(Press-News.org)
A cross-disciplinary University of Waterloo team has developed a new contact lens material that could act as a bandage for corneal wounds while releasing drugs in a controlled manner to help the eye heal faster.
Typically, corneal abrasion patients spend seven to 10 days wearing a clear, oxygen-permeable bandage contact lens, often instilled with eyedrops containing antibiotics. However, the one-time antibiotic application makes it difficult to ensure enough drugs stay on the eye for sustained treatment.
“It’s a targeted-release drug delivery system that is responsive to the body,” said Dr. Lyndon Jones, a professor at Waterloo’s School of Optometry & Vision Science and director of the Centre for Ocular Research & Education (CORE). “The more injured you are, the more drug gets delivered, which is unique and potentially a game changer.”
Jones knew there was a market for a drug-delivering bandage contact lens that could simultaneously treat the eye and allow it to heal. The question was how to develop it.
As the University of Waterloo has several researchers and entrepreneurs building technology to disrupt the boundaries of health, Jones was able to team up with Dr. Susmita Bose (PhD’23), Dr. Chau-Minh Phan (PhD’16) and Dr. Evelyn Yim, an associate professor of chemical engineering working on collagen-based materials. Rounding out the team were Dr. Muhammad Rizwan, a former postdoctoral fellow, and John Waylon Tse (MASc’18), a former graduate student, both with Yim’s lab.
Collagen is a protein naturally found in the eye that’s also often involved in the wound healing process – however, it’s too soft and weak to be a contact lens material. Yim found a way to transform gelatin methacrylate, a collagen derivative, into a biomaterial 10 times stronger.
One unique property of collagen-based materials is that they degrade when exposed to an enzyme called matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), which is naturally found in the eye.
“These enzymes are very special because they’re involved in wound healing, and when you have a wound, they’re released in greater quantity,” Phan said. “If you have a material that can be degraded in the presence of this enzyme, and we add a drug to this material, we can engineer it so it releases the drug in a way that is proportional to the amount of enzymes present at the wound. So, the bigger the wound, the higher the amount of drug released.”
The team used bovine lactoferrin as a model wound-healing drug and entrapped it in the material. In human cell culture study, the researchers achieved complete wound healing within five days using the drug-releasing novel contact lens material.
Another benefit of the material is that it only becomes activated at eye temperatures, providing an inbuilt storage mechanism.
The next step is fine-tuning the material, including entrapping different drugs in it.
The scientists believe their material has great potential – not only for the eye but potentially for other body sites, especially large skin ulcers.
A study outlining the researchers’ work was recently published in the journal Pharmaceutics.
END
High temperatures during critical periods of the reproductive cycle of sheep result in 2.1 million fewer lambs produced in Australia each year, costing sheep farmers an estimated $97 million annually.
The work, funded by Meat and Livestock Australia and conducted by a transdisciplinary team of researchers from the University of Adelaide and South Australian Research Development Institute (SARDI), found that days above 32°C during the week of mating caused the significant loss of potential lambs.
Published in Nature Food, the study found annual losses of potential lambs would increase to 2.5 million if median global warming increased ...
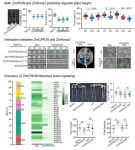
This study was led by Professor Mingliang Xu (College of Agronomy and Biotechnology, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China). Through phylogenic analysis, the authors identified a gene encoding a calcium-dependent protein kinase, ZmCPK39, as a candidate gene for plant height regulation in maize. The function of ZmCPK39 in controlling plant height has been verified using gene editing technology. Compared to the wild-type ND101, knockout of ZmCPK39 significantly reduced plant height by 40%.
The authors further ...
Cellulose, abundantly available from plant biomass, can be converted into molecules used to make a new class of recyclable polymers, to sustainably replace some plastics.
Researchers at Hokkaido University have taken a significant step forward in the drive to make recyclable yet stable plastics from plant materials. This is a key requirement to reduce the burden of plastic pollution in the environment. They developed a convenient and versatile method to make a variety of polymers from chemicals derived from plant cellulose; crucially, these polymers can be fully recycled. The method was published in the journal ACS Macro Letters.
Cellulose is one of the most abundant ...
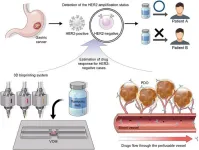
Gastric cancer ranks among the most widespread diseases in Asian populations, with South Koreans experiencing the third-highest incidence globally in 2020, as reported by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Recently, a collaborative research effort between Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) and Yonsei University achieved advancement in the realm of precision personalized medicine for gastric cancer. By using 3D bioprinting to accurately replicate the biological environment surrounding gastric cancer cells, the researchers have achieved a significant ...
LA JOLLA, CA—Neuroscientists at Scripps Research have found that inhibiting neurons involved in the body’s stress response may reduce alcohol consumption in people who have both post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and alcohol use disorder (AUD)—even if they still experience trauma-related anxiety.
The findings were published March 21 in Molecular Psychiatry. These discoveries are helping untangle the complex role that stress and trauma play in neurological disorders like PTSD and AUD, while also informing the development of new treatment options for people who experience both these conditions simultaneously.
“Traumatic ...
Embargoed access to the paper and contact details for authors are available in Notes to Editors at the end of the release.
By 2050, over three-quarters (155 of 204) of countries will not have high enough fertility rates to sustain population size over time; this will increase to 97% of countries (198 of 204) by 2100.
Pronounced shifts in patterns of livebirths are also predicted, with the share of the world’s live births nearly doubling in low-income regions from 18% in 2021 to 35% in 2100; and sub-Saharan Africa accounting for one in every two children born on the planet by 2100.
In low-income settings with higher fertility rates, better access to contraceptives and female education ...
The NHS needs an immediate cash injection of around £8.5bn a year over the next four years to make up a £32bn shortfall in funding and help tackle the current crisis, especially in areas such as waiting times, access to primary care, workforce and capital investment, say experts in the second report of The BMJ Commission on the Future of the NHS.
John Appleby and colleagues argue that, while the government’s recent spring budget funding pledges are a start, they “certainly will not make up the significant shortfall that the NHS ...
Effective processes for reporting and responding to safeguard vulnerabilities are also lacking, warn experts
Many publicly accessible artificial intelligence (AI) assistants lack adequate safeguards to consistently prevent the mass generation of health disinformation across a broad range of topics, warn experts in The BMJ today.
They call for enhanced regulation, transparency, and routine auditing to help prevent advanced AI assistants from contributing to the generation of health disinformation.
Large language models (LLMs) are a form of generative AI that have the potential to greatly improve many aspects of society, including ...
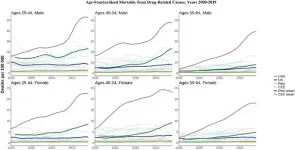
A new study by researchers at the Leverhulme Centre for Demographic Science (LCDS) and Princeton University reveals that US working-age adults are dying at higher rates than their peers in high-income countries; the UK is also falling behind. The study is published today in the International Journal of Epidemiology.
Using annual mortality data from the World Health Organization Mortality Database, the study compared trends in midlife mortality for adults aged 25-64 years between 1990 and 2019 across 15 major causes of death in 18 high-income countries, ...
Making alcohol-free beer more widely available on draught in pubs and bars may help people switch from alcoholic to alcohol-free beer, a new study published in Addiction today [21 March], has found. Pubs and bars taking part in the University of Bristol-led trial saw an increase in sales of healthier non-alcoholic draught beer.
In partnership with Bristol City Council (BCC), researchers from the University’s Tobacco and Alcohol Research Group (TARG) recruited 14 pubs and bars across the city that were willing to change the drinks that they offered on draught for a limited period. Previous research by the same group, using an online experiment as a proxy for real-world behaviour, ...