(Press-News.org)
Humans pass on more viruses to domestic and wild animals than we catch from them, according to a major new analysis of viral genomes by UCL researchers.
For the new paper published in Nature Ecology & Evolution, the team analysed all publicly available viral genome sequences, to reconstruct where viruses have jumped from one host to infect another vertebrate species.
Most emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases are caused by viruses circulating in animals. When these viruses cross over from animals into humans, a process known as zoonosis, they can cause disease outbreaks, epidemics and pandemics such as Ebola, flu or Covid-19. Given the enormous impact of zoonotic diseases on public health, humans have generally been considered as a sink for viruses rather than a source, with human-to-animal transmission of viruses receiving far less attention.
For the study, the research team developed and applied methodological tools to analyse the nearly 12 million viral genomes that have been deposited on public databases to date. Leveraging this data, they reconstructed the evolutionary histories and past host jumps of viruses across 32 viral families, and looked for which parts of the viral genomes acquired mutations during host jumps.
The scientists found that roughly twice as many host jumps were inferred to be from humans to other animals (known as anthroponosis) rather than the other way round. This pattern was consistent throughout most viral families considered. Additionally, they found even more animal-to-animal host jumps, that did not involve humans.
The team’s work highlights the high and largely underappreciated fact that human viruses frequently spread from humans into wild and domestic animals.
Co-author Professor Francois Balloux (UCL Genetics Institute) said: “We should consider humans just as one node in a vast network of hosts endlessly exchanging pathogens, rather than a sink for zoonotic bugs.
“By surveying and monitoring transmission of viruses between animals and humans, in either direction, we can better understand viral evolution and hopefully be more prepared for future outbreaks and epidemics of novel illnesses, while also aiding conservation efforts.”
The findings also show that, on average, viral host jumps are associated with an increase in genetic changes, or mutations in viruses, relative to their continued evolution alongside just one host animal, reflecting how viruses must adapt to better exploit their new hosts.
Further, viruses that already infect many different animals show weaker signals of this adaptive process, suggesting that viruses with broader host ranges may possess traits that make them inherently more capable of infecting a diverse range of hosts, whereas other viruses may require more extensive adaptations to infect a new host species.
Lead author, PhD student Cedric Tan (UCL Genetics Institute and Francis Crick Institute) said: “When animals catch viruses from humans, this can not only harm the animal and potentially pose a conservation threat to the species, but it may also cause new problems for humans by impacting food security if large numbers of livestock need to be culled to prevent an epidemic, as has been happening over recent years with the H5N1 bird flu strain.
“Additionally, if a virus carried by humans infects a new animal species, the virus might continue to thrive even if eradicated among humans, or even evolve new adaptations before it winds up infecting humans again.
“Understanding how and why viruses evolve to jump into different hosts across the wider tree of life may help us figure out how new viral diseases emerge in humans and animals.”
Cell entry is generally seen as the first step for a virus to infect a host. However, the team found that many of the adaptations associated with host jumps were not found in the viral proteins that enable them to attach to and enter host cells, which points to viral host adaptation being a complex process that remains to be fully understood.
Co-author Dr Lucy van Dorp (UCL Genetics Institute) said: “Our research was made possible only by the countless research teams that have openly shared their data via public databases. The key challenge, moving forward, is to integrate the knowledge and tools from diverse disciplines including genomics, epidemiology, and ecology to enhance our understanding of host jumps.”
END
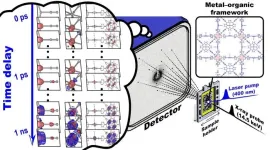
Understanding the behavior of matter is crucial for advancing scientific fields like biology, chemistry, and materials science. X-ray crystallography has been instrumental in this pursuit, allowing scientists to determine molecular structures with precision. In traditional X-ray crystallography experiments, a single crystal is exposed to X-rays multiple times to obtain diffraction signals. This poses a problem, where the sample has its structure altered or damaged by X-ray exposure.
In recent years, advances in technology have allowed for the development of “time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography” (TR-SFX). In serial ...
More efficient use of phosphorus could see limited stocks of the important fertiliser last more than 500 years and boost global food production to feed growing populations.
But these benefits will only happen if countries are less wasteful with how they use phosphorus, a study published today in Nature Food shows.
Around 30-40 per cent of farm soils have over-applications of phosphorus, with European and North American countries over-applying the most.
The global population is due to hit nearly 10 billion by 2050 and it is estimated that to feed ...
RICHLAND, Wash.— A commonplace chemical used in water treatment facilities has been repurposed for large-scale energy storage in a new battery design by researchers at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. The design provides a pathway to a safe, economical, water-based, flow battery made with Earth-abundant materials. It provides another pathway in the quest to incorporate intermittent energy sources such as wind and solar energy into the nation’s electric grid.
The researchers report ...
Scientists from The Australian National University (ANU) have discovered a gene mutation is responsible for causing psoriasis – a chronic inflammatory skin disease that causes patients to develop red, scaly and itchy patches across their body.
According to ANU researcher Dr Chelisa Cardinez, if two copies of this mutated gene (known as IKBKB) are present, patients with psoriasis may go on to develop psoriatic arthritis, leaving them with joint pain, stiffness and swelling. Thanks to the world-first discovery from ANU, scientists now know what causes the progression from a skin-only disease to a skin and joint disease.
It’s hoped the findings will lead ...
In the United States, community health centers (CHCs) mainly serve historically marginalized populations. New research reveals that both before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, females receiving care at rural CHCs were less likely to be up to date with cervical cancer screening than those in urban CHCs. Factors associated with these differences included the proportion of patients with limited English proficiency and low income, as well as area-level unemployment and primary care physician density. The findings are ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Many parents struggle deciding whether their middle or high school aged child should stay home from school if they don’t feel well, a new national poll suggests.
Among top factors: how their adolescent or teen is behaving due to symptoms and if they can get through a school day, the risk that they’re contagious and whether the student will miss a test, presentation or after school activity.
One in five parents also consider if their child needs a mental health day, according to the University of Michigan ...
Physicians in Canada, especially male physicians, are working fewer hours than they did 3 decades ago, and these long-term trends must be considered in workforce planning, according to new research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231166.
"Canadian physicians' work hours, crucial for health care access and planning, have seen a long-term decline, especially among male and married physicians, suggesting a shift towards better work–life balance," said Dr. Boris Kralj, Department of Economics, Centre for Health Economics & Policy Analysis, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario.
Using ...
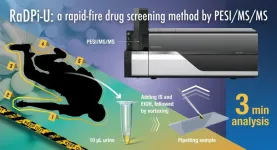
Drugs, both legal and illegal, cause millions of cases of severe intoxication every year, leading to health complications and even fatalities. Often, they are also implicated in violent and sexual harassment crimes, as well as accidents. Obtaining detailed information about the drugs consumed by a criminal or victim is often challenging. Forensic professionals rely on drug screening techniques performed on biological samples, such as blood or saliva, to gather crucial evidence.
Today, various types of practical drug screening methods exist, each with their own unique advantages ...
Hundreds of studies are published each year on attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), but more work is needed to ensure those findings improve lives.
With input from expert stakeholders across the field, researchers at the Southern California Evidence Review Center, part of the Keck School of Medicine of USC, have synthesized the latest insights so that they can ultimately inform clinical practice. Broadly, they found that both medications and psychosocial treatments work for treating ADHD and that children with the condition can and do get better.
“We have more research than ever on ADHD, but we need ...
Researchers at the University of Waterloo's Institute for Quantum Computing (IQC) have brought together two Nobel prize-winning research concepts to advance the field of quantum communication.
Scientists can now efficiently produce nearly perfect entangled photon pairs from quantum dot sources.
Entangled photons are particles of light that remain connected, even across large distances, and the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics recognized experiments on this topic. Combining entanglement with quantum dots, a technology recognized with the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2023, the IQC research team aimed to optimize the ...