(Press-News.org) NASA’s BurstCube, a shoebox-sized satellite designed to study the universe’s most powerful explosions, is on its way to the International Space Station.
The spacecraft travels aboard SpaceX’s 30th Commercial Resupply Services mission, which lifted off at 4:55 p.m. EDT on Thursday, March 21, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. After arriving at the station, BurstCube will be unpacked and later released into orbit, where it will detect, locate, and study short gamma-ray bursts – brief flashes of high-energy light.
“BurstCube may be small, but in addition to investigating these extreme events, it’s testing new technology and providing important experience for early career astronomers and aerospace engineers,” said Jeremy Perkins, BurstCube’s principal investigator at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
Short gamma-ray bursts usually occur after the collisions of neutron stars, the superdense remnants of massive stars that exploded in supernovae. The neutron stars can also emit gravitational waves, ripples in the fabric of space-time, as they spiral together.
Astronomers are interested in studying gamma-ray bursts using both light and gravitational waves because each can teach them about different aspects of the event. This approach is part of a new way of understanding the cosmos called multimessenger astronomy.
The collisions that create short gamma-ray bursts also produce heavy elements like gold and iodine, an essential ingredient for life as we know it.
Currently, the only joint observation of gravitational waves and light from the same event – called GW170817 – was in 2017. It was a watershed moment in multimessenger astronomy, and the scientific community has been hoping and preparing for additional concurrent discoveries since.
“BurstCube’s detectors are angled to allow us to detect and localize events over a wide area of the sky,” said Israel Martinez, research scientist and BurstCube team member at the University of Maryland, College Park and Goddard. “Our current gamma-ray missions can only see about 70% of the sky at any moment because Earth blocks their view. Increasing our coverage with satellites like BurstCube improves the odds we’ll catch more bursts coincident with gravitational wave detections.”
BurstCube’s main instrument detects gamma rays with energies ranging from 50,000 to 1 million electron volts. (For comparison, visible light ranges between 2 and 3 electron volts.)
When a gamma ray enters one of BurstCube’s four detectors, it encounters a cesium iodide layer called a scintillator, which converts it into visible light. The light then enters another layer, an array of 116 silicon photomultipliers, that converts it into a pulse of electrons, which is what BurstCube measures. For each gamma ray, the team sees one pulse in the instrument readout that provides the precise arrival time and energy. The angled detectors inform the team of the general direction of the event.
BurstCube belongs to a class of spacecraft called CubeSats. These small satellites come in a range of standard sizes based on a cube measuring 10 centimeters (3.9 inches) across. CubeSats provide cost-effective access to space to facilitate groundbreaking science, test new technologies, and help educate the next generation of scientists and engineers in mission development, construction, and testing.
“We were able to order many of BurstCube’s parts, like solar panels and other off-the-shelf components, which are becoming standardized for CubeSats,” said Julie Cox, a BurstCube mechanical engineer at Goddard. “That allowed us to focus on the mission’s novel aspects, like the made-in-house components and the instrument, which will demonstrate how a new generation of miniaturized gamma-ray detectors work in space.”
BurstCube is led by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It’s funded by the Science Mission Directorate’s Astrophysics Division at NASA Headquarters. The BurstCube collaboration includes: the University of Alabama in Huntsville; the University of Maryland, College Park; the University of the Virgin Islands; the Universities Space Research Association in Washington; the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington; and NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville.
END
NASA’s tiny BurstCube mission launches to study cosmic blasts
2024-03-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research reveals link between menstrual cycles, emotions, and sleep patterns in women
2024-03-22
Women experience disruptions in their sleep patterns and report heightened feelings of anger in the days leading up to their period, according to new research.
The study sheds new light on the intricate relationship between women's menstrual cycles, emotions, and sleep patterns.
Co-author Dr Jo Bower, of the University of East Anglia’s School of Psychology, said: “Our research provides valuable insights into the complex interplay between menstrual cycles, emotions, ...
Breast cancer patients can safely avoid extensive removal of lymph nodes if they respond well to primary systemic treatment
2024-03-22
Milan, Italy: Patients with breast cancer that has started to spread to the lymph nodes in the armpit can safely avoid extensive removal of the lymph nodes if their treatment is tailored to their response to cancer-killing therapies such as chemotherapy before surgery.
In a presentation to the 14th European Breast Cancer Conference today (Friday) in Milan, Annemiek Van Hemert, a doctor and PhD student in the Surgical Oncology Department of Antoni van Leeuwenhoek-Netherlands Cancer Institute (AVL-NKI) in Amsterdam (The Netherlands), said: “If we are able to predict the response based on the removal of ...
Replacing sugar with sweeteners can improve weight loss control over the long-term in adults in the overweight range, finds European randomised controlled trial
2024-03-21
*This is an early press release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) Venice 12-15 May. Please credit the Congress if using this material*
New research being presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May), suggests that replacing sugar-sweetened food and drinks with low/no energy sweetened products can help weight control for at least one year after rapid weight loss in adults, without increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
The findings of a year-long randomised controlled trial involving adults with overweight and obesity and children in the overweight range from Northern, Central and ...
Early registration opens for 2024 International Space Station Research and Development Conference in Boston
2024-03-21
BOSTON (MA), March 21, 2024 – This July, the 13th annual International Space Station Research and Development Conference (ISSRDC) returns to Boston, where leaders from the commercial sector, U.S. government agencies, and academic communities will assemble to highlight innovations and opportunities through our nation’s orbiting outpost. ISSRDC will take place July 30-August 1, 2024, at the Marriott Copley Place in Boston. Early registration is now open until May 24, 2024. Booking during early ...
Marine Biological Laboratory announces 2024 Logan Science Journalism Fellows
2024-03-21
WOODS HOLE, Mass. –Twelve accomplished science and health journalists have been awarded a highly competitive fellowship in the Logan Science Journalism Program at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL).
Now in its 37th year, the Logan Science Journalism Program provides journalists with immersive, hands-on research training, giving them invaluable insight into the practice of science as well as some of the major news stories of today. The program, which offers a Biomedical course and an Environmental course, will run May 13-23 in Woods Hole.
Biographies for the 2024 Logan Science Journalism Fellows are here. They are:
Biomedical Fellows
Pakinam Amer, Independent ...
Novel imaging platform allows researchers to study placental development in pregnant mice
2024-03-21
DURHAM, N.C. -- Physicians and biomedical engineers at Duke University have developed a method to visualize the growth of a placenta throughout a mouse’s pregnancy. By coupling an implantable window with ultrafast imaging tools, the approach provides the first opportunity to track placental development to better understand how the organ functions during pregnancy.
This new perspective gives researchers a precise way to examine how lifestyle factors like alcohol consumption and health complications like inflammation can affect the placenta and potentially lead to adverse pregnancy outcomes.
The research appears March 20 as the cover ...
AMS Science Preview: “Outdoor days,” lightning, air pollution
2024-03-21
The American Meteorological Society continuously publishes research on climate, weather, and water in its 12 journals. Many of these articles are available for early online access–they are peer-reviewed, but not yet in their final published form.
Below is a selection of articles published early online recently. To view full article text, members of the media can contact kpflaumer@ametsoc.org for press login credentials.
Observed Changes in Extreme Precipitation Associated with United States Tropical Cyclones
Journal of Climate
Rainfall ...
Illinois study: Systematic review of agricultural injuries can help inform safety measures
2024-03-21
URBANA, Ill. – Agricultural occupations are hazardous with one of the highest rates of workplace injuries and fatalities in the U.S. The manual and often strenuous nature of the work, combined with the use of machinery and exposure to environmental hazards create a challenging work environment. Understanding the nature and causes of injuries can help improve safety guidelines and policy measures. However, obtaining a comprehensive overview of injuries is hindered by the absence of a central reporting system. Two ...
New vaccine against a highly fatal tropical disease – and potential bioterror weapon – demonstrates efficacy in animal studies
2024-03-21
In a mouse study, UCLA researchers tested a vaccine against the bacterium that causes melioidosis and found it was highly protective against the disease, which is endemic in many tropical areas, causing approximately 165,000 cases with 89,000 fatalities around the world each year.
The bacterium, called Burkholderia pseudomallei, is spread through contact with contaminated soil and water through inhalation, ingestion or broken skin. It is so dangerous that it is categorized as a Tier 1 Select Agent of bioterrorism, and it can cause ...
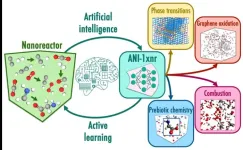
Artificial intelligence helps explore chemistry frontiers
2024-03-21
The ability to simulate the behavior of systems at the atomic level represents a powerful tool for everything from drug design to materials discovery. A team led by Los Alamos National Laboratory researchers has developed machine learning interatomic potentials that predict molecular energies and forces acting on atoms, enabling simulations that save time and expense compared with existing computational methods.
“Machine learning potentials increasingly offer an effective alternative to computationally ...