(Press-News.org) By Shawn Ballard
Nanomaterials already play a vital role in enhancing the performance of everyday products from electronics to cosmetics to food packaging. But, beyond their usefulness in making images sharper and products more stable, researchers in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis have shown nanoparticles may also be an essential tool in advancing our understanding of the brain and opening new avenues for treating neurological disorders such as Parkinson's disease and epilepsy.
Srikanth Singamaneni, the Lilyan & E. Lisle Hughes Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering & Materials Science, and Barani Raman, professor of biomedical engineering, received a three-year, $570,746 grant from the National Science Foundation to support their work to understand the fundamental mechanisms that underpin interactions between nerve cells, or neurons, and nanoparticles, which can be used to both sense and stimulate neurons.
“There’s a lot of excitement about harnessing the functional properties of nanomaterials – whether that’s magnetic nanoparticles or particles that can absorb light and turn it into heat or many other functions,” Singamaneni said. “Functional nanomaterials could be used for nongenetic modulation of neural activity and for solving some of the biggest challenges associated with diagnosing and treating neurodegenerative diseases.
“Nanoparticles can serve as a valuable toolkit,” he added. “But for that to happen, the fundamental roadblock is we still don’t know how nanoparticles interact with neurons, the fundamental building blocks that form the brain and neural circuits.”
Singamaneni and Raman, in collaboration with researchers in McKelvey Engineering and WashU’s School of Medicine, have already shown that nanoparticles can be used to boost locusts’ sense of smell by amplifying neuron signals in an insect’s brain to achieve better chemical sensing performance. With this new study, they aim to provide the physical underpinnings, or basic ground rules, for nano-neuro interactions using 2D neural cultures as a model system.
“Once we have the ground rules and understand how neurons and nanoparticles bind, then there are lots of applications,” Raman said. “For example, we could use nanoparticles for targeting select types of neurons, such as the dopaminergic neurons that are progressively lost during Parkinson’s disease. Nanoparticles can be potentially used to stimulate or control affected types of sub-neurons in the brain with fine temporal precision, then they can be safely flushed out.”
To achieve this level of fine control, Singamaneni and Raman will develop a detailed understanding of how nanoparticles mechanically bind to neurons, which they already know depends on the maturity of the neurons from their previous work. They also will explore the effects of nanoparticle binding on the electrical properties and activity of neurons, including how they process information. Both will be critical considerations to design nanomaterials to support neuroscientific discovery and minimally invasive technologies to treat neuronal disorders.
END
Demystifying nano-neuro interactions
2024-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Common viruses trigger most cases of intussusception in children
2024-03-14
Viral infections trigger more cases of intussusception, the common cause of bowel blockages in young children, than previously thought, according to a new study.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and published in Clinical Infectious Diseases, found during the COVID-19 lockdowns hospital admissions for intussusception, a medical emergency involving obstruction of the intestine, among young children significantly decreased.
For the study, 12 years of data was analysed across Victoria, NSW and Queensland. ...
New multimillion dollar research facility set to unlock secrets of quantum materials
2024-03-14
Material scientists from the University of British Columbia Stewart Blusson Quantum Matter Institute (Blusson QMI) will lead the development of a multi-million world-class crystal growth facility thanks to $5.8 million in investments by the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI) and the B.C. Knowledge Development Fund (BCKDF) announced today.
Blusson QMI Scientific Director Andrea Damascelli said the investment will strengthen Canada’s position as a leader in quantum research and technology.
“The investment enables the establishment of state-of-the-art research infrastructure that is unique in Canada and will deliver exceptional impact for quantum material design, technology ...
Improving education and human security for vulnerable refugee children
2024-03-14
‘Access to education’ is recognized as a fundamental human right and is listed as one of the United Nations’ sustainable development goals to achieve by 2030. Quality education unlocks opportunities and gives individuals the freedom to make livelihood choices and shape their own destinies. However, an increasing number of refugee children are deprived of this fundamental right. According to the UNHCR, between 2010 and 2022, the number of child refugees doubled from 20.6 million to about 43.3 million.
An overwhelming majority of these refugees are displaced to neighboring countries that are short on resources and lack adequate educational infrastructure ...
The timeless wisdom of Sanpo-yoshi for present day businesses
2024-03-14
There is a growing emphasis for corporations to consider their impact on the environment, society, and its stakeholders. Broadly falling under environmental, social and governance or ESG, this involves practices such as using sustainably sourced materials, reducing carbon emissions, improving labor practices, fostering positive community relations, and promoting ethical corporate behavior, including efforts against anti-competitive practices and corruption.
The first mention of ESG appears in a 2004 UN report ...
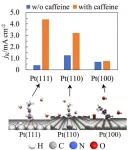
Supercharging fuel cells with caffeine
2024-03-14
With global goals set on transitioning away from fossil fuels, fuel cells stand out as a promising carbon-free energy source. Comprising an anode and a cathode separated by an electrolyte, fuel cells convert the chemical energy of fuel directly into electricity. The anode receives the fuel, while an oxidant, typically oxygen from the air, is introduced at the cathode. In a hydrogen fuel cell, hydrogen undergoes oxidation at the anode, producing hydrogen ions and electrons. The ions move through the electrolyte to the cathode, and electrons flow through an external circuit, generating electricity. At the cathode, oxygen combines with the hydrogen ions ...
Poor neighborhoods linked to elevated dementia risk and faster brain aging
2024-03-14
DURHAM, NC – Living in a poorer neighborhood is linked to accelerated brain aging and increased dementia risk early in life, regardless of income level or education, a Duke University-led study finds.
The study, which appears March 14 in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association, suggests that targeting disadvantaged neighborhoods for dementia prevention programs and encouraging clinicians to consider a patient’s address could help lower dementia risk.
“If you want to prevent dementia, and you’re not asking someone ...
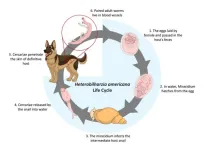
Dog-killing flatworm discovered in Southern California
2024-03-14
UC Riverside scientists confirm, for the first time, that a potentially fatal dog parasite is present in a portion of the Colorado River that runs through California.
The parasite, Heterobilharzia americana, is a flatworm commonly referred to as liver fluke. Previously found almost exclusively in Texas and other Gulf Coast states, it has never been reported this far west. The worm can cause canine schistosomiasis, an illness that impacts the liver and intestines of dogs.
“Dogs can die from this infection, so we are hoping ...
It’s hearty, it’s meaty, it’s mold
2024-03-14
With animal-free dairy products and convincing vegetarian meat substitutes already on the market, it’s easy to see how biotechnology can change the food industry. Advances in genetic engineering are allowing us to harness microorganisms to produce cruelty-free products that are healthy for consumers and healthier for the environment.
One of the most promising sources of innovative foods is fungi – a diverse kingdom of organisms that naturally produce a huge range of tasty and nutritious ...
First gene therapy tests in whole human liver
2024-03-14
In a worldwide first-of-its-kind study published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications this week, a team of scientists from Children’s Medical Research Institute (CMRI) tested novel gene therapies in a whole human liver, with the goal of developing more effective treatments for life-threatening inherited diseases.
Gene therapy is a revolutionary approach to treating serious genetic diseases that most commonly involves replacing or repairing a faulty gene. The most efficient delivery systems today are those based on a harmless virus named adeno-associated ...
Researchers target cancer’s ability to survive at low oxygen levels
2024-03-14
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have shed light on how cancer cells survive in the first few hours after being cut off from a supply of oxygen.
Published today in The EMBO Journal, this finding could one day help to prevent cancer from becoming resistant to therapy.
A major use of oxygen by cells is for energy production. When oxygen supplies are low, most cells can survive because they adapt, by changing which proteins they make, to produce energy through different processes than in normal oxygen levels. This is coordinated by a protein called HIF1α, which turns on the activity of genes.
Although HIF1α ...