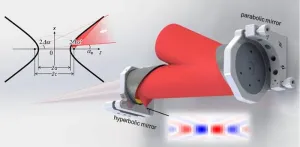
(Press-News.org) Ultra-intense ultrashort lasers are powerful tools used in various fields like physics, national security, industry, and healthcare. They help researchers delve into strong-field laser physics, laser-driven radiation sources, particle acceleration, and more.
“Peak power” measures the intensity of these lasers, like the Nova laser (Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, California, USA) with 1.5 petawatts of peak power, the Shanghai Super-intense Ultrafast Laser Facility (SULF, China) with 10 petawatts, or the Extreme Light Infrastructure – Nuclear Physics (ELI-NP, Romania) with a peak power of 10 petawatts. However, what truly matters in experiments is the focused intensity on the target. The lasers are focused onto experimental targets using off-axis parabolic mirrors. The focused intensity, not peak power, reflects the laser's capability and is crucial for users.
Enhancing focus with hyperbolic mirrors
Currently, the beam aperture of these lasers is 150 to 500 mm, and the F-number (related to focusing ability) is 2 to 10. Adding a rotational hyperbolic mirror after the parabolic one can reduce the F-number and thus the focal spot size significantly.
As reported in Advanced Photonics Nexus, this secondary focusing method can reduce the F-number by a factor of 5, which then reduces the focal spot size of the ultra-intense ultrashort laser to a single-wavelength size.
Corresponding author Zhaoyang Li of the Key Laboratory of Ultra-intense Laser Science and Technology, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (China), notes that this technique enables the smallest possible focal spot: "Utilizing hyperbolic mirrors for secondary focusing can reduce the focal spot of our ultra-intense ultrashort lasers from a several-wavelength size to just a single-wavelength size, achieving the smallest focal spot possible."
Li and his team report that single-wavelength focal spots can be achieved by adding an optimized rotational hyperbolic mirror to current femtosecond petawatt-class lasers or future single-cycle petawatt-class lasers. “In combination with our previously proposed Wide-angle Non-collinear Optical Parametric Chirped Pulse Amplification (WNOPCPA) method, it is expected to reach the highest intensity condition of an ultra-intense ultrashort laser facility, that is focusing all laser energy into a spatiotemporal focal cube edged by the laser center wavelength. This will dramatically enhance the experimental capability of ultra-intense ultrashort lasers in the application of strong-field laser physics, such as vacuum quantum electrodynamics,” says Li.
For details, see the original Gold Open Access article by Z. Li, et al., “Single-wavelength size focusing of ultra-intense ultrashort lasers with rotational hyperbolic mirrors,” Adv. Photon. Nexus 3(3) 036002 (2024), doi 10.1117/1.APN.3.3.036002
END
Focusing ultra-intense lasers to a single wavelength
An innovative mirror design revolutionizes ultra-intense ultrashort laser focus, enabling the highest intensity condition for ultra-intense ultrashort lasers, a breakthrough in strong-field laser physics
2024-04-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Combining food taxes and subsidies can lead to healthier grocery purchases for low-income households
2024-04-02
Chapel Hill, NC, April 2, 2024 — A new study that models the combined effects of a sugar-based tax on beverages and targeted subsidies for minimally processed foods and drinks found that under these policies, low-income consumers would purchase less sugar-sweetened beverages and more fruits, vegetables, and healthier drinks, particularly in households without children.
Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill developed a model to simulate what would happen if national-level taxes on less-healthy, ...
One in five people with cancer participate in medical research studies
2024-04-02
SEATTLE – April 2, 2024 – Researchers from Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network and peer institutions released new findings in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showing that when all types of cancer research studies are considered, at least one in five people with cancer, or 21.9%, participate in some form of clinical research.
The study evaluated all categories of cancer studies, such as treatment trials, biorepository studies and quality of life studies—the first time an estimate of participation in all types of cancer ...
Sunrise to sunset, new window coating blocks heat — not view
2024-04-02
Windows welcome light into interior spaces, but they also bring in unwanted heat. A new window coating blocks heat-generating ultraviolet and infrared light and lets through visible light, regardless of the sun’s angle. The coating can be incorporated onto existing windows or automobiles and can reduce air-conditioning cooling costs by more than one-third in hot climates.
“The angle between the sunshine and your window is always changing,” said Tengfei Luo, the Dorini Family Professor for Energy Studies at the University of Notre ...
Innovative molecular biology technique allows for discovery of novel targets for candidate vaccines against schistosomiasis
2024-04-02
Researchers in Brazil have used an innovative technique in molecular biology to identify targets for candidate vaccines against Schistosoma mansoni, the parasite that causes schistosomiasis.
Considered one of the world’s 17 neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), schistosomiasis affects some 200 million people in 74 countries, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Six million are estimated to be infected in Brazil, mainly in the Northeast region and Minas Gerais state.
The scientists used phage display, the study of protein interactions using bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacteria, to screen 99.6% of 119,747 DNA sequences encoding the proteins known ...
Study finds Netflix misses the mark by trivializing teenagers’ pain
2024-04-02
UCalgary led study finds Netflix misses the mark by trivializing teenagers’ pain. Findings are published in PainResearchers at the University of Calgary and the University of Bath, U.K., are calling on Netflix to do a better job of representing the kind of pain typically experienced by 12-to-18-year-olds. A new study finds the streaming channel should not emphasize stereotypes, like the heroic, stoic boy and the helpless, emotional girl who requires his rescue and prioritizes his pain and suffering.
“Media ...
TLI investigator Dr. Denise Al Alam receives $1.5 million grant from CIRM to explore genetic defects of lung disease in Down Syndrome
2024-04-02
The Lundquist Institute for Biomedical Innovation at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center (TLI) today announced that The California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM), one of the world’s largest institutions dedicated to regenerative medicine, has
awarded $1.5 million to TLI Investigator Denise Al Alam, PhD, to support research that aims to understand lung disease in individuals with Trisomy 21 (also known as Down Syndrome). Although Trisomy 21 impacts multiple organ systems, respiratory complications are a significant cause of death in children and adults with this genetic condition.
With the highest occurrence of Down Syndrome births in California within the Latinx ...
Increasing positive affect in adolescence could lead to improved health and well-being in adulthood
2024-04-02
Adolescents with high positive affect may have improved physical and mental health as adults, according to a study published April 2nd in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Eric Kim and Renae Wilkinson from Harvard University, US, and colleagues.
Positive affect is the experience of pleasurable emotions, such as happiness, joy, excitement, and calm. Research on adults has shown that positive affect is associated with healthier behaviors and decreased risk of chronic diseases, but data are limited in adolescents. Given that adolescence is a critical ...
Methods sections often lack critical details needed to reproduce an experiment, and the practice of citing previous papers instead of describing the methods in detail may contribute to this problem
2024-04-02
Methods sections often lack critical details needed to reproduce an experiment, and the practice of citing previous papers instead of describing the methods in detail may contribute to this problem
Analysis of >750 papers shows that >90% of papers use at least one shortcut citation, that these significantly impair reconstruction of the original method, and that <25% of journals have policies relating to previously described methods
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS ...
Study: AI writing, illustration emits hundreds of times less carbon than humans
2024-04-02
LAWRENCE — With the evolution of artificial intelligence comes discussion of the technology's environmental impact. A new study has found that for the tasks of writing and illustrating, AI emits hundreds of times less carbon than humans performing the same tasks. That does not mean, however, that AI can or should replace human writers and illustrators, the study’s authors argue.
Andrew Torrance, Paul E. Wilson Distinguished Professor of Law at KU, is co-author of a study that compared established systems such as ChatGPT, Bloom AI, DALL-E2 and others completing writing and illustrating to that of humans.
Like ...
Morris Animal Foundation-funded researchers develop early osteoarthritis detection tool
2024-04-02
Media Alert: DENVER/April 2, 2024 — Morris Animal Foundation-funded researchers introduced a straightforward questionnaire to help horse owners identify and monitor signs of osteoarthritis pain in their equine companions. This initiative aims to facilitate earlier and more effective treatment, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for horses.
Created by Dr. Janny de Grauw, Senior Lecturer at The Royal Veterinary College in the United Kingdom, Bryony Lancaster, Program Director, MSc Equine Science of the University of Edinburgh and Dr. Diane Howard, the questionnaire is modeled after the Brief Pain Inventory used to evaluate pain severity and its impact ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
6 in 10 US women projected to have at least one type of cardiovascular disease by 2050
People’s gut bacteria worse in areas with higher social deprivation
Unique analysis shows air-con heat relief significantly worsens climate change
Keto diet may restore exercise benefits in people with high blood sugar
Manchester researchers challenge misleading language around plastic waste solutions
Vessel traffic alters behavior, stress and population trends of marine megafauna
Your car’s tire sensors could be used to track you
Research confirms that ocean warming causes an annual decline in fish biomass of up to 19.8%
Local water supply crucial to success of hydrogen initiative in Europe
New blood test score detects hidden alcohol-related liver disease
High risk of readmission and death among heart failure patients
Code for Earth launches 2026 climate and weather data challenges
Three women named Britain’s Brightest Young Scientists, each winning ‘unrestricted’ £100,000 Blavatnik Awards prize
Have abortion-related laws affected broader access to maternal health care?
Do muscles remember being weak?
Do certain circulating small non-coding RNAs affect longevity?
How well are international guidelines followed for certain medications for high-risk pregnancies?
New blood test signals who is most likely to live longer, study finds
Global gaps in use of two life-saving antenatal treatments for premature babies, reveals worldwide analysis
Bug beats: caterpillars use complex rhythms to communicate with ants
High-risk patients account for 80% of post-surgery deaths
Celebrity dolphin of Venice doesn’t need special protection – except from humans
Tulane study reveals key differences in long-term brain effects of COVID-19 and flu
The long standing commercialization challenge of lithium batteries, often called the dream battery, has been solved.
New method to remove toxic PFAS chemicals from water
The nanozymes hypothesis of the origin of life (on Earth) proposed
Microalgae-derived biochar enables fast, low-cost detection of hydrogen peroxide
Researchers highlight promise of biochar composites for sustainable 3D printing
Machine learning helps design low-cost biochar to fight phosphorus pollution in lakes
Urine tests confirm alcohol consumption in wild African chimpanzees
[Press-News.org] Focusing ultra-intense lasers to a single wavelengthAn innovative mirror design revolutionizes ultra-intense ultrashort laser focus, enabling the highest intensity condition for ultra-intense ultrashort lasers, a breakthrough in strong-field laser physics