(Press-News.org) Take a puff of nicotine for the first time, and your DNA plays an important role, alongside social and environmental factors, in shaping what happens next.
In recent years, scientists have identified thousands of genetic variants believed to influence everything from when people first try smoking to how good that first cigarette feels to how often they light up and how hard it is to quit. Some variants influence how quickly we metabolize nicotine, while others underlie how sensitive we are to it. But little is known about how they interact with each other and with other genetic differences.
A new University of Colorado Boulder study sheds unprecedented light on these interactions and provides new insight on the most well-known smoking-related variant to date – commonly nicknamed “Mr. Big”.
“We know that smoking is highly heritable, with genetic differences accounting for 40% to 75% of the differences in people’s smoking behaviors,” said Pamela Romero Villela, a PhD student in the Department of Psychology and Neuroscience and first author of the study in the journal Drug and Alcohol Dependence. “The more we can understand what those genes do and how they interact, the better equipped we will be to develop personalized approaches to helping people quit.”
Beyond Mr. Big
About 22% adults worldwide use nicotine and smoking is linked to one in five deaths in the United States.
“A lot of people still smoke, and it is one of the hardest drugs to quit,” said Romero Villela, a researcher with CU Boulder's Institute for Behavioral Genetics.
For the study, Romero Villela collaborated with Integrative Physiology Professor Marissa Ehringer, who has studied substance use disorders for more than 20 years.
They zeroed in on the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), or genetic variant, rs16969968, known as “Mr. Big” because it has been the mostly widely replicated genetic variant associated with smoking behaviors.
Mr. Big is located in a gene called CHRNA5F (nicotinic acetylcholine receptor 5) and influences how well nicotine binds to receptors in the brain. People with a certain version of Mr. Big, known as the AA version, are less sensitive to nicotine and have been shown to smoke more.
“It kind of numbs your response so in order for you to feel the same effect as someone who smoked one cigarette you might have to smoke almost one and a half cigarettes,” said Romero Villela.
As their study reveals, the story does not end there.
A personalized approach
When analyzing genetic information from about 165,000 current or former smokers of European, South Asian, and Finnish descent, the team discovered genes and variants in a completely different region of the genome that appear to interact with Mr. Big in a way that influences smoking habits.
Notably, when people had the risk-boosting version of Mr. Big but also had a genetic variant called rs73586411, they smoked significantly less than expected.
“We basically found another variant that ameliorates the effect of Mr. Big,” said Romero Villela.
More research is needed to understand just what the genes highlighted in the study do. (Interestingly, one called TMEM230 has previously been associated with Parkinson’s disease. Nicotine is known to blunt some symptoms of the disease).
The study authors imagine a day when people could be given a “polygenic risk score” which considers their gene variants and interactions to provide personalized recommendations for quitting. For instance, preliminary studies have already suggested that people with high-risk genotypes in the CHRNA5 region may benefit more from medications targeting nicotinic receptors.
Eventually, if researchers could determine what a variant does to dull the craving to smoke, they might be able to develop medications that mimic that action.
Bigger picture, the authors hope the study inspires more research looking not just at individual genes but also how genetic variants work together.
“Genes don’t operate in a vacuum,” said Ehringer. “If our ultimate goal is more personalized medicine, we have to understand these interactions better.”
END
How genes work together to shape how much you smoke
New research helps pave the way to more personalized approaches for kicking the habit
2024-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
University of Oklahoma engineer receives NSF CAREER Award to advance gas sensing technologies
2024-03-26
NORMAN, OKLA. – Binbin Weng, Ph.D., an engineering professor at the University of Oklahoma, has been awarded a National Science Foundation CAREER Award presented to early-career faculty with the potential to serve as academic role models in research and education. The $497,370 grant will fund his project “Enabling New States of Light in Mid-Wave Infrared Photonics for Gas Sensing Applications.”
Weng says there is a growing demand for distributed gas sensing networks capable of continuously monitoring gas threats on a broad scale. However, current technologies face significant challenges in size, power consumption ...
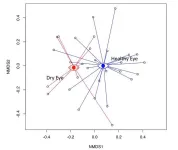
More than meets the eye: Researchers uncover the microbial secrets of dry eye
2024-03-26
Researchers have used advanced sequencing technology to determine how the mix of microbes present in patients with healthy eyes differs from the mix found in patients with dry eye. The new work could lead to improved treatments for various eye problems and for diseases affecting other parts of the body.
Microbial communities in and on our body — collectively referred to as the human microbiota — play an essential role in keeping us healthy. Although many studies have focused on microbial communities in our gut, understanding the microbiota present in other body sites is critical for advancing our knowledge of human health and developing targeted interventions ...
Researchers identify microbes that help plants thwart parasite
2024-03-26
Bacteria that could help one of Africa’s staple crops resist a major pest have been identified by researchers at the University of California, Davis. Their findings, published March 26 in Cell Reports, could improve yields of sorghum, a mainstay of food and drink in West and East African countries.
About 20 percent of Africa’s sorghum crop is lost due to witchweed (Striga hermonthica), a parasitic plant that steals nutrients and water by latching onto the plant’s roots.
In the new study, UC Davis researchers show that soil microbes induce changes in sorghum roots that make the plant more resistant to infection by witchweed. They ...
Late surgical repair for preterm babies born with inguinal hernia shows better results compared to early repair, study finds
2024-03-26
Delaying surgical inguinal hernia repair in preterm infants until after discharge from the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) appears to reduce the likelihood of serious adverse events, according to researchers at UTHealth Houston.
A study led by first and corresponding author Martin L. Blakely, MD, MS, MMHC, professor of surgery and pediatrics with McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, analyzed the safety of early versus late surgical repair for preterm infants born with an inguinal hernia. The findings were published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
“The biggest question we wanted ...
Two plant extracts with potential as GLP-1 agonist weight loss pills are identified by AI-based analysis
2024-03-26
*Note - This is an early press release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) Venice 12-15 May. Please credit the Congress if using this material*
Two plant compounds with potential as GLP-1 agonist weight loss pills have been identified in an AI (artificial intelligence)-based study, the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) (Venice 12-15 May), will hear.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists such as semaglutide and tirzepatide are highly effective at helping people lose weight. By mimicking the action of a hormone ...
nTIDE March 2024 deeper dive: Gender employment gap narrows among people with disabilities post-COVID
2024-03-26
East Hanover, NJ – March 26, 2024 – The shifting landscape of post-COVID-19 employment highlights a reduction in the gender employment gap among individuals with disabilities, a trend not observed among those without disabilities, according to last Friday’s National Trends in Disability Employment (nTIDE) Deeper Dive Lunch & Learn Webinar.
While men and women with disabilities have similar rates of employment, the data do not address whether women with disabilities in the workforce have lower-quality ...
New genetic analysis tool tracks risks tied to CRISPR edits
2024-03-26
Since its breakthrough development more than a decade ago, CRISPR has revolutionized DNA editing across a broad range of fields. Now scientists are applying the technology’s immense potential to human health and disease, targeting new therapies for an array of disorders spanning cancers, blood conditions and diabetes.
In some designed treatments, patients are injected with CRISPR-treated cells or with packaged CRISPR components with a goal of repairing diseased cells with precision gene edits. Yet, while CRISPR has shown ...
Curbside collection improves organic waste composting, reduces methane emissions
2024-03-26
URBANA, Ill. – Most organic household waste ends up in landfills where it generates methane, a powerful greenhouse gas. Composting food and garden waste instead of sending it to landfills can significantly reduce methane emissions and help mitigate global warming. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign explores the effects of curbside compost collection programs in New South Wales, Australia.
“Governments around the world are interested in composting organic waste and reducing their methane emissions, and they are looking for ways to make ...
Job flexibility and security promotes better mental health among employees
2024-03-26
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
March 26, 2024
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Job Flexibility and Security Promotes Better Mental Health
A new nationwide study indicates that workplace policies that provide stability and flexibility to employees boosts overall well-being and encourages workers to seek health services when they need it.
Employment is a recognized determinant of health, and different aspects of a job can be beneficial or deleterious to mental health.
Job flexibility and job security, in particular, are key factors that contribute to employees’ ...
Researchers find energy development and tree encroachment impact Wyoming pronghorn
2024-03-26
While Wyoming is home to some of North America’s most abundant populations of pronghorn that have largely been stable in recent years, a new analysis shows that many herds are experiencing long-term declines in fawn production.
Those declines are primarily a result of oil and gas development and encroachment of trees, according to researchers from the University of Wyoming, the University of Florida, the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, the University of Arkansas and the Northern Plains Agricultural Research Laboratory. Their findings have been published in the journal Global Ecology and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
[Press-News.org] How genes work together to shape how much you smokeNew research helps pave the way to more personalized approaches for kicking the habit