to make it translational. GastroShield was designed to be stored in liquid form in a ready-to-use kit. Additionally, it doesn’t require any activation, light, or trigger solution to form the gel, aiming to make endoscopic use easy and fast,” says Muñoz, who is currently leading the translational effort for GastroShield.
BioDevek is now working on further developing the material for possible use in patients. In addition to its potential use in colonoscopies, this gel could also be useful for treating stomach ulcers and inflammatory conditions such as Crohn’s disease, or for delivering cancer drugs, Artzi says.
###
The research was funded, in part, by the National Science Foundation.
END
New study identifies ten key components that will promote the development and implementation of sustainable, equitable, climate-smart ocean planning initiatives around the globe.
In a paper published March 12 in npj Ocean Sustainability, the researchers outlined guidelines to support marine managers and planners on how to develop climate-smart ocean plans and put them into action. Led by Catarina Frazão Santos, researcher and professor at the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon (Ciências ULisboa) and honorary research associate at the University of Oxford, the team ...
Irvine, Calif., March 12, 2024 — Scientists know relatively little about particles released into the air when a vehicle driver brakes, though evidence suggests those particles may be more harmful to health than particles exiting the tailpipe.
In a new study in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, University of California, Irvine researchers show how most of these particles emitted during light braking carry an electric charge – something that could potentially be ...
Consortium led by the University is to receive almost £11 million to open doctoral training centre
Will focus on use of biomass to replace fossil fuels and removal of CO2
“…part of the UK’s biggest-ever investment in engineering and physical sciences doctoral skills”.
Aston University is to train the next generation of scientists tasked to remove greenhouse gases from the environment.
A consortium led by the University is to receive almost £11 million to open a doctoral ...
Giraffes are a beautiful and powerful example of what adaptive evolution can achieve. However, in recent years they have attained notoriety for a completely different reason: it has been suggested that instead of one giraffe species, there might be no fewer than four different species. Such dramatic taxonomic reappraisals in highly conspicuous and well-known “flagship” taxa are very unusual. The suggestion caused some uproar in the scientific community and received a lot of media attention. Much is at stake, because the way that most nature conservation works is focused on species, meaning that each species must receive its own dedicated conservation action plan and must ...
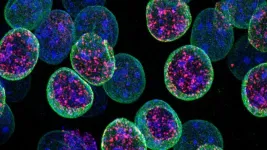
Epigenetic processes allow different cell types to emerge from a single genome. Throughout development, cells differentiate and acquire distinct characteristics by expressing the same genome in different ways. However, a less-known aspect of this process is how cells maintain their unique identities over time. A study led by the Transcriptional and Epigenetic Mechanisms of Neuronal Plasticity laboratory, headed by Angel Barco at the Institute for Neurosciences, a joint center of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) and the Miguel Hernández University (UMH) of Elche, has determined that the protein Kdm1a plays ...
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has awarded a prestigious fellowship aimed at encouraging women to study nuclear-related subjects to a University of Texas at Arlington graduate student researching isotope hydrology.
Suprina Shrestha, a master’s student in earth and environmental sciences, received a Marie Sklodowska-Curie Fellowship (MSCF) from the IAEA. She studies tracer hydrology, which is the use of natural and artificial tracers to examine hydrological processes, under the mentorship of Ricardo Sanchez-Murillo, associate professor of ...
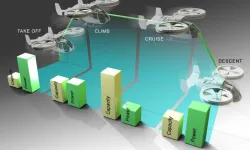
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are taking cleaner transportation to the skies by creating and evaluating new batteries for airborne electric vehicles that take off and land vertically.
These aircraft, commonly called eVTOLs, range from delivery drones to urban air taxis. They are designed to rise into the air like a helicopter and fly using wing-borne lift like an airplane. Compared with helicopters, eVTOLs generally use more rotors spinning at a lower speed, making them both safer and quieter.
The ...
Announced today, a new Centre for Doctoral Training (CDT) has been funded by a grant of over £9 million from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) to help train the next, diverse generation of research leaders in data visualization.
A collaboration between City, University of London and the University of Warwick, the EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Diversity in Data Visualization (DIVERSE CDT) will train 60 PhD students, in cohorts of 12 students, beginning in October 2025. The set-up phase will begin in July 2024.
The funding announcement is part of a wider UK Research & Innovation (UKRI) announcement of ...
WHAT:
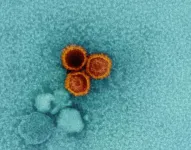
Studies of interactions between two lab-generated monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and an essential Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) protein have uncovered targets that could be exploited in designing treatments and vaccines for this extremely common virus. The research was led by Jeffrey I. Cohen, M.D., and colleagues from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. Study findings were published in the journal Immunity.
Approximately 95% of the world’s population is infected with EBV, which remains in the body permanently, typically ...
DURHAM, N.C. -- It might look like a roll of chicken wire, but this tiny cylinder of carbon atoms -- too small to see with the naked eye -- could one day be used for making electronic devices ranging from night vision goggles and motion detectors to more efficient solar cells, thanks to techniques developed by researchers at Duke University.
First discovered in the early 1990s, carbon nanotubes are made from single sheets of carbon atoms rolled up like a straw.
Carbon isn’t exactly a newfangled material. All life on Earth is based on carbon. ...