(Press-News.org) Scientists at The Florey have developed an mRNA technology approach to target the toxic protein tau, which builds up in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.
To date, mRNA has been predominantly used for vaccines, including those used to fight COVID-19.
New research published today in Brain Communications establishes The Florey as a key player in the mRNA field, with Dr Rebecca Nisbet taking the technology in a new direction.
“This is the first time mRNA has been explored for use in Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr Nisbet said. “Our work in cell models demonstrates that this technology can serve purposes other than vaccine development.”
She likened mRNA to an instruction manual for cells.
“Once delivered to the cell, the cell reads the mRNA and makes an antibody.”
The Florey team used mRNA to instruct cells in cell models to create RNJ1, an antibody Dr Nisbet developed to target tau, a protein that clumps in the brain cells of dementia patients.
“This is the first time, to our knowledge, a tau antibody has been able to directly engage tau within the cell.”
First author on the paper, PhD student Patricia Wongsodirdjo said: “Our technique can be applied to any therapeutic antibody, and we envision that this strategy, when combined with nanoparticle packaging, will enhance targeting of toxic molecules in the brain and improve patient outcomes compared to conventional strategies.”
Dr Nisbet said RNJ1 still needed further research.
She said emerging Alzheimer’s treatments, such as lecanemab, which is approved in the USA and under consideration in Australia, are promising but expensive to make and are not an efficient way of getting an active antibody into brain cells.
“With conventional antibodies, such as lecanemab, the small amount of antibody that does enter the brain can remove some harmful plaque that lies outside our brain cells but can’t access toxic proteins such as tau, which is located in our brain cells,” Dr Nisbet said.
END
Unlocking how to use mRNA to target Alzheimer’s disease
Using an mRNA technology approach to target the toxic protein tau
2024-03-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Kessler Foundation secures $770,000 in grants to advance leading-edge spinal cord research
2024-03-28
East Hanover, NJ – March 28, 2024 – Kessler Foundation received two grants from The New Jersey Commission on Spinal Cord Research that will fuel innovative research in the field of spinal cord injury (SCI). These grants will fund efforts aimed at improving the cognitive assessment of individuals with traumatic SCI and pilot-testing the first-of-its-kind Spinal Cord Injury Personal Assistance Services Survey (SCI-PASS).
Traumatic spinal cord injury (tSCI) often leads to cognitive impairment, affecting up to 60 percent of individuals living with this condition. “The challenge lies in assessing cognitive functions in people with tSCI, as many existing tests rely on upper limb ...
Going ‘back to the future’ to forecast the fate of a dead Florida coral reef
2024-03-28
Rising temperatures and disease outbreaks are decimating coral reefs throughout the tropics. Evidence suggests that higher latitude marine environments may provide crucial refuges for many at-risk, temperature-sensitive coral species. However, how coral populations expand into new areas and sustain themselves over time is constrained by the limited scope of modern observations.
What can thousands of years of history tell us about what lies ahead for coral reef communities? A lot. In a new study, Florida Atlantic University researchers and collaborators provide geological insights into coral range expansions by reconstructing the composition of a Late Holocene-aged subfossil coral ...
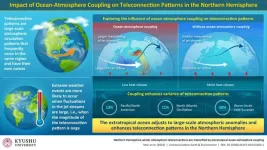
How extratropical ocean-atmosphere interactions can contribute to the variability of jet streams in the Northern Hemisphere
2024-03-28
Fukuoka, Japan—The interaction between the oceans and the atmosphere plays a vital role in shaping the Earth’s climate. Changing sea surface temperatures can heat or cool the atmosphere, and changes in the atmosphere can do the same to the ocean surface. This exchange in energy is known as “ocean-atmosphere coupling.”
Now, researchers from Kyushu University have revealed that this ocean-atmosphere coupling enhances teleconnection patterns—when climate conditions change across vast regions of the globe—in the Northern Hemisphere. In their recent ...
MSK Research Highlights, March 28, 2024
2024-03-28
Low recurrence seen with cryoablation for large breast tumors
Cryoablation, a minimally invasive technique used to freeze and destroy small tumors, is effective for breast cancer patients with larger tumors, according to research presented by MSK interventional radiologist Yolanda Bryce, MD, at the 2024 Society of Interventional Radiology Annual Scientific Meeting.
The retrospective study assessed outcomes for 60 patients who underwent cryoablation because they were not candidates for surgery or declined surgery due to other health concerns. The average size of their tumors was 2.5 centimeters. In a follow-up after 16 months, only 10% of patients experienced a recurrence ...
USDA, Nueta Hidatsa Sahnish College collaborate to support Indigenous Seed Sovereignty
2024-03-28
MANDAN, N.D., March 28, 2024—The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Agricultural Research Service (ARS) announces a cooperative agreement with the Nueta Hidatsa Sahnish (NHS) College to conduct research supporting Indigenous Seed Sovereignty. This collaborative effort will increase the number of traditional varieties of seeds of the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara (MHA) Nation crops within NHS College's traditional seed cache.
This agreement builds upon USDA’s strengthened partnerships with ...
For younger women, mental health now may predict heart health later
2024-03-28
Younger women are generally thought to have a low risk of heart disease, but new research urges clinicians to revisit that assumption, especially for women who suffer from certain mental health conditions. A new study being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session found that having anxiety or depression could accelerate the development of cardiovascular risk factors among young and middle-aged women.
The study draws new attention to the importance of cardiovascular screening and preventive care as rates of cardiovascular risk factors rise and heart attacks become more common in younger people. Anxiety and depression ...
Missed opportunity: AEDs near cardiac arrests rarely used by bystanders
2024-03-28
Automated external defibrillators (AEDs) are a common resource in public buildings, yet a new analysis reveals that they are rarely used to help resuscitate people suffering cardiac arrest. Research, which will be presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session, found that AEDs were only used in 13 of nearly 1,800 cases of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, even though many of the incidents occurred near a public AED.
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating. It is different from a heart attack, which is when a blockage prevents blood ...
Eggs may not be bad for your heart after all
2024-03-28
Whether you like your eggs sunny-side up, hard boiled or scrambled, many hesitate to eat them amid concerns that eggs may raise cholesterol levels and be bad for heart health. However, results from a prospective, controlled trial presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session show that over a four-month period cholesterol levels were similar among people who ate fortified eggs most days of the week compared with those who didn’t eat eggs.
A total of 140 patients with or at high risk for cardiovascular disease were enrolled in ...
Alcohol raises heart disease risk, particularly among women
2024-03-28
Young to middle-aged women who reported drinking eight or more alcoholic beverages per week—more than one per day, on average—were significantly more likely to develop coronary heart disease compared with those who drank less, finds a study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session. The risk was highest among both men and women who reported heavy episodic drinking, or “binge” drinking, and the link between alcohol and heart disease appears to be especially strong among women, according to the findings.
The study focused on 18- to 65-year-old ...
TTUHSC announces new center for nursing research
2024-03-28
The Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) School of Nursing announced March 27 the establishment of the TTUHSC Center for Nursing Research, Collaboration and Innovation.
“Interprofessional collaboration is essential for advancing research in health care,” TTUHSC School of Nursing Dean and Professor Holly Wei, Ph.D., said. “By bringing together professionals from various disciplines, we can harness a wide range of perspectives and skills to develop innovative solutions that significantly impact patient care and outcomes.”
For years, the TTUHSC School of Nursing has been recognized for its ability to educate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
Reduce rust by dumping your wok twice, and other kitchen tips
High-fat diet accelerates breast cancer tumor growth and invasion
Leveraging AI models, neuroscientists parse canary songs to better understand human speech
Ultraprocessed food consumption and behavioral outcomes in Canadian children
The ISSCR honors Dr. Kyle M. Loh with the 2026 Early Career Impact Award for Transformative Advances in Stem Cell Biology
The ISSCR honors Alexander Meissner with the 2026 ISSCR Momentum Award for exceptional work in developmental and stem cell epigenetics
The ISSCR honors stem cell COREdinates and CorEUstem with the 2026 ISSCR Public Service Award
Minimally invasive procedure effectively treats small kidney cancers
SwRI earns CMMC Level 2 cybersecurity certification
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
Life forms can planet hop on asteroid debris – and survive
Sylvia Hurtado voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
Mount Sinai and King Saud University Medical City forge a three-year collaboration to advance precision medicine in familial inflammatory bowel disease
AI biases can influence people’s perception of history
Prenatal opioid exposure and well-being through adolescence
Big and small dogs both impact indoor air quality, just differently
Wearing a weighted vest to strengthen bones? Make sure you’re moving
Microbe survives the pressures of impact-induced ejection from Mars
Asteroid samples offer new insights into conditions when the solar system formed
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
[Press-News.org] Unlocking how to use mRNA to target Alzheimer’s diseaseUsing an mRNA technology approach to target the toxic protein tau