(Press-News.org) Researchers say more needs to be done for depressed stroke survivors as new findings show 60% of stroke survivors would experience depression within 18 years, a much higher estimation than previous studies.
This compares to 22% of the general population experiencing depression in the same time frame.
The King’s College London study, published today in The Lancet Regional Health – Europe, also found 90% of cases of depression occurred within five years of surviving a stroke, indicating a key time for healthcare intervention.
The findings, funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research, looks at incidence of mild and severe depression in the South London Stroke Register, a cohort of 6600 survivors of stroke in the Lambeth and North Southwark boroughs.
The population was 55.4% male with a median age of 68 years. 62.5% were from a white ethnic background and 29.7% from a Black ethnic background.
While post-stroke depression is common after stroke and associated with poor functional ability and increased mortality, the study found that severe depression tended to occur earlier after stroke, had a longer duration and was quicker to recur than mild depression.
Professor Yanzhong Wang, Professor of Statistics in Population Health at King’s College London, said: “Depression is common in stroke survivors but our research shows it persists for much longer than previously thought. We know that depression can limit a stroke survivor’s mobility including simple things as walking and holding objects and can also increase the risk of death. With an aging population in the UK and an increase in the proportion of older adults, it’s essential we plan for rising healthcare demands to tackle the anticipated surge in stroke cases.”
Corresponding author Lu Liu, a PhD candidate with a clinical background at King’s College London, said: “Quality of life is important for stroke survivors as there is evidence depressed survivors have a reduced survival rate.
“There are many reasons why this could be, including disruptions to the survivor’s social life, reduced physical ability and inflammatory disorders observed in depressed patients.
“More clinical attention should be paid to patients with depression that is longer than one year because of the high risks of experiencing persistent depression.”
Read the paper here: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanepe/article/PIIS2666-7762(24)00048-6/fulltext
ENDS
END
More needs to be done for depressed stroke survivors as incidence climbs
2024-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research lights up process for turning CO2 into sustainable fuel
2024-03-26
Researchers have successfully transformed CO2 into methanol by shining sunlight on single atoms of copper deposited on a light-activated material, a discovery that paves the way for creating new green fuels.
An international team of researchers from the University of Nottingham's School of Chemistry, University of Birmingham, University of Queensland and University of Ulm have designed a material, made up of copper anchored on nanocrystalline carbon nitride. The copper atoms are nested ...
Essays on democracy draw attention to critical threats, explore safeguards ahead of Jan. 6
2024-03-25
Following the events of Jan. 6, 2021 — when a violent mob stormed the U.S. Capitol building in an effort to interrupt the certification process of the 2020 presidential election — experts began to question how to protect the next presidential election from a similar threat. To that end, University of Notre Dame political scientists have partnered with preeminent scholars of democracy from across the country to produce a set of recommendations to strengthen and safeguard democracy in America.
The University’s Rooney Center for the Study of American Democracy established the January 6th, ...
New surfactant could improve lung treatments for premature babies
2024-03-25
Scientists have developed a new lung surfactant that is produced synthetically rather than relying on the use of animal tissues. With further development, the formulation could provide a cheaper and more readily available alternative to Infasurf, a medication used to prevent and treat respiratory distress in premature babies.
Surfactants are substances that decrease surface tension where liquids interface with other liquids, gases or solids. In addition to their use in medicines, they are found in a wide range of products including detergents, cosmetics, motor oils and adhesives.
Suzanne Farver Lukjan, a lecturer in chemistry ...
Researchers uncover key biomolecule involved in whooping cough infection
2024-03-25
Researchers have identified a new complex-carbohydrate biomolecule, or glycan, that plays a key role in the nasal colonization of the Bordetella bacteria responsible for whooping cough. The discovery could make it possible to create a new drug or vaccine that interferes with the glycan to greatly reduce or even stop ongoing Bordetella transmission.
Bordetella pertussis is the cause of the respiratory infection pertussis, which is widely known as whooping cough. Today’s pertussis vaccines keep people from getting severely sick, but they don’t eliminate the bacteria because it excels at colonizing, ...
Study links long-term consumption of reused deep-fried oil with increased neurodegeneration
2024-03-25
A new study found higher levels of neurodegeneration in rats that consumed reused deep fried cooking oils and their offspring compared to rats on a normal diet. Deep frying, which involves completely submerging food in hot oil, is a common method of food preparation around the world.
Results from the study also suggest that the increased neurodegeneration is tied to the oil’s effects on the bidirectional communication network between the liver, gut and brain. The liver–gut–brain axis plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological functions, and its dysregulation has been ...
Study suggests statins could help fight gum disease
2024-03-25
Could taking statins benefit your mouth in addition to your arteries? A new study conducted in cell cultures showed that cholesterol-lowering drugs help to dampen the inflammation associated with periodontal disease by altering the behavior of macrophages, a type of immune cell.
Statins are the most common type of prescription medication in the United States today, taken by over 40 million Americans to lower cholesterol. The study suggests these drugs improve gum health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Subramanya Pandruvada, an assistant professor in the College ...
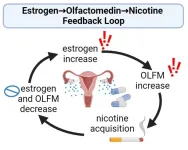
Study suggests that estrogen may drive nicotine addiction in women
2024-03-25
A newly discovered feedback loop involving estrogen may explain why women might become dependent on nicotine more quickly and with less nicotine exposure than men. The research could lead to new treatments for women who are having trouble quitting nicotine-containing products such as cigarettes.
Sally Pauss is a doctoral student at the University of Kentucky College of Medicine in Lexington. She led the project.
“Studies show that women have a higher propensity to develop addiction to nicotine than men and are less successful at quitting,” said Pauss, ...
The complexities of lung cancer screening decisions among patients with comorbidities
2024-03-25
Many individuals eligible for lung cancer screening (LCS) also suffer from multiple health issues at the same time, known as comorbid conditions. This study explores how primary care physicians (PCPs) factor comorbidities into their shared decision-making conversations with patients to discuss the harms and benefits of lung cancer screening. Researchers conducted semi-structured interviews with 15 PCPs affiliated with the Mount Sinai Health System in New York City between October 2020 and February 2021. PCPs were asked questions to examine their understanding of how comorbidities ...
ChatGPT’s potential and limits in summarizing medical research for clinicians
2024-03-25
Large language models (LLMs) are neural network–based computer programs that use a detailed statistical understanding of written language to perform many tasks, including text generation, summarization, software development, and prediction. However, LLMs can produce text that, while may seem correct, is not fact-based. This study investigates whether a popular LLM, ChatGPT-3.5, could produce high-quality, accurate, and bias-free summaries of medical research abstracts and determine the relevance of various journals and their articles to different medical specialties. Ten articles ...
Pediatric health care disrupted by COVID-19 pandemic, compounded by existing barriers such as systemic racism
2024-03-25
This study explores the extent to which pediatric health care was interrupted during and as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. This was measured based on three primary outcomes of interest: foregone care, foregone well-child or vaccination-related visits, and complete absence of well-child or vaccination-related visits. Researchers extracted data from a nationwide longitudinal survey known as CovEx (COVID Experiences Survey) that had been administered in two “waves'' to a cohort of parents of children between five and 12 years of age. Wave 1 took place October 8-November 13, 2020, and Wave 2 took place March 24-May 7, 2021, with an 82% retention rate of participants. Data was ...