Pain exposure and brain connectivity in preterm infants
JAMA Network Open
2024-03-15
(Press-News.org)
About The Study: Greater exposure to early-life pain was associated with altered maturation of neonatal structural connectivity, particularly in female infants in this study of 150 very preterm infants. Alterations in structural connectivity were associated with neurodevelopmental outcomes, with potential regional specificities.
Authors: Steven P. Miller, M.D.C.M., M.A.S., of the BC Children’s Hospital Research Institute and University of British Columbia in Vancouver, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.2551)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.2551?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=031524
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-15
What would happen if the existing disparities in physical activity levels between youth of lower and higher socioeconomic statuses were eliminated? Previous studies have shown that those between 6-17 years of age in lower socioeconomic groups get on average 10-15% less physical activity than those of higher socioeconomic groups. A new study published in the journal JAMA Health Forum on Mar. 15 shows that eliminating such disparities could end up saving society over $15 billion in direct medical costs and productivity losses. This in turn could end up benefiting all taxpayers, anyone who pays insurance ...
2024-03-15
UBC researchers believe a group of killer whales observed hunting marine mammals including sperm whales, as well as a sea turtle, in the open ocean off California and Oregon could be a new population.
Based on available evidence, the researchers posit in a new study published in Aquatic Mammals that the 49 orcas could belong to a subpopulation of transient killer whales or a unique oceanic population found in waters off the coast of California and Oregon.
“The open ocean is the largest habitat on our planet and observations of killer whales in ...
2024-03-15
CHICAGO: The March issue of the Journal of the American College of Surgeons (JACS), which includes research presented at the Southern Surgical Association 135th Annual Meeting, features new research on topics ranging from colorectal cancer and social vulnerability to operating room supply costs, the rise in school shootings since 1970, and the impact of permitless open carry laws on suicide rates, among others.
Read highlights from the issue below. The full issue is available on the JACS website.
Social Vulnerability Index and Survivorship after Colorectal Cancer Resection
Researchers analyzed whether data from the Social Vulnerability Index (SVI) can help predict complications ...
2024-03-15
The Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research (MPIDR) has researched parents' support behavior in relation to school grades. The study shows that low-income families support their children equally regardless of grades, while parents from higher income groups tend to give more support to children with lower grades. It also raises the question of whether these patterns contribute to low social mobility, as parents of high-achieving children from lower social classes do not have the same resources and strategies at their disposal as parents of low-achieving ...
2024-03-15
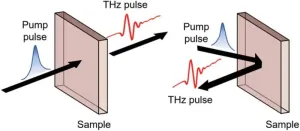
Researchers at the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, have published a review article on the terahertz (THz) radiation in quantum materials. The work, led by Surui Yang, Liang Cheng, and Jingbo Qi, offers a comprehensive exploration of the time-dependent photocurrents, shedding light on the up-to-date understanding of the physical processes involved.
The investigation, conducted at the forefront of ultrafast science, delves into the potential of THz radiation in unraveling the fundamental physics of quantum materials, with implications for the development of novel technologies. The review focuses on recent advancements in revealing the unique properties of quantum materials ...
2024-03-15
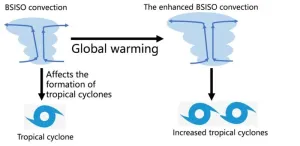
Global warming, the long-term warming of Earth’s overall temperature, has greatly accelerated in the last 100 years due to human factors such as the burning of fossil fuels. Along with this trend, certain atmospheric phenomena have also changed, such as typhoons and other types of disastrous weather becoming more intense than before and bringing about more serious impacts. The Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation (BSISO), one of the most pronounced subseasonal variabilities in the tropics during boreal summer, provides an important basis for subseasonal forecasting. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the BSISO and its changes under global warming.
Recently, ...
2024-03-15
UVA Health researchers have discovered a potential way to predict which patients with severe COVID-19 are likely to recover well and which are likely to suffer “long-haul” lung problems. That finding could help doctors better personalize treatments for individual patients.
UVA’s new research also alleviates concerns that severe COVID-19 could trigger relentless, ongoing lung scarring akin to the chronic lung disease known as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, the researchers report. That type of continuing lung damage would mean that patients’ ability to breathe would continue to worsen over time.
“We are excited ...
2024-03-15
A new study from researchers at the Johns Hopkins Center for Gun Violence Solutions and Vanderbilt University found that an average of 1,769 people were injured annually in police shootings from 2015 to 2020, 55 percent of them or 979 people, fatally. The study covered a total of 10,308 incidents involving shootings by police. The Center is based at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The majority of victims in shootings by police—84 percent overall—were reported as armed with a firearm or other weapon, such as a knife or vehicle, during ...
2024-03-15
The origin of COVID-19 is highly debated – most studies have focused on a zoonotic origin, but research from the journal Risk Analysis, examined the likelihood of an unnatural origin (i.e. from a laboratory.)
The results indicate a greater likelihood of an unnatural than natural origin of the virus. The researchers used an established risk analysis tool for differentiating natural and unnatural epidemics, the modified Grunow-Finke assessment tool (mGFT) to study the origin of COVID-19. This risk assessment cannot prove the specific origin of COVID-19 but shows that the possibility of a laboratory origin ...
2024-03-15
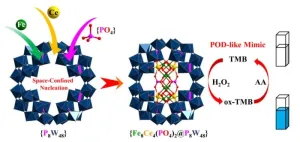
By design, synthetic molecules typically have specific jobs to prevent or accelerate reactions between other molecules. To help control more complicated reactions, researchers may harness spare space in one molecule to synthesize another chemical structure. The host-guest assembly can better induce the specific desired reaction than either component individually — if the scientists designing the assembly get it right.
A multi-institution team based in China has reported a novel cluster — the guest — that nucleated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Pain exposure and brain connectivity in preterm infants
JAMA Network Open