(Press-News.org) Hyenas are generalist predators (and scavengers) with a broad range of prey species. They are known for hunting (or scavenging) larger mammals such as antelopes and occasionally feed on smaller mammals and reptiles. Being flexible in the choice of prey is a strategy of generalists – and this even extends to small passerine birds, as scientists from the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) and the University of Ljubljana observed in Namibia: Spotted hyenas pursued red-billed queleas, picked them from the ground or the surface of a waterhole and swallowed them whole, at a success rate of approximately one bird every three minutes. These observations were described for the first time in word, photos and videos in the scientific journal “Food Webs”.
The diet breadth of hyenas is matched by few other carnivores. Spotted hyenas (Crocuta crocuta) are known to hunt a variety of larger mammals such as zebras and antelopes in southern and eastern Africa – but also ostriches, flamingos, reptiles, other carnivores. They also scavenge on carcasses from giraffes to elephants and cattle. Until now very few observations of hyenas feeding on small birds were reported. “In our paper we describe for the first time the hunting and feeding behaviour of spotted hyenas on red-billed queleas (Quelea quelea), a passerine bird known for its huge flocks, at a waterhole in the Etosha National Park in Namibia”, say Rubén Portas and Dr. Miha Krofel, scientists working for the Leibniz-IZW and the University of Ljubljana. On two different days they observed, filmed and photographed spotted hyenas chasing flying birds or picking them from the ground or the water surface, and devouring them whole at the waterhole. “We observed that a single hyena can catch on average one bird every three minutes”, the scientists conclude from their observations.
The scientists could draw some conclusions about the feeding behaviour of spotted hyenas from their observations. “It adds to the known variety of the spotted hyena diet and hunting tactics, since this behaviour has not been documented before”, says Portas. “It confirms their flexibility and ability to exploit foraging opportunities and obtaining food from unusual sources. We can also provide a first estimate on the capture rates and the food intake of hyenas hunting passerine birds.” As the observations were limited to a single waterhole, it is possible that the described foraging tactic was specific to the hyenas from the observed clan and occurred as an opportunistic response to an abundant food source, the authors say. Between May and August, thousands of wintering red-billed queleas gather at waterholes in Namibia.
Portas and Krofel regularly carry out field research on vultures, lions, leopards and hyenas and investigate carnivore-scavenger interactions and information transfer in the scavenger community for the GAIA Initiative and InterMuc projects in Etosha National Park. The GAIA Initiative is an alliance of research institutes, conservation organisations and companies with the aim of creating a high-tech early warning system for environmental changes. In several projects, the GAIA partners conduct wildlife research on selected species, their interaction and the functioning of ecosystems they inhabit. On this basis, the GAIA scientists and engineers build and utilize high-tech interfaces to the senses and intelligence of sentinel animals in order to detect critical changes or incidents in ecosystems fast and effectively. To this end, they develop a new generation of animal tags equipped with on-board artificial intelligence (AI), a camera, energy-efficient electronics and satellite-based communication technology.
END
Small birds spice up the already diverse diet of spotted hyenas in Namibia
2024-03-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
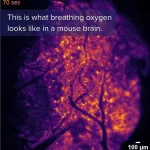
Imaging detects transient “hypoxic pockets” in the mouse brain
2024-03-28
Using a bioluminescent oxygen indicator, Felix Beinlich and colleagues discovered a spontaneous, spatially defined occurrence of “hypoxic pockets” in the mouse brain. Their technique offers a way to learn more about brain oxygen tension (pO2), a measure of oxygen delivery and demand in brain tissue that changes dynamically but is not well understood. The findings could have implications for how rest and exercise affect pO2 in the human brain, including the role of these activities in conditions such as dementia, Beinlich et al. suggest. The researchers used a genetically encoded bioluminescent oxygen indicator called Green NanoLuc in mouse cortical astrocytes to ...
Dissolved organic matter could be used to track and improve the health of freshwaters
2024-03-28
The dissolved organic matter (DOM) from hundreds of plant and animal remains could be used to track and possibly restore the health of freshwater bodies, Andrew J. Tanentzap and Jérémy A. Fonvielle write in this Perspective. The broad range of compounds, or chemodiversity, of DOM has multiple effects in freshwaters, including providing nutrients to support food web productivity, reducing or enhancing contamination from pollutants, and influencing the metabolism of microorganisms important to the biogeochemical cycle. DOM may also reduce the heat that ...
Indoor air quality standards in public buildings would boost health and economy, say international experts
2024-03-28
There should be mandatory indoor air quality standards, say an international group of experts led by Professor Lidia Morawska.
Professor Morawska, Vice-Chancellor Fellow at the University of Surrey and Distinguished Professor at Queensland University of Technology, led the appeal to the World Health Organization to recognise the airborne transmission of the virus which causes COVID-19 early in the pandemic – and help minimise it.
Now, in a paper published by the prestigious journal Science, Professor Morawska's international team recommends setting standards for ventilation rate and three key indoor pollutants: carbon ...
Positive associations between premenstrual disorders and perinatal depression
2024-03-28
Women affected by premenstrual disorders have a higher risk of perinatal depression compared with those who do not, according to research published March 28th in the open access journal PLOS Medicine. The relationship works both ways: those with perinatal depression are also more likely to develop premenstrual disorders after pregnancy and childbirth. This study suggests that a common mechanism might contribute to the two conditions.
Menstruating women experience cyclical hormone fluctuations through puberty, menstrual cycle, pregnancy ...
New imaging method illuminates oxygen's journey in the brain
2024-03-28
The human brain consumes vast amounts of energy, which is almost exclusively generated from a form of metabolism that requires oxygen. Consequently, the efficient and timely allocation and delivery of oxygen is critical to healthy brain function, however, the precise mechanics of this process have largely remained hidden from scientists.
A new bioluminescence imaging technique, described today in the journal Science, has created highly detailed, and visually striking, images of the movement ...
Researchers discover key gene for toxic alkaloid in barley
2024-03-28
All plants mediate their environmental interactions via chemical signals. An example is the alkaloid gramine produced by barley, one of the world’s most widely grown cereals. Gramine provides protection against herbivorous insects and grazing animals and inhibits the growth of other plants. Despite long-standing interest, the key gene for the formation of gramine remained elusive.
The researchers discovered a cluster of two genes in barley for gramine biosynthesis. The first gene (HvNMT) had already been discovered 18 years ago. In their study the researchers from IPK and the Leibniz University Hannover now identified a second gene (AMI synthase, HvAMIS), and ...
New approach to monitoring freshwater quality can identify sources of pollution, and predict their effects
2024-03-28
The source of pollutants in rivers and freshwater lakes can now be identified using a comprehensive new water quality analysis, according to scientists at the University of Cambridge and Trent University, Canada.
Microparticles from car tyres, pesticides from farmers’ fields, and toxins from harmful algal blooms are just some of the organic chemicals that can be detected using the new approach, which also indicates the impact these chemicals are likely to have in a particular river or lake.
Importantly, the approach can also point to the origin of specific organic matter dissolved in the water, because it has a distinct ...
Bidirectional link between premenstrual disorders and perinatal depression
2024-03-28
Women with premenstrual syndrome (PMS) or premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) have a higher risk of perinatal depression. Conversely, women with perinatal depression have a higher risk of developing premenstrual disorders. This is shown in a study from Karolinska Institutet published in the journal PLOS Medicine.
Premenstrual disorders like PMS or PMDD and perinatal depression are similar in the way that symptoms appear in connection with hormonal changes. This fact has given rise to the hypothesis ...
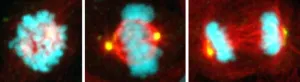
Cell division quality control ‘stopwatch’ uncovered
2024-03-28
Each day, hundreds of billions of cells in our body cycle through a period of growth and division. Yet in that time, only about 30 minutes is spent on the critical orchestration of mitosis, when chromosomes are carefully segregated from one parent cell to the next generation of two daughter cells.
It’s during this crucial period of cell division that things can go haywire. Chromosomes can be misdirected, leading to damaged and diseased cells that progress to different types of cancer. University of California San Diego scientists reporting in the journal Science have found a key mechanism that keeps track of mitosis timing and ...
Vaccine protects cattle from bovine tuberculosis, may eliminate disease
2024-03-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Bovine tuberculosis (TB) is a livestock disease that results in large economic losses to animal agriculture worldwide. The disease can also transmit to humans and cause severe illness and death. Researchers from Penn State, Addis Ababa University and the University of Cambridge have now demonstrated that a vaccine for TB currently used in humans significantly reduces infectiousness of vaccinated livestock, improving prospects for elimination and control. The study published today (March 28) in the journal Science.
The spillover ...