(Press-News.org) PULLMAN, Wash. – A broader past could mean a brighter future for Canada lynx in the U.S., according to recent research.
The study, published in the journal Biological Conservation, indicates that lynx might do well in the future in parts of Utah, central Idaho and the Yellowstone National Park region, even considering climate change and the lack of lynx in those areas now.
Using a model validated by historic records, researchers first found that in 1900, Canada lynx had more suitable habitat in the U.S. than the few northern corners of the country where they are found currently. The study showed the elusive big cat likely roamed over a larger area in the Pacific Northwest, Rocky Mountains, Great Lakes region and parts of New England.
“History matters even for wildlife,” said lead author Dan Thornton, a Washington State University wildlife ecologist. “As part of the criteria for species recovery, we have to understand their historic distribution. Otherwise, how can we help recover a species, if we don't know what we’re recovering to?”
Having a more accurate picture of a species’ past can also help avoid an effect known as “shifting baseline syndrome,” Thornton added, which is a gradual change in what people accept as normal for the environment, or specifically in this case, a species’ habitat.
True to their name, Canada lynx are still abundant in Canada, but in the U.S. their numbers have dwindled. Currently, they are only found in limited, northern portions of Washington, Idaho, Montana, Minnesota and Maine. So far, recovery plans for lynx have been based on assumptions that they were never found much beyond these areas in the U.S., although a small population was successfully re-introduced to the Colorado Rockies in 1999.
This study, which has conservation implications for not only lynx but other threatened species, proposes one new way of estimating a species’ historic range, using modelling of suitable habitat validated by historical records.
Thornton and co-author Dennis Murray of Trent University in Canada created the model using factors to determine lynx’s suitable habitat like temperature, precipitation and land use in the last 40 years. They ran that model back in time to 1900 using historic climate and land use data to discover the possible past range, which they validated using records of lynx from museums as well as hunters and trappers who have prized the big cat for its fur.
The researchers then used the model to project suitable habitat into the future of 2050 and 2070. Even when accounting for climate change effects, they found areas that could be good for lynx that fall outside the species’ current range but likely within historically occupied areas: namely in central Idaho, northern Utah and the area in, and around, Yellowstone National Park. Whether or not these areas could support viable lynx populations now or in the future would require additional research, the authors noted.
Conserving lynx as a key predator is important for maintaining the integrity of forest ecosystems, the authors contend, and lynx are an iconic species in the mountains of the Pacific Northwest.
The researchers also hope that this approach to estimating historic range could help inform conservation efforts for other species.
“Thinking about historic range is really important. It’s also quite difficult because we often have limited data on where species were in the past,” Thornton said. “But there are potential ways to go about addressing that, and we wanted to provide one possible approach in this paper.”
This research received support from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
END
Canada lynx historic range in US likely wider than previously thought
2024-04-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study documents safety, improvements from stem cell therapy after spinal cord injury
2024-04-01
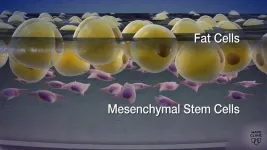
ROCHESTER, Minn. — A Mayo Clinic study shows stem cells derived from patients' own fat are safe and may improve sensation and movement after traumatic spinal cord injuries. The findings from the phase 1 clinical trial appear in Nature Communications. The results of this early research offer insights on the potential of cell therapy for people living with spinal cord injuries and paralysis for whom options to improve function are extremely limited.
In the study of 10 adults, the research team noted seven participants demonstrated ...
Simple equations clarify cloud climate conundrum
2024-04-01
New analysis based on simple equations has reduced uncertainty about how clouds will affect future climate change.
Clouds have two main effects on global temperature – cooling the planet by reflecting sunlight, and warming it by acting as insulation for Earth’s radiation.
The impact of clouds is the largest area of uncertainty in global warming predictions.
In the new study, researchers from the University of Exeter and the Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique in Paris created a model that predicts how ...
A high-boost and high-efficiency DC power converter
2024-04-01
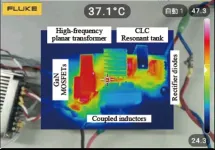
A new electrical power converter design achieves a much higher efficiency at lower cost and maintenance than before. The direct current voltage boost converter developed by Kobe University is poised to be a significant contribution to the further development of electric and electronic components across power generation, health care, mobility and information technology.
Devices that harvest energy from sunlight or vibrations, or power medical devices or hydrogen-fueled cars have one key component in common. This so-called “boost converter” converts low-voltage direct current input into high-voltage direct current output. Because it is such a ubiquitous ...
Study suggests high blood pressure could begin in childhood
2024-04-01
Study suggests high blood pressure may originate early in life and that preventing overweight and obesity during the developmental years could help reduce the substantial disease burden associated with high blood pressure in later life.
*This is an early press release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) Venice 12-15 May. Please credit the Congress if using this material*
Children and teenagers living with overweight or obesity are more likely to have high blood pressure as adults (aged 50-64 years), suggesting the processes behind the condition could begin as early as childhood, suggests new research being ...
Study finds association between TB infection and increased risk of various cancers
2024-04-01
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024, Barcelona, Spain, 27-30 April). Please credit the congress if you use this story**
A population-wide observational study to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April) shows an association between tuberculosis (TB) and cancer, with those with current or previous TB more likely ...
Swedish study indicates a significant decline of neutralising antibodies to monkeypox virus already during the first month after vaccination
2024-03-30
Previous smallpox vaccination contributes significantly to higher neutralising antibodies following first MVA-BN dose
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024, Barcelona, Spain, 27-30 April). Please credit the congress if you use this story**
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 ...
Study shows Mpox (monkeypox) antibodies wane within a year of vaccination
2024-03-30
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April) shows that the antibodies produced by Modified Vaccinia virus Ankara - Bavarian Nordic (MVA-BN) vaccination against mpox wane significantly within a year of receiving the vaccination – but in people with pre-existing immunity due to childhood smallpox vaccination in childhood, antibody levels remain high in almost all cases. The study is presented by PhD student Dr. Marc Shamier, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, Netherlands, from a research team led by Dr Rory de Vries.
During the 2022-2023 ...
Case report from Austria shows mpox breakthrough infection in man who had received both vaccine doses
2024-03-30
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April) details the case of a man who had received two doses of the monkey pox vaccine in Autumn, 2022 yet experienced a ‘breakthrough’ mpox infection in January 2024. The authors believe breakthrough should be considered in fully vaccinated individuals engaging in high-risk behaviors. They also call for further research on the need for booster ...
Scientists have a new tool in the race to improve the diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis
2024-03-29
Researchers from Lund University in Sweden have identified distinct molecular signatures associated with the clinical signs of sepsis that could provide more accurate diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis, as well as help to target specific therapies at patients who would benefit most, according to new research being presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April).
“A simple blood test when combined with a personalised risk model has the potential to save lives by providing more accurate sepsis diagnosis and determining who may go on to develop more severe clinical ...
UK Biobank study identifies ideal body weight for adults with type 2 diabetes to minimise risk of dying from cardiovascular disease
2024-03-29
*This is an early press release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) Venice 12-15 May. Please credit the Congress if using this material*
New research being presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May), identifies the optimum body weight range for adults with type 2 diabetes to minimise their risk of dying from any cardiovascular disease, including heart failure, heart disease, stroke, and chronic kidney disease.
The findings, based on health data from the UK Biobank, indicate that for adults aged 65 years or younger, maintaining a body mass index (BMI) within the normal range of 23–25 kg/m² was associated with the ...