Scientists uncover a causal relationship between remote extreme heat and the Canadian wildfires in 2023
2024-03-20
(Press-News.org)
Wildfires are events that can have significant impacts on ecosystems and human society. In the context of global warming, there has been a notable surge in the frequency and ferocity of wildfires in the Northern Hemisphere over recent years. In 2023, Canada experienced an unprecedented wildfire event, with CO2 emissions increasing by 527.1% over the average of 2001–2022 during the months of May–August. The burned area was more than 6–7 times larger than in a normal year. Notably, both Canada and more than 15 states in the northeastern United States grappled with severe disruption to air quality as a result of this cataclysmic event.
The research group of Prof. Xu YUE from Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, China, investigated the meteorological factors that ignited this catastrophic event, while also deliberating on prospective triggers and ramifications of wildfires in North America. The results have recently been published in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters.
According to this research, a noteworthy correlation between the occurrence of severe wildfires and anomalies in maximum temperatures was revealed.
"During periods of high wildfire emissions, maximum temperatures were significantly higher than in periods with low emissions. Conversely, the average precipitation during periods of high wildfire emissions did not exhibit a statistically significant departure from that during periods of low wildfire emissions. Additionally, the phenomenon of ‘rain and wildfires at the same time’ was observed", explains Prof. YUE.
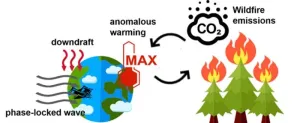
Further investigations identified notable high-temperature anomalies within the primary burn area during the 2023 Canadian wildfire eruption period. This occurrence coincided with the enduring presence of anomalous high-pressure systems over the region attributable to Rossby wave dispersion. The persistent downdraft resulted in a sustained elevation of near-surface temperatures, thereby fostering conditions conducive to wildfire (see figure below). A similar “phase-locked” phenomenon of persistent geopotential height anomalies also emerged as the principal catalyst behind the unprecedented heatwave event in North America during 2021.
"Owing to the distinctive topographical features of the Rocky Mountains, phase-locked related heat is more prone to occur in west-central Canada, consequently heightening the risk of intensified wildfire events", adds Prof. YUE.
Recurrent and severe wildfires in this area could exacerbate the warming trend through the CO2 emissions generated. Concurrently, the amplification of global warming may increase the availability of fuel in the future. Hence, greater efforts will be needed to maintain public health and ecosystem functions within affected regions.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-20
NEW ORLEANS, March 20, 2024 — From cell phones to watches to electric cars, lithium-ion rechargeable batteries power a plethora of devices. The increased use of this technology means more lithium could find its way into the environment as consumers discard electronic products. Now, researchers describe how lithium can accumulate in a common Southern crustacean: the crawfish. As the season for catching and eating mudbugs comes into full swing, the researchers’ findings highlight the potential implications for public health and the environment.
The researchers will present ...
2024-03-20
Helping teenagers to understand what is going on inside their own brains is the key to helping them mature into resilient and independent adults, research suggests.
Sheila Redfern, a consultant clinical child and adolescent psychologist, proposes that rather than focusing on stamping out difficult behaviours, parents should teach teenagers to manage their feelings and relationships in safe ways.
Dr. Redfern says that although parenting teenagers is uniquely challenging, with concerns about social media use, self-harm, ...
2024-03-20
NYU Langone Health has received a $15 million gift from innovators and philanthropists Wayne G. Holman, MD, and Wendy Holman to further elevate the world-class treatment and study of endocrine disorders in the newly named and endowed Holman Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.
“Wayne and Wendy’s generosity in this important area of medicine will help NYU Langone further enhance our exceptional research, education and clinical care within the Holman Division of Endocrinology, ...
2024-03-20
SPOKANE, Wash.—Getting dementia diagnosed can be a long and difficult process for anyone, but some may face additional challenges based on race or ethnicity and where they live, according to a study led by Washington State University researchers.
The study of nearly 95,000 Washington state residents found that people living outside of urban areas as well as Native American and Hispanic people face longer travel distances to be seen by neurologists. The researchers said these disparities could be contributing to delayed diagnoses, which can result in higher costs of care, ...
2024-03-20
Paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/144cIFPtY2VSaqV8AfFHy_hh6xlDcLShy?usp=sharing
The public are being encouraged to eat more wild fish, such as mackerel, anchovies and herring, which are often used within farmed salmon feeds. These oily fish contain essential nutrients including calcium, B12 and omega-3 but some are lost from our diets when we just eat the salmon fillet.
Scientists found that farmed salmon production leads to an overall loss of essential dietary nutrients. They say that eating more wild ‘feed’ species directly could benefit our health while reducing aquaculture demand for finite marine resources.
Researchers analysed ...
2024-03-20
Researchers from the Oxford Martin Programme on Ethical Web and Data Architectures (EWADA), University of Oxford, have called for a more considered approach when embedding ethical principles in the development and governance of AI for children.
In a perspective paper published today in Nature Machine Intelligence, the authors highlight that although there is a growing consensus around what high-level AI ethical principles should look like, too little is known about how to effectively apply them in principle for children. The study mapped the global landscape of existing ethics guidelines for AI and identified four ...
2024-03-20
NEW ORLEANS, March 20, 2024 — The 2023 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was focused on quantum dots — objects so tiny, they’re controlled by the strange and complex rules of quantum physics. Many quantum dots used in electronics are made from toxic substances, but their nontoxic counterparts are now being developed and explored for uses in medicine and in the environment. One team of researchers is focusing on carbon- and sulfur-based quantum dots, using them to create safer invisible inks and to help decontaminate water supplies.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the ...
2024-03-20
NEW ORLEANS, March 20, 2024 — From abstract-looking cloud formations to roars of snow machines on ski slopes, the transformation of liquid water into solid ice touches many facets of life. Water’s freezing point is generally accepted to be 32 degrees Fahrenheit. But that is due to ice nucleation — impurities in everyday water raise its freezing point to this temperature. Now, researchers unveil a theoretical model that shows how specific structural details on surfaces can influence water’s freezing point.
The researchers will present their results at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2024 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually ...
2024-03-20
NEW ORLEANS, March 20, 2024 — Accidents happen every day, and if you drop your smartwatch, or it gets hit really hard, the device probably won’t work anymore. But now, researchers report on a soft, flexible material with “adaptive durability,” meaning it gets stronger when hit or stretched. The material also conducts electricity, making it ideal for the next generation of wearables or personalized medical sensors.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring ...
2024-03-20
SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can damage the heart even without directly infecting the heart tissue, a National Institutes of Health-supported study has found. The research, published in the journal Circulation, specifically looked at damage to the hearts of people with SARS-CoV2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a serious lung condition that can be fatal. But researchers said the findings could have relevance to organs beyond the heart and also to viruses other than SARS-CoV-2.
Scientists have long known that COVID-19 increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and Long COVID, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists uncover a causal relationship between remote extreme heat and the Canadian wildfires in 2023