(Press-News.org) Arlington, Va. — March 28, 2024 — A new study published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) demonstrates the use of a simple pre-surgical infection prevention protocol to prevent dangerous post-surgical infections. Researchers performed this investigation at the Soroka University Medical Center in Israel.
Surgical site infections (SSIs) are a type of healthcare-associated infection with deadly consequences for some patients. According to the latest data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there were more than 110,000 SSIs linked to inpatient surgeries in the U.S. in 2015.1 These infections lead to a high rate of morbidity and mortality, with a patient’s estimated risk of death as much as 11 times higher than normal.2 SSIs also have a very high financial burden, with the average hospital stay extended by nearly 10 days and an estimated $20,000 in additional hospitalization costs per patient.3
There are a number of recommended protocols to help prevent SSIs, but lack of patient compliance, high costs, and bacterial resistance can reduce their utility and effectiveness. In this new study, researchers aimed to evaluate the results of a protocol designed to reduce SSIs through a particular focus on the Staphylococcus aureus pathogen. The approach involved a pre-surgical intranasal application of povidone-iodine and skin antisepsis using chlorhexidine gluconate (CHG).
The study involved 688 adult patients who had hip or knee arthroplasty or spine surgery at Soroka University Medical Center between February 2018 and October 2021. Their outcomes were compared to a retrospective patient cohort from 2016 and 2017 treated before the povidone-iodine component of the protocol was implemented. Patient outcomes were tracked for 90 days after surgery.
Deploying this intervention prior to surgery helped to address a broad challenge in healthcare, that some 30% of the population is colonized with S. aureus without exhibiting symptoms. The pre-surgical protocol successfully eradicated S. aureus in nearly 40% of patients found to already harbor the pathogen. This is particularly important for patient outcomes, as the researchers found that the presence of S. aureus within the day following surgery was associated with a three-fold risk of developing an SSI. Overall, the study showed a significant decrease in severe SSIs among patients who received the newer protocol.
“Our study clearly shows that we can prevent surgical site infections and keep patients safer through the use of a simple pre-surgical nasal application of povidone-iodine in combination with standard CHG bathing,” said Lisa Saidel-Odes, MD, Infectious Diseases specialist at Soroka University Medical Center and lead author of the paper. “We noted that the protocol is most effective in cases with little S. aureus present and suggest that an additional application of the povidone-iodine might be needed for patients with greater nasal colonization.”
Additional details from the study include:
Of the 688 patients included, 28 developed an SSI in the 90-day study window. Patients with diabetes were at particularly increased risk for developing an SSI.
Patients were screened for S. aureus prior to surgery. More than 16% were already colonized with either methicillin-sensitive or methicillin-resistant S. aureus.
Of patients who developed SSIs, S. aureus was not the only cause of infection. Eleven patients were infected with Enterobacterales.
“This study shows the power of applying widely available antiseptics to reduce SSIs and improve patient safety,” said Tania Bubb, PhD, RN, CIC, FAPIC, 2024 APIC president. “The results are encouraging not only because the regimen is effective in reducing SSI, but also because it is simple to implement and avoids the risk of antibiotic resistance.”
References
1. Magill, SS, O'Leary, E, Janelle, SJ, et al., "Changes in Prevalence of Health Care-Associated Infection in U.S. Hospitals". N Engl J Med, 379(18): (2018): 1732-44.
2. World Health Organization Global Guidelines for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection. [2018 Feb 23]
3. Zimlichman, E, Henderson D, Tamir O, et al., "Health care-associated infections. a meta-analysis of costs and financial impact on the US health care system". JAMA Intern Med, 173(22): (2013): 2039-46.
About APIC
Founded in 1972, the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC) is the leading association for infection preventionists and epidemiologists. With more than 15,000 members, APIC advances the science and practice of infection prevention and control. APIC carries out its mission through research, advocacy, and patient safety; education, credentialing, and certification; and fostering development of the infection prevention and control workforce of the future. Together with our members and partners, we are working toward a safer world through the prevention of infection. Join us and learn more at apic.org.
About AJIC
As the official peer-reviewed journal of APIC, The American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) is the foremost resource on infection control, epidemiology, infectious diseases, quality management, occupational health, and disease prevention. Published by Elsevier, AJIC also publishes infection control guidelines from APIC and the CDC. AJIC is included in Index Medicus and CINAHL. Visit AJIC at ajicjournal.org.
NOTES FOR EDITORS
“Getting the Drop on Staphylococcus aureus: Semi-Quantitative Staphylococcus aureus Nasal Colony Reduction in Orthopedic Surgery Reduces Surgical Site Infection,” by Lisa Saidel-Odes, Rivka Yosipovich, Vadim Benkovich, Tai Friesem, Ronit Nativ, Orli Sagi, Orly Shimoni, and Abraham Borer, was published online in AJIC on March 28, 2024. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2024.02.014
AUTHORS
Lisa Saidel-Odes, MD (corresponding author: lisa.saidel@gmail.com), Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology Unit, Soroka University Medical Center
Rivka Yosipovich, RN, Soroka University Medical Center
Vadim Benkovich, MD, Soroka University Medical Center
Tai Friesem, MD, Soroka University Medical Center
Ronit Nativ, MPH, Soroka University Medical Center
Orli Sagi, PhD, Soroka University Medical Center
Orly Shimoni, PharmD, Soroka University Medical Center
Abraham Borer, MD, Soroka University Medical Center
# # #
END
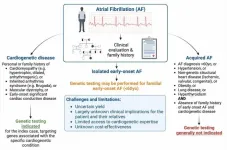
Philadelphia, March 28, 2024 – Although the vast majority of clinicians do not view atrial fibrillation (AF) as a genetic disorder, a White Paper in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, analyzes the current understanding of genetics and the role of genetic testing in AF and concludes there is an increasing appreciation that genetic culprits for potentially life-threatening ventricular cardiomyopathies and channelopathies may initially present with AF.
AF is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia and is associated with increased risks of heart failure, stroke, and death. It is ...
In a Leicester study that looked at whether artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to predict whether a person was at risk of a lethal heart rhythm, an AI tool correctly identified the condition 80 per cent of the time.
The findings of the study, led by Dr Joseph Barker working with Professor Andre Ng, Professor of Cardiac Electrophysiology and Head of Department of Cardiovascular Sciences at the University of Leicester and Consultant Cardiologist at the University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust, have been published in the European Heart Journal – Digital Health.
Ventricular arrhythmia (VA) is a heart rhythm disturbance originating from the bottom chambers (ventricles) where ...
Reconciling the tasks of producing adequate amounts of nutritious food for the increasing global population while preserving the environment and natural ecosystems simultaneously is an enormous challenge. The concept of agriculture green development (AGD) was detailed in 2017 and the necessary governmental policies were developed to address the aforementioned challenge in China and to help achieve the related global sustainable development goals. AGD emphasizes the synergy between green and development; current agriculture has to transform from the intensive farming with high inputs, high environmental impacts ...
The ALMA radio telescope has detected more than 100 molecular species, including many indicative of different star formation and evolution processes, in a galaxy where stars are forming much more actively than in the Milky Way. This is far more molecules than were found in previous studies. Now the team will try to apply this knowledge to other galaxies.
A team of researchers led by Sergio Martin of the European Southern Observatory/Joint ALMA Observatory, Nanase Harada of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, and Jeff Mangum of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory ...
A case study on the effects of open waste burning on air quality in Northwestern Greenland calls attention to the importance of no-one-left-behind sustainable air quality monitoring in the Arctic region.
To better understand the air quality risks faced by remote Arctic communities, an international team monitored aerial pollutants at a community in Northwestern Greenland. Their findings, published in Atmospheric Science Letters, reveal that open waste burning elevates the concern of health risks to the community.
The study focused on Qaanaaq, a small village in Northwestern Greenland with a population of approximately 600. During the summer of 2022, the team conducted the first-time measurement ...
Researchers have used Google Street View to study hundreds of elements of the built environment, including buildings, green spaces, pavements and roads, and how these elements relate to each other and influence coronary artery disease in people living in these neighbourhoods.
Their findings, published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Thursday), show that these factors can predict 63% of the variation in the risk of coronary heart disease from one area to another.
Coronary heart disease, where a build-up of fatty substances in the coronary arteries ...
Kyoto, Japan -- Branching patterns are prevalent in our natural environment and the human body, such as in the lungs and kidneys. For example, specific genes that express growth factor proteins are known to influence the development of the lungs' complex branches. Still, until now the mechanics behind this phenomenon have remained a mystery.
Kyoto University researchers have unveiled a regulatory system linking signal, force, and shape in mouse lung structure development. The team recognized that the signal protein ERK plays an active role in causing growing lung tissue to curve.
"ERK signals the cell tissue to stretch outward to smoothen its ...
SAN ANTONIO, March 27, 2024 – Autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may be preventable if parents avoid toxic exposures and adopt interventions such as environmental house calls, according to a published study led by researchers from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio).
Using a validated, self-administered questionnaire now used worldwide to identify individuals with chemical intolerance – the Quick Environmental ...
Niigata, Japan - A new Japanese nationwide study revealed that from 2006 to 2021, the number of patients with incident renal RRT due to RPGN increased, with an increase in the age-specific incidence of RRT due to RPGN in the older age groups (≥70 years old). Given the increasing trend in the incidence of RRT in older age groups and the ongoing population aging in Japan, the number of patients with incident RRT due to RPGN is likely to continue to increase in the future.
"RPGN is clinical syndrome that causes a rapid loss of kidney function, usually within a few days to a ...
The subversive nature of skateboarding is not likely to be affected by its continuing place in the corporate world of the Olympics, experts have predicted.
The inclusion of the street sport – which happened for the first time in Tokyo 2020 – could help to promote pacifism and egalitarianism and help to combat sexism, homophobia and racism, research suggests.
Some had suggested the subversive sport and its links to rebellion, pools, ramps, and skateparks, as well as less typical type of competition, would not fit easily into a world ...