ABT199/Venetoclax synergism with thiotepa in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells
2024-03-25
(Press-News.org)
“[...] the combination of ABT199/venetoclax and Thio enhances the cytotoxicity of (Flu+Clad+Bu) in AML cell lines and leukemia patient-derived cell samples.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 25, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on March 14, 2024, entitled, “ABT199/venetoclax synergism with thiotepa enhances the cytotoxicity of fludarabine, cladribine and busulfan in AML cells.”
ABT199/venetoclax, an inhibitor of the pro-survival BCL-2 protein, has improved AML treatment. Its efficacy in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), when combined with other chemotherapeutic drugs, has not been thoroughly investigated. In this new study, researchers Benigno C. Valdez, Bin Yuan, David Murray, Jeremy L. Ramdial, Uday Popat, Yago Nieto, and Borje S. Andersson from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and the University of Alberta demonstrate the synergistic cytotoxicity of ABT199/venetoclax with the DNA alkylator thiotepa (Thio) in AML cells.
“The results may provide relevant information for the design of clinical trials using these drugs to circumvent recognized drug-resistance mechanisms when used as part of pre-transplant conditioning regimens for AML patients undergoing allogenic HSCT.”
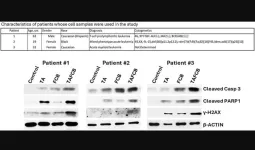
Cleavage of Caspase 3, PARP1 and HSP90, as well as increased Annexin V positivity, suggest potent activation of apoptosis by this two-drug combination; increased levels of γ-H2AX, P-CHK1 (S317), P-CHK2 (S19) and P-SMC1 (S957) indicate an enhanced DNA damage response. Likewise, the increased level of P-SAPK/JNK (T183/Y185) and decreased P-PI3Kp85 (Y458) suggest enhanced activation of stress signaling pathways. These molecular readouts were synergistically enhanced when ABT199/venetoclax and Thio were combined with fludarabine, cladribine and busulfan.
The five-drug combination decreased the levels of BCL-2, BCL-xL and MCL-1, suggesting its potential clinical relevance in overcoming ABT199/venetoclax resistance. Moreover, this combination is active against P53-negative and FLT3-ITD-positive cell lines. Enhanced activation of apoptosis was observed in leukemia patient-derived cell samples exposed to the five-drug combination, suggesting a clinical relevance.
“The results provide a rationale for clinical trials using these two- and five-drug combinations as part of a conditioning regimen for AML patients undergoing HSCT.”
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28563
Correspondence to: Benigno C. Valdez
Email: mbalasik@yahoo.com
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia, pre-transplant regimens, venetoclax, thiotepa, busulfan
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X, formerly Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
Reddit
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Street., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-25
Research Highlights:
A large study of residents in Ningbo, China, a major city of more than 8.2 million residents, found that exposure to more artificial, outdoor, nighttime light was associated with a higher risk of conditions that affect brain health.
Excessive exposure to air pollution and artificial, bright light at night were both independently linked to a higher risk of developing cerebrovascular disease and having a stroke.
Embargoed until 1 p.m. CT/2 p.m. ET, Monday, March 25, 2024
DALLAS, March 25, 2024 — People continuously ...
2024-03-25
Investigators from the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center will discuss the latest breakthroughs and cutting-edge science at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR), which attracts more than 20,000 oncology professionals from around the world.
The annual meeting will feature more than 40 regular, late-breaking and clinical trial abstracts from UCLA physicians and scientists, who will present their latest work in key areas of translational and basic scientific ...
2024-03-25
ITHACA, N.Y. -- By studying individuals who spontaneously clear hepatitis C infections, a team of researchers has identified viable vaccine targets for a disease that infects 70 million worldwide with case numbers increasing every year.
It turns out that a quarter of people who become infected with the hepatitis C virus clear the infection on their own without treatment, while the remaining three-quarters of people develop chronic infections that can last for years. The blood-borne disease – which causes liver cirrhosis, liver ...
2024-03-25
For centuries, the Cerne Giant, a figure carved into a hillside in Dorset depicting a nude man carrying a club and stretching some 180 feet high, has fascinated locals and visitors to the area. The history of the giant, however, and in particular, its age, has long been a mystery. A new paper in Speculum: A Journal of Medieval Studies proposes that the Cerne Giant can in fact be dated to the early Middle Ages, and, as a result, its cultural context and significance more clearly understood.
“The Cerne Giant in its Early Medieval Context,” by authors Thomas Morcom and Helen Gittos, acknowledges that previous attempts to date the giant placed ...
2024-03-25
25 March 2024: RCSI research has found that venetoclax, a medication currently approved for leukaemia, has benefits for patients with multiple myeloma when used in combination with another drug. This discovery offers a new avenue of treatment options for the currently incurable disease.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a type of blood cancer that is newly diagnosed in around 400 people in Ireland each year. Despite treatment advances in recent years, it remains incurable. The search for innovative treatment strategies is crucial, particularly for patients whose cancer is resistant to standard care.
In the new study published in Haematologica, researchers at the RCSI Department of ...
2024-03-25
Philadelphia, March 25, 2024 – Food insecurity among college students is associated with negative physical and mental health and lower academic performance and graduation rates. A recent research study in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published by Elsevier, investigates why over half of college students eligible for the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)—the nation’s largest food assistance program—do not apply.
Lead study author Suzanna M. Martinez, PhD, MS, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, University of California San Francisco, explained, “In California, ...
2024-03-25
Professor Jinyang Liang’s team is advancing in imaging speed with a new ultrafast camera system.
Pushing for a higher speed isn’t just for athletes. Researchers, too, can achieve such feats with their discoveries. This is the case for Jinyang Liang, Professor at the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS), and his team, whose research results have recently been published in Nature Communications.
The group based at INRS’ Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications Research Centre has developed a new ultrafast camera system that can capture up to 156.3 trillion ...
2024-03-25
New research has found no evidence of a difference between recovery time and complications when comparing standard and keyhole surgical incisions for the treatment of oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). The study, led by the University of Bristol Medical School and published in the British Journal of Surgery, showed surgeons treating patients with oesophageal cancer do not need to change their practice if they have a strong preference for either procedure type.
Oesophageal cancer is the tenth most common cancer globally. It causes one in 18 cancer-related deaths. ...
2024-03-25
Key Takeaways
In a retrospective analysis of 105,517 patients with colorectal cancer, researchers found that colorectal cancer surgical cases fell by 17.3% during the first year of the pandemic.
Patients who underwent surgery for colorectal cancer in 2020 displayed more advanced stages of cancer compared to those treated in 2019.
The authors attribute these findings to multiple factors, including delays in screening, fear of COVID-19 exposure that may have prevented some people from seeking care, and disparities in cancer care that were likely exacerbated during the pandemic.
CHICAGO: While the COVID-19 pandemic is no longer considered a public ...
2024-03-25
In nanomaterials, shape is destiny. That is, the geometry of the particle in the material defines the physical characteristics of the resulting material.
“A crystal made of nano-ball bearings will arrange themselves differently than a crystal made of nano-dice and these arrangements will produce very different physical properties,” said Wendy Gu, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Stanford University, introducing her latest paper which appears in the journal Nature Communications. “We’ve used a 3D nanoprinting technique to produce one of the most promising ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] ABT199/Venetoclax synergism with thiotepa in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells