(Press-News.org) New research published in Nature Human Behavior suggests that text nudges encouraging people to get the COVID-19 vaccine, which had proven effective in prior real-world field tests, are also effective at prompting people to get a booster.
The key in both cases is to include in the text a sense of ownership in the dose awaiting them.
The paper, led by Hengchen Dai, an associate professor of management and organizations and behavioral decision making at the UCLA Anderson School of Management, and Silvia Saccardo, an associate professor of social and decision sciences at Carnegie Mellon University, draws on previous research published in Nature that examined the effectiveness of different types of text messages encouraging patients to get a COVID-19 vaccine. As described in UCLA Anderson Review, that research revealed that a text message implying a hint of ownership, with a note to “Claim your dose by making a vaccination appointment,” was more effective than a text that merely included a link to an online vaccination scheduling tool.
The new paper focuses on a potential schism between what people in a hypothetical scenario say they will do, and what they actually do. The researchers found that adding that sense of ownership to the booster dose was more effective than research dependent on hypothetical scenarios or expert predictions.
“Given the importance of reproducibility to the field of behavioral science, numerous studies have focused on replication attempts of laboratory findings, but replications in the field have been infrequent,” Dai said. “We take a stride in this direction by assessing the transferability of insights gained in one field context to another, and from hypothetical and prediction surveys to field settings.”
The researchers texted more than 300,000 patients in the UCLA Health system with one of 14 messages that prior field tests, lab research or expert surveys suggested might encourage recipients to get the booster shot. A control group did not receive a text message. They found that adding a note to play up the psychological sense of ownership (“claim your dose”) turned out to be more effective than if the reminder simply told patients the booster was available, as shown in Dai and Saccardo’s previous field test. All other nudges added on top of a text reminder were ineffective in moving the needle.
Some messages leveraged the consistency principle in the form of “You have completed a COVID-19 vaccine primary series. Great job protecting your health.” One message was worded as an appeal explaining that the booster was different than the original vaccine and specifically designed to combat the most recent strain of COVID-19. Another cited the ongoing severity of the virus. Other messages reminded people that they could get the flu shot at the same time as the COVID-19 booster — a strategy used by pharmacies like CVS and Walgreens. The messages with additional content performed no better than simple text reminders.
Although the researchers note that their findings are limited to the field of COVID-19 booster vaccinations, they point out that their work raises questions about the efficacy of research built on hypotheticals or theoretical assumptions.
“While hypothetical surveys and self-reports are undoubtedly valuable for providing foundational evidence on the mechanisms of human behavior, our findings suggest that they may not always translate to complex real-world situations where various factors can affect behavior,” Saccardo said. “It is critical to accumulate knowledge about the impact of interventions in the real world.”
Study co-authors are Dr. Maria Han, Sitaram Vangala, Juyea Hoo and Dr. Jeffrey Fujimoto of the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
About UCLA Anderson School of Management
UCLA Anderson School of Management is a world-renowned learning and research institution. As part of the nation’s No. 1 public university, its mission is to advance management thinking and prepare transformative leaders to make positive business and societal impact. Located in Los Angeles, one of the nation’s most diverse and dynamic cities and the creative capital of the world, UCLA Anderson places more MBAs on the West Coast than any other business school, and its graduates also bring an innovative and inclusive West Coast sensibility to leading organizations across the U.S. and the world. Each year, UCLA Anderson’s MBA, Fully Employed MBA, Executive MBA, UCLA-NUS Executive MBA, Master of Financial Engineering, Master of Science in Business Analytics and doctoral programs educate more than 2,000 students, while the Executive Education program trains an additional 1,800 professionals. This next generation of transformative leaders will help shape the future of both business and society.
END
Text nudges can increase uptake of COVID-19 boosters– if they play up a sense of ownership of the vaccine
By contrast, encouragement based on lab findings and experts’ insights proved less effective at convincing people to get the booster
2024-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new study shows how neurochemicals affect fMRI readings
2024-03-18
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – The brain is an incredibly complex and active organ that uses electricity and chemicals to transmit and receive signals between its sub-regions.
Researchers have explored various technologies to directly or indirectly measure these signals to learn more about the brain. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), for example, allows them to detect brain activity via changes related to blood flow.
Yen-Yu Ian Shih, PhD, professor of neurology and associate director of UNC’s Biomedical Research Imaging Center, and his fellow lab members have long been curious about how neurochemicals in the brain regulate and influence neural activity, ...
Digital reminders for flu vaccination improves turnout, but not clinical outcomes in older adults
2024-03-18
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 18 March 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. Digital reminders for flu vaccination improves ...
Avatar will not lie... or will it? Scientists investigate how often we change our minds in virtual environments
2024-03-18
How confident are you in your judgments and how well can you defend your opinions? Chances are that they will change under the influence of a group of avatars in a virtual environment. Scientists from SWPS University investigated the human tendency to be influenced by the opinions of others, including virtual characters.
We usually conform to the views of others for two reasons. First, we succumb to group pressure and want to gain social acceptance. Second, we lack sufficient knowledge and perceive the group as a source of a better interpretation of the current situation, describes Dr. Konrad Bocian from the Institute of Psychology at SWPS University.
So far, only a few studies ...
8-hour time-restricted eating linked to a 91% higher risk of cardiovascular death
2024-03-18
Research Highlights:
A study of over 20,000 adults found that those who followed an 8-hour time-restricted eating schedule, a type of intermittent fasting, had a 91% higher risk of death from cardiovascular disease.
People with heart disease or cancer also had an increased risk of cardiovascular death.
Compared with a standard schedule of eating across 12-16 hours per day, limiting food intake to less than 8 hours per day was not associated with living longer.
Embargoed until 3 p.m. CT/4 p.m. ET, Monday, March 18, 2024
CHICAGO, March 18, 2024 — An analysis ...
Alternative tidal wetlands in plain sight overlooked Blue Carbon superstars
2024-03-18
Blue Carbon projects are expanding globally; however, demand for credits outweighs the available credits for purchase.
Currently, only three types of wetlands are considered Blue Carbon ecosystems: mangroves, saltmarsh and seagrass.
However, other tidal wetlands also comply with the characteristics of what is considered Blue Carbon, such as tidal freshwater wetlands, transitional forests and brackish marshes.
In a new study, scientists from Australia, Indonesia, Singapore, South Africa, Vietnam, the US and Mexico have highlighted the increasing opportunities for Blue Carbon projects for the conservation, restoration and improved management of highly threatened ...
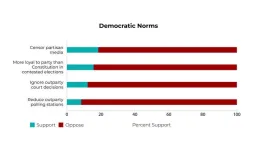
The majority of Americans do not support anti-democratic behavior, even when elected officials do
2024-03-18
EMBARGOED UNTIL MARCH 18 AT 3 P.M. EST
Recently, fundamental tenets of democracy have come under threat, from attempts to overturn the 2020 election to mass closures of polling places.
A new study from the Polarization Research Lab, a collaboration among researchers at the Annenberg School for Communication at the University of Pennsylvania, Dartmouth College, and Stanford University, has found that despite this surge in anti-democratic behavior by U.S. politicians, the majority of Americans oppose anti-democratic attitudes and reject partisan violence.
From September 2022 to October 2023, a period which included the 2022 midterm ...
Genes identified that allow bacteria to thrive despite toxic heavy metal in soil
2024-03-18
VANCOUVER, Wash. -- Some soil bacteria can acquire sets of genes that enable them to pump the heavy metal nickel out of their systems, a study has found. This enables the bacteria to not only thrive in otherwise toxic soils but help plants grow there as well.
A Washington State University-led research team pinpointed a set of genes in wild soil bacteria that allows them to do this in serpentine soils which have naturally high concentrations of toxic nickel. The genetic discovery, detailed in the journal Proceedings of the National Academies ...
Scientists’ discovery could reduce dependence on animals for vital anti-blood clot drug
2024-03-18
Heparin, the world’s most widely used blood thinner, is used during procedures ranging from kidney dialysis to open heart surgery. Currently, heparin is derived from pig intestines, but scientists at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have discovered how to make it in the lab. They have also developed a path to a biomanufacturing process that could potentially revolutionize how the world gets its supply of this crucial medicine.
“In recent years, with disease and contamination issues disrupting the global supply chain of pig heparin and potentially putting millions of patients at risk, it’s clear we need to diversify ...
Artificial streams reveal how drought shapes California’s alpine ecosystems
2024-03-18
Berkeley — A network of artificial streams is teaching scientists how California’s mountain waterways — and the ecosystems that depend on them — may be impacted by a warmer, drier climate.
Over the next century, climate change is projected to bring less snowfall to the Sierra Nevada. Smaller snowpacks, paired with warmer conditions, will shift the annual snowmelt earlier into the year, leaving less water to feed streams and rivers during the hot summer months. By 2100, mountain streams are predicted to reach their annual base, or “low-flow,” conditions an average of six ...
Not in my backyard? Wind turbines have little effect on US property values
2024-03-18
“The impact of wind turbines on house prices is much smaller than generally feared: In the U.S., it’s about one percent for a house that has at least one wind turbine in a 10 km radius”, explains Maximilian Auffhammer, a Professor in the Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics at the University of California, Berkeley and co-author of the study. “And what really surprised me is that the house value bounces back to the original price over the years.” The study authors also found that there was no longer any ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
[Press-News.org] Text nudges can increase uptake of COVID-19 boosters– if they play up a sense of ownership of the vaccineBy contrast, encouragement based on lab findings and experts’ insights proved less effective at convincing people to get the booster